Abstract
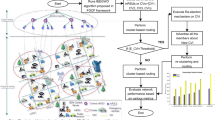
Internet of Vehicle (IoV) technology is a promising application of Internet of Things (IoT) employed in smart city environment for smart communication. Traffic handling and non-delay tolerant communication services are expected from the communicating vehicles to improve its application efficiency. With the consideration of IoV in healthcare applications, this manuscript introduces a rapid connection aware neighbor selection (RCNS) for improving the efficiency in handling medical information. The selection process is induced by an instantaneous reward based learning algorithm (RLA) for ease of neighbor selection. The multi-attributes of the neighbors in the information transmitting route are estimated with the knowledge of their position. Distance and reward of the neighbors in the transmission direction are assessed using a beacon-assisted vehicle discovery that minimizes the impact of collision. Different from the other neighbor selection schemes, this method is relies on renewed attribute estimated at the time of transmission. This aids the transmitter to decide transmission and modify transmission attributes. The performance of the proposed neighbor selection method is estimated through extensive simulation using the metrics: delay, delivery ratio, selection overhead and outage.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang FC, Wang SG, Li JL, Liu ZH, Sun QB (2014) An overview of internet of vehicles. China Commun Veh Netw 11(10):1–15
Lu N, Cheng N, Zhang N, Shen X, Mark JW (2014) Connectedvehicles: solutions and challenges. IEEE Internet Things J 1(4):289–299
Ning Z, Hu X, Chen Z, Zhou M, Hu B, Cheng J, Obaidat MS (2018) A cooperative quality-aware service access system for social internet of vehicles. IEEE Internet Things J 5(4):2506–2517
Jeong Y-S, Shin S-S (2016) An IoT healthcare service model of a vehicle using implantable devices. Clust Comput 21(1):1059–1068
Pedan M, Gregor M, Plinta D (2017) Implementation of automated guided vehicle system in healthcare facility. Procedia Eng 192:665–670
Detti P, Papalini F, Lara GZMD (2017) A multi-depot dial-a-ride problem with heterogeneous vehicles and compatibility constraints in healthcare. Omega 70:1–14
Shakeel PM (2014) Neural networks based prediction of wind energy using pitch angle control. Int J Innov Sci Eng Res (IJISER) 1(1):33–37
Tong W, Hussain A, Bo WX, Maharjan S (2019) Artificial intelligence for vehicle-to-everything: a survey. IEEE Access 7:10823–10843
Wang X et al (2019) Optimizing content dissemination for real-time traffic Management in Large-Scale Internet of vehicle systems. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 68(2):1093–1105
Shah SS, Malik AW, Rahman AU, Iqbal S, Khan SU (2019) Time barrier-based emergency message dissemination in vehicular ad-hoc networks. IEEE Access 7:16494–16503
Ullah A, Yaqoob S, Imran M, Ning H (2019) Emergency message dissemination schemes based on congestion avoidance in VANET and vehicular FoG computing. IEEE Access 7:1570–1585
Tiennoy S, Saivichit C (2018) Using a distributed roadside unit for the data dissemination protocol in VANET with the named data architecture. IEEE Access 6:32612–32623
Qiu T, Wang X, Chen C, Atiquzzaman M, Liu L (2018) TMED: a spider-web-like transmission mechanism for emergency data in vehicular Ad Hoc networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 67(9):8682–8694
Modesto FM, Boukerche A (2018) SEVeN: a novel service-based architecture for information-centric vehicular network. Comput Commun 117:133–146
Meneguette RI, Boukerche A, Silva FA, Villas L, Ruiz LB, Loureiro AAF (2018) A novel self-adaptive content delivery protocol for vehicular networks. Ad Hoc Netw 73:1–13
Aadil F, Ahsan W, Rehman ZU, Shah PA, Rho S, Mehmood I (2018) Clustering algorithm for internet of vehicles (IoV) based on dragonfly optimizer (CAVDO). J Supercomput 74(9):4542–4567
Zhang C, Cho H-H, Chen C-Y (2019) Emergency-level-based healthcare information offloading over fog network. Peer-to-Peer Netw Appl
Mahmood DA, Horváth G (2018) Analysis of the message propagation on the highway in VANET. Arab J Sci Eng:3405–3444
Duarte JM, Kalogeiton E, Soua R, Manzo G, Palattella MR, Maio AD, Braun T, Engel T, Villas LA, Rizzo GA (2017) A multi-pronged approach to adaptive and context aware content dissemination in VANETs. Mob Netw Appl 23(5):1247–1259
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thirugnanam, T., Ghalib, M.R. A reward based connectivity-aware IoV neighbor selection for improving reliability in healthcare information exchange. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 13, 2112–2122 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-019-00829-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-019-00829-w