Abstract
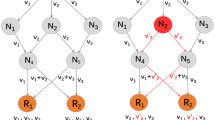
A linearly homomorphic signature (LHS) enables linear computation on signed data and has been investigated in many contexts, such as network coding to resist pollution attacks and computation on outsourced data. Traditional LHS security relies entirely on the secrecy of the signing keys. The exposure of signing keys necessitates updating all generated signatures. However, with the increasing use of relatively insecure mobile devices in network coding and data outsourcing systems, key exposure has become more prevalent. To mitigate the hazard of key exposure in the LHS setting, we integrate key update mechanisms into the LHS by presenting a forward-secure linearly homomorphic signature (FSLHS). Specifically, we formalize the definition and security notions for the FSLHS scheme and present a concrete implementation. We prove our scheme to be forward secure against adaptively chosen message attacks, assuming the hardness of the CDH problem. Compared to previous works, our performance analysis shows that all parameters of our scheme exhibit logarithmic complexity with respect to the total number of time periods.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this article.
References
Jin JQ, Ho T, Viswanathan H (2006) Comparison of network coding and nonnetwork coding schemes for multi-hop wireless networks. In: Proc. IEEE international symposium on information theory, pp 197-201
Wu Y, Chou P, Kung SY (2005) Minimum-energy multicast in mobile ad hoc networks using network coding. IEEE Trans Commun 53(11):1906–1918
Chen WB, Lei H, Qi K (2016) Lattice-based linearly homomorphic signatures in the standard model. Theor Comput Sci 634(27):47–54
Li SYR, Yeung R, Cai N (2003) Linear network coding. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 49(2):371–381
Liu X, Huang J, Wu Y, Zong G (2019) A privacy-preserving signature scheme for network coding. IEEE Access 7:109739–109750
Hu X, Zheng S, Gong J, et al (9) Enabling Linearly Homomorphic Signatures in Network Coding-based Named Data Networking. In: Proc. CFI 2019, pp 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1145/3341188.3341191
Charles D, Jain K, Lauter K (2006) Signatures for network coding. In: Proc. 40th Annu Conf Inf Sci Syst Mar, IEEE, Princeton, NJ, pp 857–863
Yu Z, Wei Y, Ramkumar B, Guan Y (2008) An efficient signature-based scheme for securing network coding against pollution attacks. In: Proc. INFOCOM, IEEE, Phoenix, AZ, pp 1409–1417
Zhang P, Jiang Y, Lin C, Yao H, Wasef A et al (2011) Padding for orthogonality: efficient subspace authentication for network coding. in Proc. IEEE INFOCOM, Shanghai, pp 1026–1034
Boneh D, Freeman D, Katz J, Waters J (2009) Signing a Linear Subspace: Signature Schemes for Network Coding. In: Proc. PKC 2009, LNCS, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, vol 5443 pp 68–87
Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Li B, Zhang M (2017) An efficient identity-based homomorphic signature scheme for network coding. In: Proc. EIDWT 2017, LNCS, Springer, Cham, vol 6 pp 524–531
Sadrhaghighi S, Khorsandi S (2016) An identity-based digital signature scheme to detect pollution attacks in intra-session network coding. In: Proc. ISCISC 2016, Tehran, Iran, pp 7–12
Lin Q, Yan H, Huang Z, Chen W, Shen J, Tang Y (2018) An ID-based linearly homomorphic signature scheme and its application in blockchain. IEEE Access 6:20632–20640
Chang J, Ma H, Zhang A, Xu M, Xue R (2019) RKA security of identity-based homomorphic signature scheme. IEEE Access 6:50858–50868
Li Y, Zhang F, Liu X (2020) Secure data delivery with identity-based linearly homomorphic network coding signature scheme in IoT. IEEE Trans Serv Comput 15(4):2202–2212
Yu H, Shi J (2022) Certificateless homomorphism network coding signature scheme. IEEE Sens J 22(13):13707–13715
Li Y, Zhang F, Sun Y (2021) Lightweight certificateless linearly homomorphic network coding signature scheme for electronic health system. IET Inf Secur 15(1):131–146
Wu B, Wang C, Yao H (2021) A certificateless linearly homomorphic signature scheme for network coding and its application in the IoT. Peer-to-Peer Netw Appl 14:852–872
Schabhüser L, Butin D, Buchmann J (2019) Context hiding multi-key linearly homomorphic authenticators. In: Proc. CT-RSA 2019, LNCS, Springer, Cham, vol 11405 pp 493–513
Schabhuser L, Buchmann J, Struck P (2017) A linearly homomorphic signature scheme from weaker assumption. In: Proc. IMACC2017, LNCS, Springer, Cham, vol 10655 pp 261–279
Li T, Chen W, Tang T, Yan H (2018) A homomorphic network coding signature scheme for multiple sources and its application in IoT. Secur Commun Netwo 2018:1–6
Lai RW, Tai RK, Wong HW, Chow SS (2018) Multi-key homomorphic signatures unforgeable under insider corruption. In: Proc. ASIACRYPT 2018, LNCS, Springer, Cham, vol 11273 pp 465–492
Cai J, Jiang H, Wang H et al (2020) Lattice-based linearly homomorphic signature scheme over \( F_2 \). Secur Commun Netw 2020:1–7
Gu Y, Shen L, Zhang F et al (2022) Provably secure linearly homomorphic aggregate signature scheme for electronic healthcare system. Mathematics 10(15):2588
Wang C, Wu B (2023) A linear homomorphic proxy signature scheme based on blockchain for internet of things. Comput Model Eng Sci. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2023.026153.
Li Y, Yao H, Chen M, Jaggi S et al (2010) RIPPLE authentication for network coding. In: Proc. IEEE INFOCOM, San Diego, CA, USA, pp 1–9
Esfahani A, Mantas G, Rodriguez J (2016) An efficient null space-based homomorphic MAC scheme against tag pollution attacks in RLNC. IEEE Commun Lett 20(5):918–921
Esfahani A, Yang D, Mantas G et al (2015) Dual homomorphic message authentication code scheme for network coding enable wireless sensor networks. Int J Distrib Sens Netw 11(7):510251
Wu X, Xu Y, Yuen C, Xiang L (2014) A tag encoding scheme against pollution attack to linear network coding. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 25(1):33–42
Kehdi K, Li B (2009) Null Keys: limiting malicious attacks via null space properties of network coding. In: Proc. IEEE INFOCOM 2009, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, pp 1224–1232
Cheng C, Lee J, Jiang T, Takagi T (2016) Security analysis and improvements on two homomorphic authentication schemes for network coding. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 11(5):993–1002
Boneh D, Freema D (2011) Homomorphic signatures for polynomial functions. In: Proc. AEUROCRYPT 2011, LNCS, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, vol 6632 pp 149–168
Catalano D, Fiore D, Warinschi B (2014) Homomorphic signatures with efficient verification for polynomial functions. In: Proc. CRYPTO 2014, LNCS, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, vol 8616 pp 371–389
Gorbunov S, Vaikuntanathan V, Wichs D (2015) Leveled fully homomorphic signatures from standard lattices. In: Proc. STOC 2015, LNCS, Springer, Cham vol 9290 pp 469–477
Wang C, Wu B, Yao H (2020) Leveled adaptively strong-unforgeable identity-based fully homomorphic signatures. IEEE Access 8:119431–119447
Fiore D, Pagnin E (2018) Matrioska: A Compiler for Multi-Key Homomorphic Signatures. In: Proc. SCN 2018, LNCS, Springer, Cham, vol 11035 pp.43–62
Fiore D, Mitrokotsa A, Nizzardo L, et al (2016) Multi-key homomorphic authenticators. In Proc. ASIACRYPT 2016, LNCS, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, vol 10032 pp 1–41
Samarin SD, Fiore D, Venturi D et al (2021) A compiler for multi-key homomorphic signatures for Turing machines. Theor Comput Sci 889:145–170
Li S, Liang B, Mitrokotsa A et al (2021) Homomorphic signcryption with public plaintext-result checkability. IET Inf Secur 15(5):333–350
Wang Y, Wang M (2020) A new fully homomorphic signatures from standard lattices. In: Proc. WASA 2020, Qingdao, China, Springer, pp 494–506
Li R, Wang F, Zhang R, et al (2022) NTRU-Based Fully Homomorphic Signature. Secur Commun Netw 2022
Li S, Wang X, Xue R (2022) Toward both privacy and efficiency of homomorphic MACs for polynomial functions and its applications. Comput J 65(4):1020–1028
Anderson R (1997) Two remarks on public-key cryptology. In: Proc. ACM-CCS 1997. http://wwwcl.cam.ac.uk/users/rja14
Bellare M, Miner SK (1999) A forward-secure digital signature scheme. In: Proc. CRYPTO 1999, Santa Barbara, California, USA, pp 431–448
Fiat A, Shamir A (1986) How to prove yourself: practical solutions to identification and signature problems. In: Proc. CRYPTO 1986, LNCS vol. 263, Santa Barbara, California, USA, pp 186–194
Abdalla M, Reyzin L (2000) A new forward-secure digital signature scheme. In: Proc. ASIACRYPT 2000, Springer, Kyoto, pp 116–129
Itkis G, Reyzin L (2001) Forward-secure signatures with optimal signing and verifying. In: Proc. CRYPTO 2001, Springer, Santa Barbara, CA, pp 332–354
Kozlov A, Reyzin L (2003) Forward-secure signatures with fast key update. In: Proc. SCN 2003, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 241–256
Malkin T, Micciancio D, Miner S (2002) Efficient generic forward-secure signatures with an unbounded number of time periods. In: Proc. EUROCRYPT 2002, Springer, Amsterdam, pp 400–417
Yu J, Kong F, Cheng X, Hao R, Li G (2008) Construction of yet another forward secure signature scheme using bilinear maps. In: Proc. ProvSec 2008, LNCS, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, vol 5324 pp 83-97
Canetti R, Halevi S, Katz J (2003) A forward-secure public-key encryption scheme. In: Proc. EUROCRYPT 2003, LNCS, Warsaw, Poland, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, vol 2656 pp 255-271
Hu F, Wu CH, Irwin JD (2003) A new forward secure signature scheme using bilinear maps. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Report 2003/188. http://eprint.iacr.org/2003/188
Kang BG, Park JH, Hahn SG (2004) A new forward secure signature scheme. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Report 2004/183. http://eprint.iacr.org/2004/183
Liu Y, Yin X, Qiu L (2008) ID-based forward-secure signature scheme from the bilinear pairings. In: Proc. ISECS 2008, Guangzhou, China, pp 179–183
Yu J, Hao R, Kong F et al (2011) Forward-secure identity-based signature: security notions and construction. Inf Sci 181(3):648–660
Yu J, Xia H, Zhao H, Hao R et al (2016) Forward secure identity-based signature scheme in untrusted update environments. Wirel Person Commun 86(3):1467–1491
Wei J, Liu W, Hu X (2017) Forward-secure identity-based signature with efficient revocation. Int J Comput Math 94(7):1390–1411
Oh H, Kim J, Shin JS (2018) Forward-Secure ID based Digital Signature Scheme with Forward-Secure Private Key Generator. Inf Sci 454-455
Li J, Teng H, Huang X et al (2015) A forward-secure certificate-based signature scheme. Comput J 58(4):853–866
Lu Y, Li J (2019) A forward-secure certificate-based signature scheme with enhanced security in the standard model. KSII Trans Int Inf Syst 13(3):1502–1522
Li Z, Wang D (2019) Achieving one-round password-based authenticated key exchange over lattices. IEEE Trans Serv Comput 15(1):308–321
Li Z, Wang D, Morais E (2020) Quantum-safe round-optimal password authentication for mobile devices. IEEE Trans Dependable Secure Comput 19(3):1885–1899
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to the reviewers and editors for their invaluable assistance. This preprint has been submitted and is currently undergoing the prescreening process.
Funding
This research was supported by the Gansu Provincial Department of Education through the Innovation Fund Project for University Teachers (2023A-041) and by the Young Scholars Science Foundation of Lanzhou Jiaotong University (2022011), and by the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province(25JRRA156).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Bin Wu, Ning Shi. Formal analysis: Bin Wu, Yahong Li. Methodology: Bin Wu, Yahong Li. Resources: Bin Wu, Caifen Wang, Kaijun Wu. Software: Bin Wu, Kaijun Wu. Writing-original draft: Bin Wu, Caifen Wang. Writing-review & editing: Bin Wu, Ning Shi, Yahong Li.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of Topical Collection: 1- Track on Networking and Applications
Guest Editor: Vojislav B. Misic
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, B., Shi, N., Li, Y. et al. A key leakage resistant linearly homomorphic signature scheme and its application. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 18, 101 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-025-01917-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-025-01917-w