Abstract
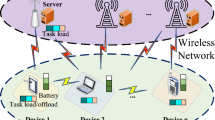
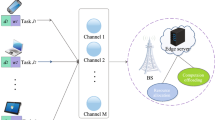
The research on Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) has attracted considerable attention in recent years. However, previous studies often confined themselves to exploring the issue of task resource scheduling from a single perspective of mobile terminals or edge servers, or failed to take into account the growth of users, thus unable to face complex and diverse practical scenarios and effectively address various challenges in task offloading. In view of this, this paper adopts a more comprehensive and in-depth perspective, considering not only the user’s performance benefits and the service provider’s economic benefits, but also conducting a thorough analysis of the potential continuous growth of user numbers in actual scenarios. To effectively address the rapid increase in user numbers within large-scale networks, we employ a decentralized approach where each user independently makes decisions regarding their own offloading strategies, rather than relying on centralized decision-making by the server. Based on this, we propose an innovative edge computing task offloading scheme that is particularly suitable for large-scale network environments. Specifically, we combine the Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (TD3) algorithm and innovatively propose a decentralized task offloading scheme called DSMECO-DP. In this scheme, considering the dynamic nature of networks and user volatility, the server aims to maximize profit through coarse time scale dynamic pricing, while the mobile terminal reduces its own costs by bidding on a narrow time scale considering multiple objectives such as time delay, energy consumption, and payment cost. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the TD3 algorithm compared to other reinforcement learning algorithms, as well as the effectiveness of the dynamic pricing mechanism. Furthermore, the processing time of this algorithm is significantly reduced compared to other centralized algorithms.












Similar content being viewed by others

Data Availability
No additional data are available.
References
Zhang W, Wen Y, Wu J, Li H (2013) Toward a unified elastic computing platform for smartphones with cloud support. IEEE Netw. https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2013.6616113
Satyanarayanan M, Bahl P, Caceres R, Davies N (2009) The case for vm-based cloudlets in mobile computing. IEEE Perv Comput. https://doi.org/10.1109/MPRV.2009.82
Islam A, Debnath A, Ghose M, Chakraborty S (2021) A survey on task offloading in multi-access edge computing. J Syst Arch. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sysarc.2021.102225
Jiang C, Cheng X, Gao H, Zhou X, Wan J (2019) Toward computation offloading in edge computing: A survey. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2938660
Zhang W, Wen Y, Guan K, Kilper D, Luo H, Wu D O (2013) Energy-optimal mobile cloud computing under stochastic wireless channel. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2013.072513.121842
Mahmoodi S E, Uma R N, Subbalakshmi K P (2016) Optimal joint scheduling and cloud offloading for mobile applications. IEEE Trans Cloud Comput. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCC.2016.2560808
Van Hasselt H, Guez A, Silver D (2016) Deep reinforcement learning with double q-learning. Proceed AAAI Conf Art Intell. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v30i1.10295
Silver D, Lever G, Heess N, Degris T, Wierstra D, Riedmiller M (2014) Deterministic policy gradient algorithms. Int Conf Mach Learn. http://proceedings.mlr.press/v32/silver14.html
Timothy P L, Jonathan J H, Alexander P, Nicolas H, Tom E, Yuval T, David S, Daan W (2015) Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv1509.02971
Fujimoto S, Hoof H, Meger D (2018) Addressing function approximation error in actor-critic methods. Int Conf Mach Learn. http://proceedings.mlr.press/v80/fujimoto18a.html
Chen Z, Wang X (2020) Decentralized computation offloading for multi-user mobile edge computing: A deep reinforcement learning approach. EURASIP J Wireless Commun Netw. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-020-01801-6
Chen S, Li L, Chen Z, Li S (2020) Dynamic pricing for smart mobile edge computing: A reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Wireless Commun Lett. https://doi.org/10.1109/LWC.2020.3039863
Hu Z, Niu J, Ren T, Dai B, Li Q, Xu M, Das S K (2021) An efficient online computation offloading approach for large-scale mobile edge computing via deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans Serv Comput. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSC.2021.3116280
Mao Y, Zhang J, Song S H, Letaief K B (2016) Power-delay tradeoff in multi-user mobile-edge computing systems IEEE Global Commun Conf. https://doi.org/10.1109/GLOCOM.2016.7842160
Huang L, Bi S, Zhang Y J A (2019) Deep reinforcement learning for online computation offloading in wireless powered mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2019.2928811
Liu L, Chang Z, Guo X, Mao S, Ristaniemi T (2017) Multiobjective optimization for computation offloading in fog computing. IEEE Int Things J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2017.2780236
Raju M R, Sai K M, Manoj K S (2023) MITS: Mobility-aware Intelligent Task Scheduling in Vehicular Fog Networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/tvt.2023.3321806
Xue J, Xiangrui G (2023) Collaborative computation offloading and resource allocation based on dynamic pricing in mobile edge computing. Comput Commun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2022.11.012
Tang M, Vincent WS W (2020) Deep reinforcement learning for task offloading in mobile edge computing systems. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2020.3036871
Zhou J, et al. (2021) Distributed task offloading optimization with queueing dynamics in multiagent mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Int Things J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3063509
Chen S, Chen B, Tao X, Xie X, Li K (2022) An online dynamic pricing framework for resource allocation in edge computing. J Syst Arch. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sysarc.2022.102759
Lyu F, Cai X, Wu F, Lu H, Duan S, Ren J (2022) Dynamic Pricing Scheme for Edge Computing Services: A Two-layer Reinforcement Learning Approach. 2022 IEEE/ACM 30th Int Symp Quality of Serv. https://doi.org/10.1109/IWQoS54832.2022.9812869
Wang X, Ye J, Lui J C (2022) Decentralized Scheduling and Dynamic Pricing for Edge Computing: A Mean Field Game Approach. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNET.2022.3204698
Baek B, et al (2020) Three dynamic pricing schemes for resource allocation of edge computing for IoT environment. IEEE Int Things J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.2966627
Tong Z, Deng X, Mei J, et al. (2023) Stackelberg game-based task offloading and pricing with computing capacity constraint in Journal of Systems Architecture. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sysarc.2023.102847
Ngo H Q, Larsson E G, Marzetta T L (2013) Energy and spectral efficiency of very large multiuser MIMO systems. IEEE Trans Commun. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCOMM.2013.020413.110848
Suraweera H A, Tsiftsis T A, Karagiannidis G K, Nallanathan A (2011) Effect of feedback delay on amplify-and-forward relay networks with beamforming. IEEE Trans Veh Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2011.2112786
Abramowitz M, Stegun I A, Romer R H (1988) Handbook of mathematical functions with formulas, graphs, and mathematical tables. https://doi.org/10.1119/1.15378
Burd TD, Brodersen RW (1996) Processor design for portable systems. J VLSI Sign Process Syst Sign Image Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01130406
Huang, L, et al. (2022) Distributed deep learning-based offloading for mobile edge computing networks. Mobile Netw Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-018-1177-x
Suzhi B, et al. (2021) Lyapunov-guided deep reinforcement learning for stable online computation offloading in mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun. arXiv:2010.01370
Chen Z, Zhang L, Pei Y, Jiang C, Yin L (2022) NOMA-Based Multi-User Mobile Edge Computation Offloading via Cooperative Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans Cogn Commun Netw. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCCN.2021.3093436
Jian S, Yong C, Minming L, Jiezhong Q, Buyya R. Energy-traffic tradeoff cooperative offloading for mobile cloud computing 2014 IEEE 22nd International Symposium of Quality of Service (IWQoS) https://doi.org/10.1109/IWQoS.2014.6914329
Sun W, Zhang H, Wang R, Zhang Y (2020) Reducing Offloading Latency for Digital Twin Edge. Netw 6G IEEE Trans Veh Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2020.3018817
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L., Tan, L. A decentralized scheme for multi-user edge computing task offloading based on dynamic pricing. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 18, 91 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-025-01904-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-025-01904-1