Abstract
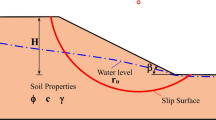
The stability of rock slopes is a difficult problem in the field of geotechnical and geological engineering. Less than 20% of all landslides are predictable each year, so a simple, fast, reliable and low-cost method to predict the stability of slopes is urgently needed. This study investigates a new regularized online sequential extreme learning machine, incorporated with the variable forgetting factor (FOS-ELM), based on intelligence computation to predict the factor of safety of a rock slope (F). The Bayesian information criterion (BIC) is applied to establish seven input combinations based on the parameters of the Hoek-Brown criterion and geometrical and mechanical parameters of the slope, such as the geological strength index (GSI), disturbance factor (D), rock material constant (mi), uniaxial compressive strength (σci), unit weight of the rock mass (γ), slope height (H) and slope angle (β). Seven models are established and evaluated to determine the optimal input combination. Various statistical indicators are calculated for the prediction accuracy examination. Compared to the classical extreme learning machine (ELM) model predictions of F, the results of the applied FOS-ELM model demonstrate a better prediction accuracy and are more effective when accounting for an increase in data. The FOS-ELM model with all seven input parameters is used to establish stability charts with the influence coefficient of slope angle change (ηβ), disturbance change (ηD) and slope height change (ηH). Using stability charts with a combination of ηβ, ηD and ηH can be used to quickly and preliminarily analyze rock stability as a guide for engineering practitioners in rock slope design.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bou-Rabee M, Sulaiman SA, Saleh MS, Marafi S (2017) Using artificial neural networks to estimate solar radiation in Kuwait. Renew Sust Energ Rev 72:434–438
Chen M, Lu W, Xin X, Zhao H, Bao X, Jiang X (2016) Critical geometric parameters of slope and their sensitivity analysis: a case study in jilin, northeast china. Environmental Earth Sciences 75(9):832
Cho SE (2009) Probabilistic stability analyses of slopes using the ANN-based response surface. Comput Geotech 36(5):787–797
Chung CJF, Fabbri AG (2003) Validation of spatial prediction models for landslide hazard mapping. Nat Hazards 30(3):451–472
Clausen J, Damkilde L (2008) An exact implementation of the Hoek-Brown criterion for elasto-plastic finite element calculations. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 45(6):831–847
Crisosto C, Hofmann M, Mubarak R, Seckmeyer G (2018) One-hour prediction of the global solar irradiance from all-sky images using artificial neural networks. Energies 11:2906
Deng J, Lee C (2001) Displacement back analysis for a steep slope at the three gorges project site. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences 38(2):259–268
Deng DP, Liang L, Wang JF, Zhao LH (2016) Limit equilibrium method for rock slope stability analysis by using the generalized Hoek-Brown criterion. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 89:176–184
Eberhardt E (2012) The Hoek-Brown failure criterion. Rock mechanics and rock Engineering 45(6):981–988
Erzin Y, Cetin T (2013) The prediction of the critical factor of safety of homogeneous finite slopes using neural networks and multiple regressions. Comput Geosci 51(51):305–313
Fallah-Zazuli, M., Vafaeinejad, A., Alesheykh, A.A., Modiri M., Aghamohammadi H (2019) Mapping landslide susceptibility in the Zagros Mountains, Iran: a comparative study of different data mining models Earth Science Informatics,https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-019-00389-w, 12, 615, 628
Gao Y, Zhang F, Lei GH, Li D, Wu Y, Zhang N (2013) Stability charts for 3d failures of homogeneous slopes. J Geotech Geoenviron 139(9):1528–1538
Gao Y, Wu D, Zhang F (2015) Effects of nonlinear failure criterion on the three-dimensional stability analysis of uniform slopes. Eng Geol 198:87–93
Guzzetti F, Carrara A, Cardinali M, Reichenbach P, Giardino JR, Marston D et al (1999) Landslide hazard evaluation:a review of current techniques and their application in a multi-scale study, Central Italy. Geomor-phology 31(1–4):181–216
Hoek E (1994) Strength of rock and rock masses. International Society for Rock Mechanics News Journal 2(2):4–16
Hoek E, Brown T, (1980) Underground excavations in rocks.London: institution of mining and metallurgy, 527
Hoek E, Brown T, (1988) The Hoek-Brown criterion-a 1988 update[C]// CURRAN J C ed. proceedings of the 15th Canada rock mechanics symposium. Toronto: University of Toronto, 31-38
Hoek E., Brown T. (2018) The Hoek-Brown failure criterion and GSI-2018 edition. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering
Hoek E., Wood D., Shah S., (1992) A modified Hoek-Brown criterion for jointed rock masses[C]// HUDSON J A ed. Proceedings of the Rock Characterization, Symposium of ISRM. London: British Geotechnical Society, 209–214
Hoek E, Carranza-Tomes C, Corkum B. (2002) Hoek-Brown failure criterion-2002 edition.In: proceedings of the north American rock mechanics symposium Toronto
Hou M, Zhang TL, Weng F, Ali M, Al-Ansari N, Yaseen ZM (2018) Global solar radiation prediction using hybrid online sequential extreme learning machine model. Energies 11
Huang F, Huang J, Jiang S, Zhou C (2017) Landslide displacement prediction based on multivariate chaotic model and extreme learning machine. Engineering Geology 218(Complete):173–186
Johari A, Mehrabani Lari A (2017) System probabilistic model of rock slope stability considering correlated failure modes. Comput Geotech 81:26–38
Kumar M, Raghuwanshi N, Singh R, Wallender W, Pruitt W (2002) Estimating evapotranspiration using artificial neural network. J Irrig Drain Eng 128:224–233
Li AJ, Merifield RS, Lyamin AV (2008) Stability charts for rock slopes based on the Hoek-Brown failure criterion. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences 45(5):689–700
Li AJ, Merifield RS, Lyamin AV (2011) Effect of rock mass disturbance on the stability of rock slopes using the Hoek-Brown failure criterion. Comput Geotech 38(4):546–558
Li AJ, Khoo S, Lyamin AV, Wang Y (2016) Rock slope stability analyses using extreme learning neural network and terminal steepest descent algorithm. Autom Constr 65:42–50
Li X, Zhang L, Zhang S (2018) Efficient Bayesian networks for slope safety evaluation with large quantity monitoring information. Geosci Front 9(6):1679–1687
Liu Z, Shao J, Xu W, Chen H, Zhang Y (2014) An extreme learning machine approach for slope stability evaluation and prediction. Nat Hazards 73(2):787–804
Liu SY, Shao LT, Li HJ (2015) Slope stability analysis using the limit equilibrium method and two finite element methods. Comput Geotech 63(63):291–298
Marinos V, Marinos P, Hoek E (2005) The geological strength index: applications and limitations. Bull Eng Geol Environ 64(1):55–65
Paleologu C, Benesty J, Ciochina S (2008) A robust variable forgetting factor recursive least-squares algorithm for system identification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 15:597–600
Priest SD (2005) Determination of shear strength and three-dimensional yield strength for the Hoek-Brown criterion. Rock Mech Rock Eng 38(4):299–327
Qian ZG, Li AJ, Lyamin AV, Wang CC (2017) Parametric studies of disturbed rock slope stability based on finite element limit analysis methods. Comput Geotech 81:155–166
Saade A, Aboujaoude G, Wartman J (2016) Regional-scale co-seismic landslide assessment using limit equilibrium analysis. Eng Geol 204:53–64
Schwarz G (1978) Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Stat 6:461–464
Shafizadeh-Moghadam H, Minaei M, Shahabi H, Hagenauer J (2019) Big data in Geohazard; pattern mining and large scale analysis of landslides in Iran. Earth Sci Inf 12:1–17
Siad L (2003) Seismic stability analysis of fractured rock slopes by yield design theory. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 23(3):21–30
Sinha S, Singh TN, Singh VK, Verma AK (2010) Epoch determination for neural network by self-organized map (SOM). Comput Geosci 14(1):199–206
Sonmez H, Ulusay R (1999) Modifications to the geological strength index (GSI) and their applicability to stability of slopes. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 36(6):743–760
Steward T, Sivakugan N, Shukla SK, Das BM (2010) Taylor’s slope stability charts revisited. International Journal of Geomechanics 11(4):348–352
Sun D, Chen Z, Du B, Cao Y (1997) Modifications to the RMR-SMR system for slope stability evaluation. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,16(4), 297–304
Taylor DW (1937) Stability of earth slopes.Journal of the. Boston Society of Civil Engineers 24(3):197–246
Wang Y, Cao Z, Au SK (2010) Efficient Monte Carlo simulation of parameter sensitivity in probabilistic slope stability analysis. Comput Geotech 37(7):1015–1022
Wenkai F, Shan D, Qi W, Xiaoyu Y, Zhigang L, Huilin B (2018) Improving the Hoek-Brown criterion based on the disturbance factor and geological strength index quantification. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 108:96–104
Xu J, Yang X (2018) Seismic stability analysis and charts of a 3d rock slope in Hoek-Brown media. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 112:64–76
Yun, L., Keping, Z., Jielin, L. (2018) Prediction of slope stability using four supervised learning methods. IEEE Access,1–1
Zanbak C (1983) Design charts for rock slopes susceptible to toppling. J Geotech Eng ASCE 190(8):1039–1062
Zhang Z, Liu Z, Zheng L, Zhang Y (2014) Development of an adaptive relevance vector machine approach for slope stability inference. Neural Comput & Applic 25(7–8):2025–2035
Zhao J (2000) Applicability of Mohr-coulomb and Hoek-Brown strength criteria to the dynamic strength of brittle rock. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences 37(7):1115–1121
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (2017zzts178; 2018zzts322);.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, C., Hu, H., Zhang, T. et al. Rock slope stability analysis and charts based on hybrid online sequential extreme learning machine model. Earth Sci Inform 13, 729–746 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00458-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00458-5