Abstract
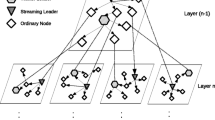
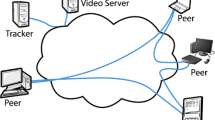
Coolstreaming is a mesh based peer-to-peer (P2P) video streaming system in which single video stream is decomposed into multiple sub-streams. A client-peer node retrieves the sub-streams from multiple parent-peer nodes, combining them into the original video stream. Each client-peer node has two buffers, a synchronization buffer and a cache buffer, and arriving data blocks are synchronized at the synchronization buffer and then forwarded to the cache buffer. In this buffering system, data-block synchronization is important to guarantee high video quality. In this paper, we consider the effect of churn on the performance of data-block synchronization scheme with which data blocks are simultaneously forwarded just after all the data blocks composing a macro data block arrive at the synchronization buffer. It is assumed that data blocks belonging to a sub-stream arrive at the client-peer node according to an interrupted Poisson process. The synchronization buffer is modeled as a multiple-buffer queueing system with homogeneous interrupted Poisson processes, and the mean forwarding interval is derived. Numerical examples show that the average forwarding interval increases as parent-peer nodes leave more frequently.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
BitTorrent. http://www.bittorrent.com
Castro M, Druschel P, Kermarrec AM, Nandi A, Rowstron A, Singh A (2003) SplitStream: high-bandwidth content distribution in cooperative environments. In: Proceedings of SOSP, pp 292–303
Deering S (1988) Multicast routing in Internetworks and extended LANs. In: Proceedings of ACM SIGCOMM, pp 55–64
Jurca D, Chakareski J, Wagner JP, Frossard P (2007) Enabling adaptive video streaming in P2P systems. IEEE Commun Mag 45:108–114
Kumar R, Liu Y, Ross K (2007) Stochastic fluid theory for P2P streaming systems. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM 2007, pp 919–927
Leonard D, Yao Z, Rai V, Loguinov D (2007) On lifetime-based node failure and stochastic resilience of decentralized peer-to-peer networks. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 15:644–656
Li B, Yin H (2007) Peer-to-peer live video streaming on the Internet: issues, existing approaches, and challenges. IEEE Commun Mag 45:94–99
Li B, Xie S, Keung GY, Zhang X (2007) Coolstreaming: design, theory, and practice. IEEE Trans Multimedia 9:1661–1671
Li B, Xie S, Qu Y, Keung GY, Lin C, Liu J, Zhang X (2008) Inside the new coolstreaming: principles, measurements and performance implications. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, pp 1031–1039
Nanao S, Masuyama H, Kasahara S, Takahashi Y (2010) Performance analysis of data block synchronization mechanism in coolstreaming. In: Proceedings of queueing theory and network applications, pp 53–58. The extended version of this paper will appear in Journal of Industrial and Management Optimization. Available: http://infosys.sys.i.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~kasahara/tmp/nmkt2011.pdf
Padmanabhan VN, Wang HJ, Chou PA, Sripanidkulchai K (2002) Distributing streaming media content using cooperative networking. In: Proceedings of NOSSDAV, pp 177–186
PPlive. http://www.pplive.com
Sopcast. http://www.sopcast.org
Wu D, Hou YT, Zhang Y (2000) Transporting real-time video over the internet: challenges and approaches. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, pp 1855–1877
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nanao, S., Masuyama, H., Kasahara, S. et al. Effect of node churn on frame interval for peer-to-peer video streaming with data-block synchronization mechanism. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 5, 244–256 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-011-0120-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-011-0120-8