Abstract
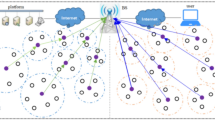
The energy consumption and the Quality of Service (QoS) are the major concern in Wireless Sensor Network (WSN). Dissimilar sensor nodes in the heterogeneous network are the efficient network strategy. Since it has some capabilities like enhanced processing ability, additional memory power and distant transmission ability. For effective clustering and route formation among the pair of nodes, an efficient Enhanced Fuzzy C means and Adaptive TDMA Scheduling (ECATS) method is proposed as a protocol to facilitate communication within the network. So that data packets can be delivered within time to the mobile sink. Here introducing the novel protocol named as Neural Elliptic Galois (NEG) cryptography for efficient data security. Also, the location privacy (Threshold fault node detection) is taken in to account for better security. Cluster head (CH) selection is done on the basis of energy to manage the data aggregation among a number of nodes in the network. Here, hybridization of TDMA based Ant Lion Optimization scheduling is introduced for optimal CH selection is used for better energy efficiency. Finally, ECATS can be done with optimized WSN performance metrics such as packet delivery ratio, throughput, minimum energy consumptions, communication overheads & end to end delay. Thus, we can increase the reliability of the network while minimizing the energy consumption and the results are compared with few existing routing protocols using MATLAB simulation tool.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chong CY, Kumar SP (2003) Sensor networks: Evolution, opportunities, and challenges. Proc IEEE 91(8):1247–1256
Cardei M, Wu J (2006) Energy-efficient coverage problems in wireless ad-hoc sensor networks. Comput Commun 29(4):413–420
Cui S, Goldsmith AJ, Bahai A (2004) Energy-efficiency of MIMO and cooperative MIMO techniques in sensor networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communication 22(6):1089–1098
Daly DC, Chandrakasan AP (2007) An energy-efficient OOK transceiver for wireless sensor networks. IEEE J Solid State Circuits 42(5):1003–1011
Tan HÖ, Körpeoǧlu I (2003) Power efficient data gathering and aggregation in wireless sensor networks. ACM SIGMOD Rec 32(4):66–71
Ye W, Heidemann J, Estrin D (2002) An energy-efficient MAC protocol for wireless sensor networks. Proc IEEE 3(1):1567–1576
Chamberland JF, Veeravalli VV (2004) Asymptotic results for decentralized detection in power constrained wireless sensor networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 22(6):1007–1015
Koubâa A, Severino R, Alves M, Tovar E (2009) Improving quality-of-service in wireless sensor networks by mitigating hidden-node collisions. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 5(3):299–313
Gungor VC, Hancke GP (2009) Industrial wireless sensor networks: Challenges, design principles, and technical approaches. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 56(10):4258–4265
Cardei M, Du DZ (2005) Improving wireless sensor network lifetime through power aware organization. Wirel Netw 11(3):333–340
Felemban E, Lee CG, Ekici E (2006) MMSPEED: Multipath multi-SPEED protocol for QoS guarantee of reliability and timeliness in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 5(6):738–754
Wang C, Li B, Sohraby K, Daneshmand M, Hu Y (2007) Upstream congestion control in wireless sensor networks through cross-layer optimization. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 25(4):786–795
Huang X, Fang Y (2008) Multi-constrained QoS multipath routing in wireless sensor networks. Wirel Netw 14(4):465–478
Akyildiz IF, Melodia T, Chowdhury KR (2008) Wireless multimedia sensor networks: Applications and testbeds. Proc IEEE 96(10):1588–1605
Liu Y, Zhu Y, Ni L, Xue G (2011) A reliability-oriented transmission service in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems 22(12):2100–2107
Liang Y, Yu HB, Zeng P (2005) Routing protocols for wireless sensor networks. Information and Control-Shenyang 34(3):325
Heinzelman WB, Chandrakasan AP, Balakrishnan H (2002) An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless micro-sensor networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 1(4):660–670
Al-Karaki JN, Kamal AE (2004) Routing techniques in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Wirel Commun 11(6):6–28
Karlof C, Wagner D (2003) Secure routing in wireless sensor networks. Attacks and Countermeasures Ad hoc Networks 1(2):293–315
Wattenhofer R, Li L, Bahl P, Wang YM (2001) Distributed topology control for power efficient operation in multihop wireless ad hoc networks. IEEE Computer and Communications Societies 3(1):1388–1397
Long J, Dong M, Ota K, Liu A (2017) A green TDMA scheduling algorithm for prolonging lifetime in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Syst J 11(2):868–877
Haseeb K, Abu Bakar K, Abdullah AH, Darwish T (2017) Adaptive energy aware cluster-based routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. Wirel Netw 23(6):1953–1966
Liu Y, Dong M, Ota K, Liu A (2016) Active trust: Secure and trustable routing in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 11(9):2013–2027
Khabiri M, Ghaffari A (2018) Energy-aware clustering-based routing in wireless sensor networks using cuckoo optimization algorithm. Wirel Pers Commun 98(3):2473–2495
Li G, Dong M, Ota K, Wu J, Li J, Ye T (2017) Towards QoE named content-centric wireless multimedia sensor networks with mobile sinks. In Communications (ICC), 2017 IEEE International Conference on IEEE, p 1–6
Dong M, Liu OKA, Guo M (2016) Joint optimization of lifetime and transport delay under reliability constraint wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems 27(1):225–236
Qiu C, Xiao J, Han L, Iqbal MN (2014) Enhanced interval type-2 fuzzy c-means algorithm with improved initial center. Pattern Recogn Lett 38:86–92
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kavidha, V., Ananthakumaran, S. Novel energy-efficient secure routing protocol for wireless sensor networks with Mobile sink. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 12, 881–892 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-018-0688-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-018-0688-3