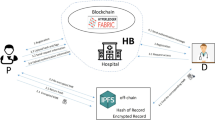
Abstract
The sharing of electronic medical records (EMRs) is of immense value for disease research and epidemic prevention. It has received considerable attention from researchers. EMR sharing and management which based on blockchain have demonstrated remarkable achievement. Nevertheless, there remain certain obstacles that necessitate attention and resolution. Most blockchain-based eHealth systems store EMRs on outsourcing companies. The outsourcing companies may leak electronic medical records. Moreover, patients cannot decide who can access their electronic medical records and lose control of their EMR completely. To solve these problems, we propose a patient-centered EMR sharing and management scheme based on blockchain with proxy re-encryption algorithm to protect the interests of the patient and use smart contracts to achieve patients control on their electronic medical records. Moreover, a decentralized proxy that re-encrypts the electronic medical records is adopted to improve the security and availability of our system. Furthermore, we use an architecture to compute the hash root with chameleon hash to implement additional features such as electronic medical record modification, emergency access, and access revocation. To evaluate our scheme, our scheme is deployed on Hyperledger Fabric. The results which published by Hyperledger Caliper show the successful performance of our scheme in achieving security and privacy requirements.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Azaria A, Ekblaw A, Vieira T et al (2016) Medrec: using blockchain for medical data access and permission management. In: 2016 2nd international conference on open and big data (OBD). IEEE, pp 25–30
Azbeg K, Ouchetto O, Andaloussi SJ (2022) Blockmedcare: A healthcare system based on iot, blockchain and ipfs for data management security. Egypt Inform J 23(2):329–343
Blaze M, Bleumer G, Strauss M (1998) Divertible protocols and atomic proxy cryptography. In: International conference on the theory and applications of cryptographic techniques. Springer, pp 127–144
Chen HY, Wu ZY, Chen TL et al (2021) Security privacy and policy for cryptographic based electronic medical information system. Sensors 21(3)
Da Costa L, Pinheiro B, Cordeiro W et al (2023) Sec-health: A blockchain-based protocol for securing health records. IEEE Access 11:16605–16620
Du M, Chen Q, Chen J et al (2020) An optimized consortium blockchain for medical information sharing. IEEE Trans Eng Manage 68(6):1677–1689
Durao F, Carvalho JFS, Fonseka A et al (2014) A systematic review on cloud computing. J Supercomput 68:1321–1346
Fabric H (2020) A blockchain platform for the enterprise
Fiore M, Capodici A, Rucci P et al (2023) Blockchain for the healthcare supply chain: A systematic literature review. Appl Sci 13(2):686
Hoang HD, Thi Thu Hien D, Nhut TC et al (2021) A blockchain-based secured and privacy-preserved personal healthcare record exchange system. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applied Network Technologies (ICMLANT), pp 1–5
Hu M, Ren Y, Chen C (2023) Privacy-preserving medical data-sharing system with symmetric encryption based on blockchain. Symmetry 15(5)
Huang J, Qi YW, Asghar MR et al (2022) Sharing medical data using a blockchain-based secure ehr system for new zealand. IET Blockchain 2
Kuzlu M, Pipattanasomporn M, Gurses L et al (2019) Performance analysis of a hyperledger fabric blockchain framework: Throughput, latency and scalability. In: 2019 IEEE international conference on blockchain (Blockchain). IEEE, pp 536–540
Lee JP, Kim YH, Lee JK (2014) Ssl application for managed security between the mobile and his biometric information collection client. In: 2014 28th International conference on advanced information networking and applications workshops. IEEE, pp 55–60
Lee JS, Chew CJ, Liu JY et al (2022) Medical blockchain: Data sharing and privacy preserving of ehr based on smart contract. J Inf Secur Appl 65:103117
Li H, Yang Y, Dai Y et al (2017) Achieving secure and efficient dynamic searchable symmetric encryption over medical cloud data. IEEE Trans Cloud Comput 8(2):484–494
Lin G, Wang H, Wan J et al (2022) A blockchain-based fine-grained data sharing scheme for e-healthcare system. J Syst Architect 132:102731
Liu X, Xia Y, Yang W et al (2018) Secure and efficient querying over personal health records in cloud computing. Neurocomputing 274:99–105
Liu X, Yan J, Shan S et al (2022) A blockchain-assisted electronic medical records by using proxy reencryption and multisignature. Secur Commun Netw 2022
Lu Y (2019) The blockchain: State-of-the-art and research challenges. J Ind Inf Integr 15:80–90
Khalili M, Dakhilalian M, Susilo W (2020) Efficient chameleon hash functions in the enhanced collision resistant model. Inf Sci 510:155–164
Nakamoto S (2008) Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system. Decentralized business review
Park YH, Kim Y, Lee SO et al (2021) Secure outsourced blockchain-based medical data sharing system using proxy re-encryption. Appl Sci 11(20):9422
Parthiban L, Sammeta N, Malathi ACJ et al (2023) Blockchain-based privacy-preserving electronics healthcare records in healthcare 4.0 using proxy re-encryption. In: Integrating blockchain and artificial intelligence for industry 4.0 innovations. Springer, pp 101–120
Shamir A (1979) How to share a secret. Commun ACM 22(11):612–613
Sharma S, Chen K, Sheth A (2018) Toward practical privacy-preserving analytics for iot and cloud-based healthcare systems. IEEE Internet Comput 22(2):42–51
Shen B, Guo J, Yang Y (2019) Medchain: Efficient healthcare data sharing via blockchain. Appl Sci 9(6):1207
Trombetta A, Masoomeh S, Maryam S (2017) Secure data sharing in cloud usingan efficient inner-product proxyre-encryption scheme. J Cyber Secur Mobil 6:339–378
Wood G (2014) Ethereum: A secure decentralised generalised transaction ledger. Ethereum Project Yellow Paper, 151(2014), 1–32
Xia Q, Sifah EB, Asamoah KO et al (2017) Medshare: Trust-less medical data sharing among cloud service providers via blockchain. IEEE Access 5:14757–14767
Yang H, Yang B (2017) A blockchain-based approach to the secure sharing of healthcare data. In: Proceedings of the norwegian information security conference, Nisk J Oslo, Norway, pp 100–111
Yuan WX, Yan B, Li W et al (2023) Blockchain-based medical health record access control scheme with efficient protection mechanism and patient control. Multimed Tools Appl 82(11):16279–16300
Zhang J, Sun J, Yang Y et al (2006) Image-based electronic patient records for secured collaborative medical applications. In: 2005 IEEE Engineering in medicine and biology 27th annual conference. IEEE, pp 3218–3220
Zhang X, Xi P, Liu W et al (2022) Emrsharechain: A privacy-preserving emr sharing system model based on the consortium blockchain. In: International symposium on bioinformatics research and applications. Springer, pp 343–355
Zou R, Lv X, Zhao J (2021) Spchain: Blockchain-based medical data sharing and privacy-preserving ehealth system. Information Processing & Management 58(4):102604
Funding
This work was granted by Qin Xin Talents Cultivation Program (No. QXTCP C202115), Beijing Information Science & Technology University; the Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Future Blockchain and Privacy Computing Fund (No.GJJ-23); National Social Science Foundation, China (No.21BTQ079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hanlin Zhou: Methodology, Conceptualization, Software, and Original Draft. Xia-Meng Si: Supervision, Review & Editing. Bobai Zhao: Validation, Investigation. Yaochen Zhang: Validation, Formal analysis, Software. YuanJun Qu: Visualization, Formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Si, XM., Zhao, B. et al. Secure electronic medical records sharing scheme based on blockchain by using proxy re-encryption. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 17, 4197–4209 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-024-01775-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-024-01775-y