Abstract
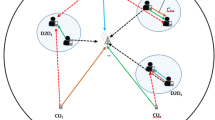
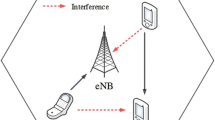
Device-to-Device (D2D) based communication plays a major part in improving the 5G network’s system capacity. In pursuance of accomplishing this, effective resource and power allocation algorithms have to be designed for D2D users. As D2D users are considered as secondary users, their interference with cellular users (CUs) should not restrict the communication which is performed based on CU. Most of the existing methodologies performed on bandwidth allocation assume full Channel State Information (CSI) at the base station (BS), which resulted in uncertainty resource allocation. Hence to resolve this, the proposed scheme is developed with an efficient handoff strategy based on bandwidth allocation using Thompson Sampling Bandwidth (TSB) and Magnetic Force Optimization (MFO) for D2D and CU communications along with guaranteed QoS constraint. Here, the available free bandwidth is selected using the TSB technique which in turn is based on overall data rate, level of interference and number of CU users. In this, Magnetic Force optimization (MFO) is utilized for base station selection. This is done based on signal strength variation, coverage area between user and base station, and bandwidth capacity. Thus it results in guaranteed QoS constraint, i.e., parameters like Packet delay; throughput, data rate and reduction in allocated sub-carriers are attained. Finally, the simulation outcomes are performed and the results are estimated in terms of average delay, throughput, node deployment, and data rate. Therefore, the comparative analysis is carried out between the attained outcomes with that of the existing techniques to prove the efficacy of the proposed TSB-MFO technique.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emara M et al (2018) Optimal caching in 5G networks with opportunistic spectrum access. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 17:4447–4461
Wang C et al (2018) Energy-efficient cooperative spectrum sensing with reporting errors in hybrid spectrum sharing CRNs. IEEE Access 6:48391–48402
da Mata SH, Guardieiro PR (2017) Resource allocation for the LTE uplink based on Genetic Algorithms in mixed traffic environments. Comput Commun 107:125–137
Deotale N et al (2018) Optimal transmit antenna selection for LTE system using self-adaptive grey wolf optimization. Multiagent Grid Syst 14:67–82
Parmar S, Mishra K (2019) Use of Moth Flame Optimization for improvement in wireless communication systems
Lee YL et al (2017) Multi-objective resource allocation for LTE/LTE-A femtocell/HeNB networks using ant colony optimization. Wirel Pers Commun 92:565–586
Ahuja K et al (2016) Network selection based on available link bandwidth in multi-access networks. Digit Commun Netw 2:15–23
Modi N et al (2017) QoS driven channel selection algorithm for cognitive radio network: Multi-user multi-armed bandit approach. IEEE Trans Cogn Commun Netw 3:49–66
Tian Z et al (2019) Distributed NOMA-Based Multi-Armed Bandit Approach for Channel Access in Cognitive Radio Networks. IEEE Wirel Commun Lett 8:1112–1115
Nandakumar S et al (2019) Efficient spectrum handoff using hybrid priority queuing model in cognitive radio networks. Wirel Pers Commun 108:203–212
Mir U, Munir A (2018) An adaptive handoff strategy for cognitive radio networks. Wirel Netw 24:2077–2092
Safavi SE, Subbalakshmi K (2015) Effective bandwidth for delay tolerant secondary user traffic in multi-PU, multi-SU dynamic spectrum access networks. IEEE Trans Cogn Commun Netw 1:175–184
Falcão MR et al (2018) A flexible-bandwidth model with channel reservation and channel aggregation for three-layered Cognitive Radio Networks. Comput Netw 135:213–225
Darabi M et al (2018) Packet size adjustment for minimizing the average delay in buffer-aided cognitive machine-to-machine networks. Comput Electr Eng 68:298–309
Darabi M et al (2017) Adaptive mode selection in cognitive buffer-aided full-duplex relay networks with imperfect self-interference cancellation for power and delay limited cases,“ in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), pp 918–923
Mashoodha P, Kumar KV (2016) Risk and QoE driven channel allocation in CRN. Procedia Technol 24:1629–1634
Gahane L et al (2017) An improved energy detector for mobile cognitive users over generalized fading channels. IEEE Trans Commun 66:534–545
Yu W et al (2017) Statistical delay QoS driven energy efficiency and effective capacity tradeoff for uplink multi-user multi-carrier systems. IEEE Trans Commun 65:3494–3508
Khakurel S et al (2018) Qos-aware utility-based resource allocation in mixed-traffic multi-user ofdm systems. IEEE Access 6:21646–21657
Yu W et al (2016) Tradeoff analysis and joint optimization of link-layer energy efficiency and effective capacity toward green communications. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 15:3339–3353
Farooq-I-Azam M et al (2018) Location Assisted Subcarrier and Power Allocation in Underlay Mobile Cognitive Radio Networks. In: 2018 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), pp 1–6
Khuntia P, Hazra R (2018) Resource sharing for device-to-device communication underlaying cellular network. In: 2018 4th International Conference on Recent Advances in Information Technology (RAIT), pp 1–5
Ferdouse L et al (20170) Interference and throughput aware resource allocation for multi-class D2D in 5G networks. Iet Commun 11:1241–1250
Ahmed E et al (2017) Social-aware resource allocation and optimization for D2D communication. IEEE Wirel Commun 24:122–129
Mohan D, Amalanathan GM (2018) A survey on long term evolution scheduling in data mining. Wirel Pers Commun 102:2363–2387
Omitola OO, Srivastava VM (2018) Group handover strategy for mobile relays in LTE-A networks. J Commun 13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection: Special Issue on P2P Computing for Beyond 5G Network and Internet-of-Everything
Guest Editors: Prakasam P, Ajayan John, Shohel Sayeed
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohan, D., Amalanathan, G.M. The efficacy of handoff strategy based spectrum allocation using TSB-MFO for D2D and CU communications. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 14, 279–295 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-020-00935-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-020-00935-0