Abstract
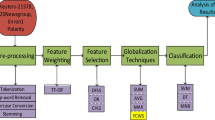
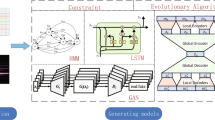
Novel style recognition is of great reference significance for analyzing the quality and readability of works. Writing stylistics is the analysis of an author's writing style through statistical methods. In this paper, our main purpose is to identify the style of English novels based on text analysis methods. We use the method of information entropy calculation which is an evolutionary intelligent method to identify the style of English novels, so as to provide reference for better grasping the content of literary works. We focus on how to process text data and mine text intrinsic features to better identify English novel style. To better solve the problems, we design following strategies in our proposed method. First, we need to collect and process English novel samples. Then tokenize the text and consider the object content that needs to be analyzed. The next step is to count the number of words and calculate the information entropy. Finally, the data is processed and analyzed to get a conclusion. The experimental results prove that the method proposed in this paper has good evaluation performance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holmes DI (1985) The analysis of literary style—a review. J Royal Stat Soc: Series A (General) 148(4):328–341
Xue X, Huang Q (2022) Generative adversarial learning for optimizing ontology alignment. Expert Syst. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12936
Swan A, Carr L (2008) Institutions, their repositories and the web. Ser Rev 34(1):31–35
Chang CH, Kayed M, Girgis MR et al (2006) A survey of web information extraction systems. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 18(10):1411–1428
Khosmood F, Levinson R A (2008) Automatic natural language style classification and transformation, In: BCS-IRSG workshop on corpus profiling. 1–11.
Vijayakumar T, Vinothkanna R (2020) Capsule network on font style classification. J Artif Intell 2(02):64–76
Bharath V, Rani N S (2017) A font style classification system for English OCR. In: 2017 international conference on intelligent computing and control (I2C2). IEEE, 2017: 1–5.
Raschka S (2014) Naive bayes and text classification i-introduction and theory. arXiv preprint arXiv:1410.5329.
Xu S (2018) Bayesian Naïve Bayes classifiers to text classification. J Inf Sci 44(1):48–59
Kolluri J, Razia S (2020) Text classification using Naïve Bayes classifier. Mater Today: Proc.
Noble WS (2006) What is a support vector machine? Nat Biotechnol 24(12):1565–1567
Suthaharan S (2016) Support vector machine–machine learning models and algorithms for big data classification. Springer, Boston, pp 207–235
Kramer O (2013) K-nearest neighbors//Dimensionality reduction with unsupervised nearest neighbors. Springer, Berlin, pp 13–23
Keller JM, Gray MR, Givens JA (1985) A fuzzy k-nearest neighbor algorithm. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 4:580–585
Joachims T (1996) A probabilistic analysis of the rocchio algorithm with TFIDF for text categorization. Carnegie-mellon univ pittsburgh pa dept of computer science.
Chowdhary K R (2020) Natural language processing. Fund Artif Intell, 603–649.
Nadkarni PM, Ohno-Machado L, Chapman WW (2011) Natural language processing: an introduction. J Am Med Inform Assoc 18(5):544–551
Loper E, Bird S (2002) Nltk: the natural language toolkit. arXiv preprint cs/0205028.
van Rossum G (1995) Python reference manual. Department of Computer Science [CS], (R 9525).
Csiszár I, Shields PC (2004) Information theory and statistics: a tutorial. Found Trends® Commun Inf Theory 1(4):417–528
Chaitin GJ (1977) Algorithmic information theory. IBM J Res Dev 21(4):350–359
Brillouin L (2013) Science and information theory. Courier Corporation
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflicts of interest in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y. Evolutionary intelligence driven style recognition of English novels based on text analysis. Evol. Intel. 16, 1573–1579 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-022-00790-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-022-00790-3