Abstract
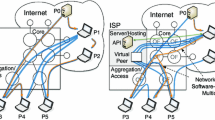
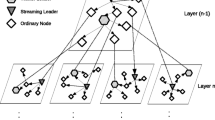
Combining the advantages of Peer-to-Peer (P2P) content distribution concept and metadata driven adaptation of videos in compressed domain, in this paper, we propose a simple but scalable design of distributed adaptation and overlay streaming using MPEG-21 gBSD, called DAg-stream. The objective is not only to shift the bandwidth burden to end participating peers, but also to move the computation load for adapting video contents away from dedicated media-streaming/adaptation servers. It is an initiative to merge the adaptation operations and the P2P streaming basics to support the expansion of context-aware mobile P2P systems. DAg-stream organizes mobile and heterogeneous peers into overlays. For each video, a separate overlay is formed. No control message is exchanged among peers for overlay maintenance. We present a combination of infrastructure-centric and application end-point architecture. The infrastructure-centric architecture refers to a tree controller, named DAg-master, which is responsible for tree/overlay administering and maintenance. The application end-point architecture refers to video sharing, streaming and adaptation by the participating resourceful peers. The motivation for this work is based on the experiences and lessons learned so far about developing a video adaptation system for heterogeneous devices. In this article, we present our architecture and some experimental evaluations supporting the design concept for overlay video streaming and online adaptation.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The term “node” is used interchangeably with “peer” and “client” throughout this manuscript.
Share-ratio is calculated from the total amount of data uploaded over total amount of data downloaded.
‘Frameset’ refers to the number of frames equal to the frame rate at which the raw video is being encoded (usually 30 fps). After adaptation for 15 frames per second (fps), there will be 15 frames in each frameset of that clip/video.
I = Intra Frame, B = Bi-directional Frame, P = Inter Frame.
References
Iqbal R, Shirmohammadi S, El Saddik A, Zhao J, 2 (2008) Compressed domain video processing for adaptation, encryption, and authentication. IEEE MultiMedia 15:38–50
Liu D, Setton E, Shen B, Chen S (2007) PAT: peer-assisted transcoding for overlay streaming to heterogeneous devices, in Proc. of NOSSDAV
ISO/IEC 21000-7:2004, Information Technology Multimedia Framework Part 7: DIA
Hosseini M, Ahmed DT, Shirmohammadi S, Georganas ND (2007) A survey of application-layer multicast protocols. IEEE Comm. Surveys and Tutorials 9(3):58–74
Banerjee S, Bhattacharjee B, Kommareddy C (2002) Scalable application layer multicast, in Proc. of SIGCOMM, pp. 205 – 217
Tran DA, Hua KA, Do TT (2004) A peer-to-peer architecture for media streaming, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, pp. 121– 133
Padmanabhan VN, Wang HJ, Chou PA, Sripanidkulchai K (2002) Distributing streaming media content using cooperative networking, in Proc. of NOSSDAV
Zhu Y, Li B, Guo J (2004) Multicast with network coding in application-layer overlay networks, IEEE J. Selected Areas Communication, no. 22, pp. 107–120
Zhang M, Luo JG, Zhao L, Yang SQ (2005) A peer-to-peer network for live media streaming using a push-pull approach, in Proc. of ACM intl. Conf. MM, pp. 287–290
Setton E, Baccichet P, Girod B (2008) Peer-to-peer Live multicast: A video perspective, in Proc. of IEEE, Vol. 96, No. 1
Tan X, Datta S (2005) Building multicast trees for multimedia streaming in heterogeneous P2P networks, in Proc. of Systems Communications, pp. 141 – 146
Rodriguez A, Kostic D, Vahdat A (2004) Scalability in adaptive multi-metric overlays, in Proc. of Intl Conf. on Distributed Computing Systems, pp. 112 – 121
Rejaie R, Ortega A (2003) PALS: Peer-to-peer adaptive layered streaming, in Proc. of NOSSDAV, pp. 153 – 161
Xiaofeng X et al (2004) A peer-to-peer video-on-demand system using multiple description coding and server diversity, in Proc. of ICIP, pp. 1759–1762
Exarchakos G, Antonopoulos N (2007) Resource sharing architecture for cooperative heterogeneous P2P overlays. J Netw Syst Manag 15:311–334
Shen B, Tan W, Huve F (2008) Dynamic video transcoding in mobile environments, IEEE Multimedia
Iqbal R, Ahmed DT, Shirmohammadi S (2008) Distributed video adaptation and streaming for heterogeneous devices, in IEEE Workshop on Mobile Peer-to-Peer Computing, in Proc. of IEEE PerCom Workshops, pp. 492 – 497
Iqbal R, Hariri B, Shirmohammadi S (2008) Modeling and evaluation of overlay generation problem for peer-assisted video adaptation and streaming, in Proc. of NOSSDAV, pp. 87 – 92
Sripanidkulchai K, Ganjam A, Maggs B, Zhang H (2004) The feasibility of supporting large-scale live streaming applications with dynamic application endpoints, in Proc. of SIGCOMM
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iqbal, R., Shirmohammadi, S. DAg-stream: Distributed video adaptation for overlay streaming to heterogeneous devices. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2, 202–216 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-009-0031-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-009-0031-0