Abstract
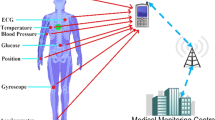
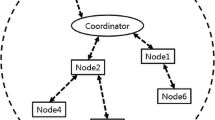
Wireless body area network (WBAN) can collect and analyze human health signs data of various modes in real time by virtue of low-energy consumption high-precision sensing technology, and it needs to protect health sensitive data related to personal privacy in the process of data transmission. In order to solve the important problem of reliable data transmission in wireless body area network, a new strategy is proposed in this paper. From the two levels of single-hop communication and two-hop communication, the channel characteristics and node data rate in WBAN are fully considered. The reliable data transmission in wireless body area network is realized by using time slot allocation and relay strategy. The introduction of TDMA mechanism of dynamic time slot allocation improves the energy efficiency of strategy and avoids the energy consumption caused by competition, while dynamic time slot allocation satisfies the change of node flow. Time slot allocation strategy based on channel condition and data traffic, exist some nodes in the practical use of the status of the data transmission reliability not guaranteed, we use the relay for this strategy to improve its, meet the requirements of the reliability of data transmission in the network, to bring the additional energy consumption, and strategy information dynamic relay selection depend on the channel information and energy, so that improve the energy efficiency, its energy consumption is reduced. Simulation results show that our transmission strategy can significantly improve the transmission success rate and reduce packet loss, and can adjust the channel changes to improve the reliability of data transmission.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hossain MA, Elshafiey I, Al-Sanie A (2019) Cooperative vehicle positioning with multi-sensor data fusion and vehicular communications. Wirel Netw 25(3):1403–1413
Nada D, Bousbia-Salah M, Bettayeb M (2018) Multi-sensor data fusion for wheelchair position estimation with unscented Kalman filter. Int J Autom Comput 15(2):1–11
Schilling H, Bulatov D, Niessner R et al (2018) Detection of vehicles in multisensor data via multibranch convolutional neural networks. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing PP(99):1–18
Habib C, Makhoul A, Darazi R et al (2016) Multisensor data fusion and decision support in wireless body sensor networks. In: Network Operations & Management Symposium
Habib C, Makhoul A, Darazi R, Salim C (2016) Self-adaptive data collection and fusion for health monitoring based on body sensor networks. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 12(6):2342–2352
Fei X, Xiaofang LI (2016) Wireless sensor network data fusion algorithm based on compressed sensing theory. Journal of Jilin University 54(3):575–579
Hanaoka G, Nishioka T, Zheng Y et al (2018) A hierarchical non-interactive key-sharing scheme with low memory size and high resistance against collusion attacks. Comput J 45(3):293–303
Bai S, Geng Y, Shi J et al (2018) Privacy-preserving oriented floating-point number fully homomorphic encryption scheme. Security and Communication Networks 2018:1–14
Bai X, Wang Z, Li S et al (2018) Reliable data fusion of hierarchical wireless sensor networks with asynchronous measurement for greenhouse monitoring. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol PP(99):1–11
Huang Y, Yi L, Miao R (2018) An auxiliary blind guide system based on multi-sensor data fusion. In: International Conference on Cyber-enabled Distributed Computing & Knowledge Discovery
Bhardwaj J, Gupta KK, Gupta R (2018) Towards a cyber-physical era: soft computing framework based multi-sensor array for water quality monitoring. Drink Water Eng Sci 11:1):1–1):7
Long X, Yang P, Guo H et al (2019) A CBA-KELM-based recognition method for fault diagnosis of wind turbines with time-domain analysis and multisensor data fusion. Shock Vib 2019:11):1–11)14
Sun G, Liu Y, Shen G et al (2018) Multi-objective optimization for distributed collaborative beamforming in mobile wireless sensor networks. In: 2018 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC)
Kim M, Song C, Liu K (2019) A generic health index approach for multisensor degradation modeling and sensor selection. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng PP(99):1–12
Venkatesh V, Raj P, Balakrishnan P (2017) An energy-efficient fuzzy based data fusion and tree based clustering algorithm for wireless sensor networks. In: International Symposium on Intelligent Systems Technologies & Applications
Pannetier B, Doumerc R, Moras J et al (2016) Data fusion for target tracking and classification with wireless sensor network. In: Unmanned/unattended Sensors & Sensor Networks XII
Zhao W, Lu H, Dong W (2018) Multisensor image fusion and enhancement in spectral Total variation domain. IEEE Trans Multimedia 20(4):866–879
Xiuwu YU, Fan F, Zhou L et al (2017) Adaptive forecast weighting data fusion algorithm for wireless sensor network. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators 30(5):772–776
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Henan Department of Science and Technology Research Project (No. 182102311126), Henan Education Department Natural Science Research Project (No. 16A520106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection: Special Issue on Fog/Edge Networking for Multimedia Applications
Guest Editors: Yong Jin, Hang Shen, Daniele D'Agostino, Nadjib Achir, and James Nightingale
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W. A data fusion privacy protection strategy with low energy consumption based on time slot allocation and relay in WBAN. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 12, 1575–1584 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-019-00788-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-019-00788-2