Abstract
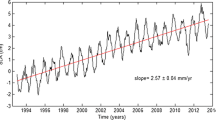
The sea level change is a crucial indicator of our climate. The spatial sampling offered by satellite altimetry and its continuity during the past years are the major assets to provide an improved vision of the Mediterranean sea level changes. In this paper, an automatic signal extraction approach, based on Singular Spectrum Analysis (SSA), is utilized for analysis and seasonal adjustment of the Mediterranean Sea level series. This automatic approach enables us to overcome the difficulties of visual identification of trend constituents that sometimes we encounter when using the conventional SSA method. The results indicate that the Mediterranean mean sea level is dominated by several harmonic components. The annual signal is particularly strong and almost covers 73.62 % of the original sea level series variation whiles its amplitude is about 15 cm. The extracted trend also indicates that the Mediterranean main sea level has significantly been raised during the period 1993–2012 by 2.44 ± 0.4 mm yr−1. As an important consequence, considering the current situation, if this trend continues, the Mediterranean Sea level will be raised about 22 cm by the end of this century, which makes a dramatic effect on several issues such as land, flora, fauna, and people activities established along the Mediterranean coastlines.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
TOPEX. Ocean TOPography Experiment
NASA. National Aeronautics and Space Administration - USA
Available at http://www.pdmi.ras.ru/~theo/autossa
References
Ablain M, Cazenave A, Guinehut S, Valladeau G (2009) A new assessment of global mean sea level from altimeters highlights a reduction of global slope from 2005 to 2008 in agreement with in situ measurements. Ocean Sci 5:193–201
Alexandrov T (2006) Software package for automatic extraction and forecast of additive components of time series in the framework of the Caterpillar-SSA approach, PhD thesis, St. Petersburg State University. [In Russian]. http://www.pdmi.ras.ru/_theo/autossa
Alexandrov T (2009) A method of trend extraction using singular spectrum analysis. RevStat-Stat J 7(1):1–22
Alexandrov T, Golyandina N (2005) Automatic extraction and forecast of time series cyclic components within the framework of SSA. In Proc. of the 5th St.Petersburg Workshop on Simulation, 45–50
Alexandrov T, Bianconcini S, Dagum EB, Maass P, McElroy T (2008) A review of some modern approaches to the problem of trend extraction. U.S. Census Bureau, Statistical Research Division, Research Report Series, Statistics #2008-3. http://www.census.gov/srd/papers/pdf/rrs2008-03.pdf
Allen MR, Smith LA (1996) Monte Carlo SSA: detecting irregular oscillations in the presence of colored noise. J Clim 9:3373–404
Béthoux JP, Gentili B (1999) Functioning of the Mediterranean Sea: past and present changes related to freshwater input and climate changes. J Mar Syst 20:33–47
Béthoux JP, Gentili B, Raunet J, Tailliez D (1990) Warming trend in the western Mediterranean deep water. Nature 347:660–662
Cartwright DE, Edden AC (1973) Corrected tables of tidal harmonics. Geophys J Int 33(3):253–264
Cartwright DE, Tayler RJ (1971) New computations of the tide-generating potential. Geophys J R Astron Soc 23(1):45–73
Caseiro P, Fonseca-Pinto R, Andrade A (2010) Screening of obstructive sleep apnea using Hilbert-Huang decomposition of oronasal airway pressure recordings. Med Eng Phys 32(6):561–568
Chau K-W, Wu CL, Li YS (2005) Comparison of several flood forecasting models in Yangtze river. J Hydrol Eng ASCE 10(6):485–491. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2005)10:6(485)
Chen W, Chau K-W (2006) Intelligent manipulation and calibration of parameters for hydrological models. Int J Environ Pollut 28(3–4):432–447
Cheng CT, Chau K-W (2001) Fuzzy iteration methodology for reservoir flood control operation. J Am Water Resour Assoc 37(5):1381–1388
Coughlin KT, Tung KK (2004) 11-Year solar cycle in the stratosphere extracted by the empirical mode decomposition method. Adv Space Res 34:323–329
Danilov D, Zhigljavsky A (eds) (1997) Principal components of time series: The ‘Caterpillar’ method. University of St. Petersburg, St. Petersburg [in Russian]
Ding H, Huang Z, Song Z, Yan Y (2007) Hilbert–Huang transform based signal analysis for the characterization of gas–liquid two phase flow. Flow Meas Instrum 18:37–46
Fereydooni M, Rahnemaei M, Babazadeh H, Sedghi H, Elhami MR (2012) Comparison of artificial neural networks and stochastic models in river discharge forecasting, (Case study: Ghara- Aghaj River, Fars Province, Iran). Afr J Agric Res 7(40):5446–5458. doi:10.5897/AJAR11.1091
Flandrin P, Goncalves P, Rilling G (2004) Detrending and denoising with empirical mode decomposition. in EUSIPCO 2004, September 6–10, Vienna, Austria. http://perso.ens-lyon.fr/patrick.flandrin/EUSIPCO04_PFPGGR.pdf
Ghodsi M, Hassani H, Sanei S, Hicks Y (2009) The use of noise information for detection of temporomandibular disorder. J Biomed Signal Process Control 4(2):79–85
Ghodsi M, Hassani H, Sanei S (2010) Extracting fetal heart signal from noisy maternal ECG by singular spectrum analysis. Stat Interface 3(3):399–411
Golyandina N, Nekrutkin V, Zhigljavsky A (2001) Analysis of time series structure: SSA and related techniques. Chapman & Hall/CRC, New York
Haddad M, Taibi H, Mohammed Arezki SM (2013) On the recent global mean sea level changes: Trend extraction and El Nino’s impact. Comptes rendus geoscience. In press. doi :10.1016/j.crte.2013.03.002
Hassani H (2007) Singular spectrum analysis: methodology and comparison. J Data Sci 5(2):239–257
Hassani H (2009) Singular spectrum analysis based on the minimum variance estimator. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 11(3):2065–2077
Hassani H, Thomakos D (2010) A review on singular spectrum analysis for economic and financial time series. Stat Interface 3(3):377–397
Hassani H, Zhigljavsky A (2009) Singular spectrum analysis: methodology and application to economics data. J Syst Sci Complex 22(3):372–394
Hassani H, Dionisio A, Ghodsi M (2009a) The effect of noise reduction in measuring the linear and nonlinear dependency of financial markets. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 11(1):492–502
Hassani H, Heravi S, Zhigljavsky A (2009b) Forecasting European industrial production with singular spectrum analysis. Int J Forecast 25(1):103–118
Hassani H, Soofi A, Zhigljavsky A (2009c) Predicting daily exchange rate with singular spectrum analysis. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 11(3):2023–2034
Hassani H, Mahmoudvand R, Yarmohammadi M (2010) Filtering and denoising in the linear regression model. Fluctuation Noise Lett 9(4):343–358
Hassani H, Zhigljavsky A, Zhengyuan X (2011) Singular spectrum analysis based on the perturbation theory. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 12(5):2752–2766
Huang NE, Shen Z, Long SR, Wu MC, Shih HH, Zheng Q, Yen N-C, Tung CC, Liu HH (1998) The Empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and nonstationary time-series analysis. Proc R Soc Lond A 454(1971):903–995. doi:10.1098/rspa.1998.0193
Huang W, Shen Z, Huang NE, Fung YC (1998) Use of intrinsic modes in biology: examples of indicial response of pulmonary blood pressure to ± step hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(22):12766–12771
Huang W, Sher YP, Peck K, Fung CB (2002) Matching gene activity with physiological functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(5):2603–2608
Huang NE, Wu M-L, Qu W, Long SR, Shen SSP (2003) Applications of Hilbert-Huang transform to non-stationary financial time series analysis. Appl Stoch Model Bus Ind 19(3):245–268. doi:10.1002/asmb.501
Hubick KT (1992) Artificial neural networks in Australia. Department of industry, Technology & Commerce, Canberra, p 132
Landerer FW, Volkov DL (2013) The anatomy of recent large sea level fluctuations in the Mediterranean Sea. Geophysical Research Letters 40:553–557. doi:10.1002/grl.50140
Lemoine FG, Zelensky NP, Chinn DS, Pavlis DE, Rowlands DD, Beckley BD, Luthcke SB, Willis P, Ziebart M, Sibthorpe A, Boy JP, Luceri V (2010) Towards development of a consistent orbit series for TOPEX, Jason-1, and Jason-2. Adv Space Res 46:1513–1540. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2010.05.007
Maier HR, Dandy GC (2000) Neural networks for the prediction and forecasting of water resources variable: a review of modeling issues and application. Environ Model Softw 15(1):101–124
Maier HR, Morgan N, Chow CWK (2004) Use of artificial neural networks for predicting optimal alum doses and treated water quality parameters. Environ Model Softw 19(5):485–494
Mhamdi F, Poggi J-M, Jaidane M (2010) Empirical mode decomposition for trend extraction: application to electrical data. Proc COMPSTAT 454:1391–1398, Paris
Mhamdi F, Poggi J-M, Jaїdane M (2011) Trend extraction for seasonal time series using ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Adv Adapt Data Anal 3(3):363–383. doi:10.1142/S1793536911000696
Moghtaderi A, Borgnat P, Flandrin P (2011) Trend filtering: Empirical mode decompositions versus ℓ1 and Hodrick-Prescott. Adv Adapt Data Anal 3(1&2):41–61. doi:10.1142/S1793536911000751
Moghtaderi A, Flandrin P, Borgnat P (2013) Trend filtering via empirical mode decompositions. Comput Stat Data Anal 58:114–126
Mudelsee M (2010) Climate time series analysis: Classical statistical and bootstrap methods. Springer, Dordrecht
Muttil N, Chau KW (2006) Neural network and genetic programming for modelling coastal algal blooms. Int J Environ Pollut 28(3–4):223–238
Nerem RS, Chambers D, Choe C, Mitchum GT (2010) Estimating mean Sea level change from the TOPEX and Jason altimeter missions. Mar Geod 33(sup1):435–446. doi:10.1080/01490419.2010.491031
Pascual A, Marcos M, Gomis D (2008) Comparing the sea level response to pressure and wind forcing of two barotropic models: Validation with tide gauge and altimetry data. J Geophys Res 113(C7):11–16. doi:10.1029/2007JC004459
Peltier WR (2001) Global glacial isostatic adjustment and modern instrumental records of relative sea level history. International Geophysics. Sea Level Rise—History and Consequences ed. 75:65–95. doi:10.1016/S0074-6142(01)80007-3
Peltier WR (2002) Global glacial isostatic adjustment: palaeogeodetic and space-geodetic tests of the ICE-4G (VM2) model. J Quat Sci 17(5–6):491–510
Peltier WR (2009) Closure of the budget of global sea level rise over the GRACE era: the importance and magnitudes of the required corrections for global glacial isostatic adjustment. Quat Sci Rev 28:1658–1674
Peltier WR, Luthcke SB (2009) On the origins of Earth rotation anomalies: New insights on the basis of both “paleogeodetic” data and Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data. J Geophys Res 114(B11)
Quek T, Tua S, Wang Q (2003) Detecting anomalies in beams and plate based on the Hilbert-Huang transform of real signals. Smart Mater Struct 12:447–460
Rao R, Hsu E-C (2008) Hilbert-Huang transform analysis of hydrological and environmental time series. Water Sci Technol Libr 60
Ray RD (1999) A Global Ocean Tide Model From TOPEX/Poseidon Altimetry: GOT99.2. NASA Techincal Memo 1999–209478, 58 pp. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
Roether W, Manca BB, Klein B, Bregant D, Georgopoulos D, Beitzel V, Kovacevic V, Luchetta A (1996) Recent changes in Eastern Mediterranean deep waters. Science 271:333–335
Rohling E, Bryden H (1992) Man-induced salinity and temperature increases in the Western Mediterranean Deep Water. J Geophys Res 97:11191–11198
Ross T, Garrett C, Le Traon PY (2000) Western Mediterranean sea-level rise: changing exchange flow through the Strait of Gibraltar. Geophys Res Lett 27:2949–2952
Salisbury J, Sun Y (2007) Rapid screening test for sleep apnea using a nonlinear and nonstationary signal processing technique. Med Eng Phys 29(3):336–43
Suling J, Yanqin G, Qiang W, Jian Z (2009) Trend extraction and similarity matching of financial time series based on EMD method. CSIE ’09 Proceedings of the 2009 WRI World Congress on Computer Science and Information Engineering 4:526–530. doi:10.1109/CSIE.2009.654
Tang J, Zou Q, Tang Y, Liu B, Zhang XK (2007) Hilbert-Huang Transform for ECG De-Noising. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering (ICBBE) 8:664–667. doi:10.1109/ICBBE.2007.173
Taormina R, Chau K-W, Sethi R (2012) Artificial Neural Network simulation of hourly groundwater levels in a coastal aquifer system of the Venice lagoon. Eng Appl Artif Intell 25(8):1670–1676
Task Committee ASCE (2000) Artificial neural networks in hydrology. Preliminary concepts. J Hydrol Eng ASCE 5(2):115–123
Tran N, Labroue S, Philipps S, Bronner E, Picot N (2010) Overview and update of the Sea state bias corrections for the Jason-2, Jason-1 and TOPEX missions. Mar Geod 33(1,1):348
Tsimplis MN, Baker TF (2000) Sea level drop in the Mediterranean Sea: an indicator of deep water salinity and temperature changes? Geophys Res Lett 27(12):1731–1734
Tsimplis M, Marcos M, Somot S (2008) 21st Century Mediterranean Sea level rise: steric and atmosphere pressure contributions from a regional model. Glob Planet Chang 63(2–3):105–111
Wahr JM (1985) Deformation induced by polar motion. J Geophys Res 90(B11):9363
Wu Z, Huang NE, Long SR, Peng C-K (2007) On the trend, detrending, and variability of nonlinear and nonstationary time series. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(38):14889–14894. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701020104
Wu CL, Chau K-W, Li YS (2009) Predicting monthly streamflow using data-driven models coupled with data-preprocessing techniques. Water Resour Res 45:W08432. doi:10.1029/2007WR006737
Xun J, Yan S (2008) A revised Hilbert–Huang transformation based on the neural networks and its application in vibration signal analysis of a deployable structure. Mech Syst Signal Process 22:1705–1723
Zhang RR, Ma S, Safak E, Hartzell S (2003) Hilbert-Huang transform analysis of dynamic and earthquake motion recordings. J Eng Mech 129:861–875
Internet/Web sites
AutoSSA software (2007) http://www.pdmi.ras.ru/~theo/autossa, [accessed 15 December, 2010]
Sea level time series, KNMI Climate Exoplorer http://climexp.knmi.nl/start.cgi?someone@somewhere, [accessed 27 February, 2013].
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Dr. Theodore Alexandrov for providing the AutoSSA computer program. We also thank the Colorado Center for Astrodynamics Research of the University of Colorado—Boulder for providing the Mediterranean Sea level time series. We are enormously grateful to the reviewers for helpful comments and suggestions that led us to improve our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Hassan Babaie
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haddad, M., Hassani, H. & Taibi, H. Sea level in the Mediterranean Sea: seasonal adjustment and trend extraction within the framework of SSA. Earth Sci Inform 6, 99–111 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-013-0114-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-013-0114-6