Abstract
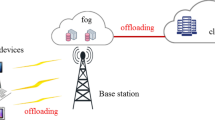
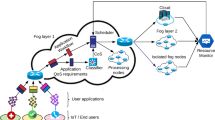
In this paper, we consider the computation offloading optimization problem with heterogeneous resources in a fog-cloud computing system. The problem is common in many real-time and mobile applications, where tasks are massive and computation-intensive, and the computing resources could involve both fog devices and cloud platforms. The challenges lie in proposing effective, efficient and robust algorithms with the objectives of minimizing both the total delay and the energy consumption. A bi-objective task scheduling model is formulated, in which the queuing models for the delay estimation and the energy consumption models for heterogeneous resources are introduced. A Pareto-optimization-based Massive Task Scheduling Framework is proposed to schedule massive tasks within one time unit. It starts from a non-dominated solution set obtained by the energy-ware and the transmission delay-aware local search procedures. A tree-based local search method is proposed to further improve the non-dominated solutions. The proposed algorithm is compared to four classical algorithms for the similar problems. Their performances are evaluated by the Pareto-optimization metrics on multiple aspects. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposal for the problem under study.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiang M, Zhang T (2016) Fog and iot: An overview of research opportunities. IEEE Internet Things 3(6):854–864
Al-Fuqaha A, Guizani M, Mohammadi M, Aledhari M, Ayyash M (2015) Internet of things: A survey on enabling technologies, protocols, and applications. IEEE Comm Surv Tut 17(4):2347–2376
Stankovic JA (2014) Research directions for the internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J 1 (1):3–9
Du J, Zhao L, Feng J, Chu X (2018) Computation offloading and resource allocation in mixed fog/cloud computing systems with min-max fairness guarantee. IEEE Trans Commun 66(4):1594–1608
Jiang Y, Chen Y, Yang S, Wu C (2019) Energy-efficient task offloading for time-sensitive applications in fog computing. IEEE Syst J 13(3):2930–2941
Wang J, Liu K, Li B, Liu T, Li R, Han Z (2019) Delay-sensitive multi-period computation offloading with reliability guarantees in fog networks. IEEE T Mobile Comput :1–1
Du J, Zhao L, Chu X, Yu FR, Feng J, CI (2019) Enabling low-latency applications in lte-a based mixed fog/cloud computing systems. IEEE T Veh Technol 68(2):1757–1771
Wang K, Zhou Y, Liu Z, Shao Z, Luo X, Yang Y (2020) Online task scheduling and resource allocation for intelligent noma-based industrial internet of things. IEEE J Sel Area Comm 38(5):803–815
Zhang G, Shen F, Liu Z, Yang Y, Wang K, Zhou M (2019) Femto: Fair and energy-minimized task offloading for fog-enabled iot networks. IEEE Internet Things J 6(3):4388–4400
Wei X, Tang C, Fan J, Subramaniam S (2019) Joint optimization of energy consumption and delay in cloud-to-thing continuum. IEEE Internet Things J 6(2):2325–2337
Dong Y, Guo S, Liu J, Yang Y (2019) Energy-efficient fair cooperation fog computing in mobile edge networks for smart city. IEEE Internet Things J 6(5):7543–7554
Liu L, Chang Z, Guo X, Mao S, Ristaniemi T (2018) Multiobjective optimization for computation offloading in fog computing. IEEE Internet Things J 5(1):283–294
Topcuoglu H, Hariri S, Min-You WU (2002) Performance-effective and low-complexity task scheduling for heterogeneous computing. IEEE Trans Parall Distr Syst 13(3):260–274
Zhu J, Li X, Ruiz R, Xu X (2018) Scheduling stochastic multi-stage jobs to elastic hybrid cloud resources. IEEE Trans Parall Distr Syst 29(6):1401–1415
Rubaiee S, Cinar S, Yildirim MB (2019) An energy-aware multiobjective optimization framework to minimize total tardiness and energy cost on a single-machine nonpreemptive scheduling. IEEE T Eng Manage 66(4):699–714
Zhu J, Li X, Ruiz R, Li W, Huang H, Zomaya AY (2020) Scheduling periodical multi-stage jobs with fuzziness to elastic cloud resources. IEEE Trans Parall Distr Syst 31(12):2819– 2833
Tan K, Goh C-K, Yang Y, Lee T (2006) Evolving better population distribution and exploration in evolutionary multi-objective optimization. Eur J Oper Res 171:463–495, 06
Zitzler E, Thiele L, Laumanns M, Fonseca CM, da Fonseca VG (2003) Performance assessment of multiobjective optimizers: an analysis and review. IEEE T Evolut Comput 7(2):117– 132
Zhang D, Haider F, St-Hilaire M, Makaya C (2019) Model and algorithms for the planning of fog computing networks. IEEE Internet Things J 6(2):3873–3884
Bitam S, Zeadally S, Mellouk A (2018) Fog computing job scheduling optimization based on bees swarm. Enterp Inform Syst 12(4):373–397
Bukhsh R, Javaid N, Khan ZA, Ishmanov F, Afzal MK, Wadud Z (2018) Towards fast response, reduced processing and balanced load in fog-based data-driven smart grid. ENERGIES 11(12)
Wu C, Li W, Wang L, Zomaya A (2018) Hybrid evolutionary scheduling for energy-efficient fog-enhanced internet of things. IEEE Trans Cloud Comput :1–1
Liu L, Chang Z, Guo X (2018) Socially aware dynamic computation offloading scheme for fog computing system with energy harvesting devices. IEEE Internet Things J 5(3):1869–1879
Xiaolong XU, Shucun FU, Cai Q, Tian W, Liu W, Dou W, Sun X, Liu AX (2018) Dynamic resource allocation for load balancing in fog environment. Wireless Commun Mobile Comput :1–15
Deng R, Rongxing LU, Lai C, Luan TH, Hao L (2016) Optimal workload allocation in fog-cloud computing towards balanced delay and power consumption. IEEE Internet Things J 3(6):1171–1181
Chen S, Zheng Y, Lu W, Varadarajan V, Wang K (2020) Energy-optimal dynamic computation offloading for industrial iot in fog computing. IEEE Trans Green Commun Network 4(2):566– 576
Zhu T, Shi T, Li J, Cai Z, Zhou X (2019) Task scheduling in deadline-aware mobile edge computing systems. IEEE Internet Things J 6(3):4854–4866
Vu D-N, Dao N-N, Jang Y, Na W, Kwon Y-B, Kang H, Jung JJ, Cho S (2019) Joint energy and latency optimization for upstream iot offloading services in fog radio access networks. T Emerg Telecommun T 30(4):e3497. e3497 ett.3497.
Sun G, Zhang F, Liao D, Yu H, Du X, Guizani M (2019) Optimal energy trading for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles based on fog computing. IEEE Internet Things J 6(2):2309–2324
Kunlun LI, Wang J (2017) Multi-objective optimization for cloud task scheduling based on the anp model. Chinese J Electron 5:889–898
Huang T, Lin W, Xiong C, Pan R, Huang J (2020) An ant colony optimization-based multiobjective service replicas placement strategy for fog computing. IEEE T Cybernetics :1–14
Rao L, Liu X, Ilic MD, Liu J (2012) Distributed coordination of internet data centers under multiregional electricity markets. P IEEE 100(1):269–282
Li BB, Wang L (2007) A hybrid quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for multiobjective flow shop scheduling. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 37(3):576–591
Rao L, Liu X, Xie L, Liu W (2012) Coordinated energy cost management of distributed internet data centers in smart grid. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 3(1):50–58
Barzegaran M, Cervin A, Pop P (2019) Towards quality-of-control-aware scheduling of industrial applications on fog computing platforms. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Fog Computing and the IoT, IoT-Fog ’19. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, pp 1–5
Acknowledgment
This work is sponsored by the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (Grant No. 18KJB520039), the National Science Foundation for Post-doctoral Scientists of China (Grant No. 2018M640510), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20201375), the National Natural Science Foundations of China (Grant Nos. 62072252).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, M., Zhu, J. & Huang, H. Energy and delay-ware massive task scheduling in fog-cloud computing system. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 14, 2139–2155 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-021-01118-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-021-01118-1