Abstract
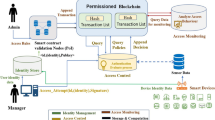
In the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), the data integrity in secure transmission improves the reliability of data analysis. To further reduce bandwidth consumption, the aggregate signature (AS) methodology is widely deployed in IIoT. Nevertheless, existing solutions are infeasible for digital twin empowered IIoT due to the following limitations: (i) the inconsistent time state of the data; and (ii) the ignored addition/removal issues of devices. Therefore, we propose a blockchain-based synchronized data transmission protocol (BT-SDT), which provides a synchronized clock for digital twin and implements dynamic device management. Specifically, we deploy the chaincode to maintain a clock synchronization service for AS between virtual space and physical space and re-design the chameleon hash modular on the redactable blockchain to update device information. We implement state-of-the-art solutions and BT-SDT to evaluate their computational and communication cost under a real IIoT dataset in Raspberry Pi and blockchain, which confirms the practical feasibility of BT-SDT.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Sisinni E, Saifullah A, Han S, Jennehag U, Gidlund M (2018) Industrial internet of things: challenges, opportunities, and directions. IEEE Trans Industr Inf 14(11):4724–4734
Tao F, Zhang H, Liu A, Nee AY (2018) Digital twin in industry: state-of-the-art. IEEE Trans Industr Inf 15(4):2405–2415
Digital Twins (2024) The key to smart product development. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/industrials-and-electronics/our-insights/digital-twins-the-key-to-smart-product-development
Alanezi K, Mishra S (2024) An iot architecture leveraging digital twins: Compromised node detection scenario. IEEE Syst J 18(2):1224–1235
Merkle RC (1987) A digital signature based on a conventional encryption function. In: Conference on the theory and application of cryptographic techniques. Springer, pp 369–378
Boneh D, Gentry C, Lynn B, Shacham H (2003) Aggregate and verifiably encrypted signatures from bilinear maps. In: Advances in cryptology—EUROCRYPT 2003: international conference on the theory and applications of cryptographic techniques, Warsaw, Poland, May 4–8, 2003 Proceedings 22. Springer, pp 416–432
Cheon JH, Kim Y, Yoon HJ (2004) A new id-based signature with batch verification. Cryptology EPrint Archive
Xu Y, Huang L, Tian M, Zhong H, Cui J (2016) A provably secure and compact certificateless aggregate signature scheme. Acta Electron Sin 44(8):1845–1850
Radhakrishnan P, Sugumar PK, Ponnan P, Varadharajan GP (2024) Certificate-less aggregate signature authentication scheme (clasas) for secure and efficient data transmission in wireless sensor networks (wsns). Peer-to-Peer Netw Appl 17(4):2572–2594
Yang X, Liu R, Wang M, Chen G (2019) Identity-based aggregate signature scheme in vehicle ad-hoc network. In: 2019 4th International Conference on Mechanical, Control and Computer Engineering (ICMCCE). IEEE, pp 1046–10463
Kumar P, Kumari S, Sharma V, Sangaiah AK, Wei J, Li X (2018) A certificateless aggregate signature scheme for healthcare wireless sensor network. Sustain Comput: Inform Syst 18:80–89
Cui J, Zhang J, Zhong H, Shi R, Xu Y (2018) An efficient certificateless aggregate signature without pairings for vehicular ad hoc networks. Inf Sci 451:1–15
Liu M, Wang L, Zhang K, Long Y, Qin B (2024) A pairing-free certificate-based key-insulated aggregate signature scheme for wireless medical sensor networks. Peer-to-Peer Netw Appl 17(2):685–700
Li T, Wang H, He D, Yu J (2022) Synchronized provable data possession based on blockchain for digital twin. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 17:472–485
Deng L, Yang Y, Gao R (2021) Certificateless designated verifier anonymous aggregate signature scheme for healthcare wireless sensor networks. IEEE Internet Things J 8(11):8897–8909
Deng L, Wang T, Feng S, Qu Y, Li S (2022) Secure identity-based designated verifier anonymous aggregate signature scheme suitable for smart grids. IEEE Internet Things J 10(1):57–65
Li T, Wang H, He D, Yu J (2020) Permissioned blockchain-based anonymous and traceable aggregate signature scheme for industrial internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J 8(10):8387–8398
Li T, Wang H, He D, Yu J (2023) Designated-verifier aggregate signature scheme with sensitive data privacy protection for permissioned blockchain-assisted iiot. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur
Signature-Based P-S (2023) Synchronized aggregate signature. In: Information security and cryptology–ICISC 2022: 25th International Conference, ICISC 2022, Seoul, South Korea, November 30–December 2, 2022, Revised Selected Papers, vol 13849. Springer, p 317
Ateniese G, Magri B, Venturi D, Andrade E (2017) Redactable blockchain–or–rewriting history in bitcoin and friends. In: 2017 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS &P). IEEE, pp 111–126
Kaggle Dataset (2024). https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/gmkeshav/tetuan-city-power-consumption
Krawczyk H, Rabin T (1998) Chameleon hashing and signatures. Cryptology ePrint Archive
Sun Y, Chen X, Du X (2013) An efficient elliptic curve discrete logarithm based trapdoor hash scheme without key exposure. J Comput 8(11):2851–2856
Nakamoto S et al (2008) Bitcoin. A peer-to-peer electronic cash system 21260
Li Z, Kang J, Yu R, Ye D, Deng Q, Zhang Y (2017) Consortium blockchain for secure energy trading in industrial internet of things. IEEE Trans Industr Inf 14(8):3690–3700
Pointcheval D, Stern J (2000) Security arguments for digital signatures and blind signatures. J Cryptol 13:361–396
Akinyele JA, Garman C, Miers I, Pagano MW, Rushanan M, Green M, Rubin AD (2013) Charm: a framework for rapidly prototyping cryptosystems. J Cryptogr Eng 3:111–128
Nik-U/pbc (2024). https://github.com/Nik-U/pbc
Xu J, Zhang Z, Feng D (2005) Id-based aggregate signatures from bilinear pairings. In: Cryptology and network security: 4th international conference, CANS 2005, Xiamen, China, December 14-16, 2005. Proceedings 4. Springer, pp 110–119
Gentry C, Ramzan Z (2006) Identity-based aggregate signatures. In: Public Key Cryptography-PKC 2006: 9th International Conference on Theory and Practice in Public-Key Cryptography, New York, NY, USA, April 24-26, 2006. Proceedings 9. Springer, pp 257–273
Selvi SSD, Vivek SS, Shriram J, Rangan CP (2012) Identity based partial aggregate signature scheme without pairing. In: 2012 35th IEEE sarnoff symposium. IEEE, pp 1–6
Kar J (2012) Provably secure identity-based aggregate signature scheme. In: 2012 International conference on cyber-enabled distributed computing and knowledge discovery. IEEE, pp 137–142
Ahn JH, Green M, Hohenberger S (2010) Synchronized aggregate signatures: new definitions, constructions and applications. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM conference on computer and communications security, pp 473–484
Hohenberger S, Waters B (2018) Synchronized aggregate signatures from the rsa assumption. In: Annual international conference on the theory and applications of cryptographic techniques. Springer, pp 197–229
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62372285), Shanghai Rising-Star Program (22QA1403800), Open Fund of Advanced Cryptography and System Security Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (No. SKLACSS-202310).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Le Chang, Kai Zhang and Jian Zhao researched the methodology. Le Chang, Xinyan Yang and Kai Zhang wrote the main manuscript text. Le chang, Xinyan Yang and Zhimei Sui conducted experiment and result analysis. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics statement.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection: Special Issue on 2 - Track on Security and Privacy
Guest Editor: Rongxing Lu
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, L., Yang, X., Zhang, K. et al. Blockchain-based synchronized data transmission with dynamic device management for digital twin in IIoT. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 18, 85 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-025-01910-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-025-01910-3