Abstract
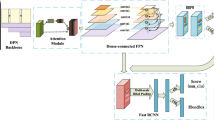
The seismic fortification intensity requirements of buildings of various heights are different. Identifying the heights of different buildings using a specific method can reduce secondary disasters such as building damage and house collapse caused by destructive earthquakes. The traditional building object detection model uses the feature expression of the dataset based on manually sketching the shape of the building in the remote sensing images, which will cause less acquired image information, unclear target features of buildings, and the decrease of target detection accuracy of identifying building types. The real-time target detection algorithm YOLO has fast detection speed and high accuracy, but its main disadvantage is the inaccurate positioning of the building bounding box and the misjudgment of partially overlapping building objects. Image feature retrieval using large data set domain adaptive fast algorithm is a new research hotspot in current image recognition. This research proposes a multi-branch network with the addition of a module using attention mechanism to coordinate the salient and sub-salient information of images. The algorithm adds channel and spatial attention mechanisms to the feature extraction network, and uses weighting and filtering methods to perform residual fusion on the original features vectors in images. The model is deployed on the remote sensing geographic information evaluation platform to conduct various building target detection experiments. The average detection accuracy of the urban buildings can reach 81.8%, and the detection speed for remote sensing segmentation images is 26 per second. The mAP@0.5 of the YOLOv5 algorithm with the attention mechanism is 12% higher than that of the unimproved YOLOv5 algorithm on the urban street view image dataset.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Fang E, Qian J (1999) Issues of seismic resistant design for tall buildings in China. China Civil Engineering Journal 32:3–8
Wang Y (2009) An overview of recent revision of seismic design codes after the 5.12 Wenchuan Earthquake. China Civil Engineering Journal 42(5):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-85168-452
miao ZD, Ming WD (2021) Application of building spatial distribution method based on remote sensing image in earthquake disaster loss pre-assessment. Technol Earthq Disaster Prev 16:510–518
Huo FF, Hou ML, Yang S (2019) Automatic extraction of building Rooftop outlines using airborne LiDAR: a review. Geomatics World 26:1–13
Reite A, Kangas S, Steck Z (2019) Unsupervised Feature Learning in Remote Sensing, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2529791
Bai SY, Agethen S, Chao TH, Hsu W (2015) Semi-supervised learning for convolutional neural networks via online graph construction, Computer Science, arXiv:1511.06104
Zang N, Cao Y, Wang Y (2021) Land-use mapping for high-spatial resolution remote sensing image via deep learning: a review. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Observations Remote Sens 99(1):1–10
Gong M, Zhou Z, Ma J (2012) Change detection in synthetic aperture radar images based on image fusion and fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(4):2141–2151
Gong M, Su L, Jia M (2014) Fuzzy clustering with a modified MRF energy function for change detection in synthetic aperture radar images. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 22(1):98–109
Lu-yang L, Jia Z-h, Yang J (2019) and K. Nikola, SAR image change detection using double difference images and PCA algorithm, Computer Engineering and Design, vol. 40 (7):5–15 DOI: https://doi.org/10.16208/j.issn10007024.2019.07.033
Wang Y, Ma H, Alifu K (2021) Remote sensing image description based on word embedding and end-to-end deep learning. Sci Rep 11(1):1–10
Nogueira K, Penatti O, Santos J (2016) Towards Better exploiting Convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification. Pattern Recogn 61(1):539–556
Cheng G, Yang C, Yao X (2018) When deep learning meets metric learning: remote sensing image scene classification via learning discriminative CNNs. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(5):2811–2821
Zhang Yy, Fei XY, Wang J (2020) Suvery of building extraction methods based on high resolution remote sensing images. Geomatics & Spatical Information Technology 43(4):76–79
Liu J, Mao ZY (2009) A survey on segmentation techniques and application strategy of high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens Inform 24(6):95–101. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.10003177.2009.06.020
Jung RSCR (2004) Rectangle detection based on a windowed hough Transform, in Brazilian Symposium on Computer Graphics & Image Processing (SIBGRAPI), 113–120
Kawahito K (2008) Recognition-driven two-dimensional competing priors toward automatic and accurate building detection. IEEE Trans Geoscience Remote Sens 47(1):133–144. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2008.2002027
Zhao CX, Chen X, Yang L (2016) Optimization of aerial DSM with building boundary constraint. Remote Sens Inform 31(4):16–21. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2016.04.003
Redmon J, Farhadi A (2018) YOLOv3: An incremental improvement, arXiv e-prints, Doi https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.02767.pdf
Li S, Gu X, Xu X, Xu D, Dong Q (2021) Detection of concealed cracks from ground penetrating radar images based on deep learning algorithm. Constr Build Mater 273:121949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121949
Cai Y, Luan T, Gao H (2021) YOLOv4-5D: an effective and efficient object detector for Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 70(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2021.3065438
Rezatofighi H, Tsoi N, Gwak JY (2019) Generalized Intersection Over Union: A Metric and a Loss for Bounding Box Regression, in IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 1–10
Woo S, Park J, Lee J-Y, Kweon IS (2018) CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module, in 15th Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (ECCV), Munich, Germany
Bottou Le, Curtis FE, Nocedal J (2016) Optimization methods for large-scale machine learning. Siam Rev 60(2):1–95. https://doi.org/10.1137/16M1080173
Rezende DJ, Mohamed S, Wierstra D (2014) Stochastic Backpropagation and Approximate Inference in Deep Generative Models, in 31st International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Beijing, China, 1–15
Wang G, Duan M, Niu C (2018) Stochastic gradient descent algorithm based on convolution neural network, Computer Engineering and Design, 39 (2): 441–445, DOI:https://doi.org/10.16208/j.issn1000-7024.2018.02.026
Xu F, Dong P, Wang H (2019) Intelligent detection and autonomous capture systemof seafood based on underwater robot. J Beijing Univ Aeronaut Astronaut 45(12):2393–2402. https://doi.org/10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0377
Xu X, Ma M, Thompson SG (2021) Intelligent co-detection of cyclists and motorcyclists based on an improved deep learning method. Meas Sci Technol 32(2):025402. https://doi.org/10.1088/13616501/abb745
Alhichri H, Alsuwayed A, Y YB (2021) Classification of Remote sensing images using EfficientNet-B3 CNN model with attention. IEEE Access 9(1):14078–14094. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3051085
Wang Q, Wu B, Zhu P ECA-net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks, in 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and, Recognition P (2020) (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 1–10
Acknowledgements
This work is partially sponsored by funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant No. 42174104, U1939204, 41204014], the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei province of China [Grant No.ZRMS2020000813], and the open fund of Wuhan gravitation and solid earth tides national observation and research station [No.WHYWZ202109].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work. We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.




Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, W., Zhang, L. & Yang, G. Building detection algorithm in multi-scale remote sensing images based on attention mechanism. Evol. Intel. 16, 1717–1728 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-023-00849-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-023-00849-9