Abstract
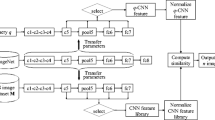
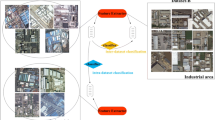
Generally, traditional convolutional neural networks (CNN) models require a long training time and output high-dimensional features for content-based remote sensing image retrieval (CBRSIR). This paper aims to examine the retrieval performance of the MobileNets model and fine-tune it by changing the dimensions of the final fully connected layer to learn low dimensional representations for CBRSIR. Experimental results show that the MobileNets model achieves the best retrieval performance in term of retrieval accuracy and training speed, and the improvement of mean average precision is between 11.2% and 44.39% compared with the next best model ResNet152. Besides, 32-dimensional features of the fine-tuning MobileNet reach better retrieval performance than the original MobileNets and the principal component analysis method, and the maximum improvement of mean average precision is 11.56% and 9.8%, respectively. Overall, the MobileNets and the proposed fine-tuning models are simple, but they can indeed greatly improve retrieval performance compared with the commonly used CNN models.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida M, Laskaridis S, Leontiadis I, Venieris SI, Lane ND (2019) EmBench: quantifying performance variations of deep neural networks across modern commodity devices. In: the 3rd international workshop on deep learning for Mobile systems and applications. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1145/3325413.3329793
Bapu JJ, Florinabel DJ (2020) Automatic annotation of satellite images with multi class support vector machine. Earth Sci Inf. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00471-8
Cao R, Zhang Q, Zhu J, Li Q, Li Q, Liu B, Qiu G (2020) Enhancing remote sensing image retrieval using a triplet deep metric learning network. Int J Remote Sens 41(2):740–751. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704x.2019.1647368
Cheng G, Han J, Lu X (2017) Remote sensing image scene classification: benchmark and state of the art. Proc IEEE 105(10):1865–1883. https://doi.org/10.1109/jproc.2017.2675998
Du Z, Li X, Lu X (2016) Local structure learning in high resolution remote sensing image retrieval. Neurocomputing 207:813–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.05.061
Ge Y, Jiang S, Xu Q, Jiang C, Ye F (2017) Exploiting representations from pre-trained convolutional neural networks for high-resolution remote sensing image retrieval. Multimed Tools Appl 77(13):17489–17515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5314-5
Ge Y, Tang Y, Jiang S, Leng L, Xu S, Ye F (2018) Region-based cascade pooling of convolutional features for HRRS image retrieval. Remote Sens Lett 9(10):1002–1010. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2018.1504334
Hinton GE, Salakhutdinov RR (2006) Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 313:504–507. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1127647
Hou D, Miao Z, Xing H, Wu H (2019) V-RSIR: an open access web-based image annotation tool for remote sensing image retrieval. IEEE Access 7:83852–83862. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2924933
Howard AG et al. (2017) Mobilenets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:170404861
Li P, Ren P (2017) Partial randomness hashing for large-scale remote sensing image retrieval. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 14(3):464–468. https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2017.2651056
Napoletano P (2018) Visual descriptors for content-based retrieval of remote-sensing images. Int J Remote Sens 39(5):1343–1376. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2017.1399472
Qi H, Liu W, Liu L (2017) An efficient deep learning hashing neural network for mobile visual search. In: 2017 IEEE global conference on signal and information processing (GlobalSIP), IEEE, Montreal, pp 701–704. https://doi.org/10.1109/GlobalSIP.2017.8309050
Shao Z, Yang K, Zhou W (2018) Performance evaluation of single-label and multi-label remote sensing image retrieval using a dense labeling dataset. Remote Sens 10(6):964. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060964
Shao Z, Zhou W, Deng X, Zhang M, Cheng Q (2020) Multilabel remote sensing image retrieval based on fully convolutional network. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 13:318–328. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2961634
Sudha S, Aji S (2019) A review on recent advances in remote sensing image retrieval techniques. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 47:2129–2139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-01049-8
Tong XY, Xia GS, Hu F, Zhong Y, Datcu M, Zhang L (2019) Exploiting deep features for remote sensing image retrieval: a systematic investigation. IEEE Trans Big Data. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBDATA.2019.2948924
Wang Y, Ji S, Lu M, Zhang Y (2020) Attention boosted bilinear pooling for remote sensing image retrieval. Int J Remote Sens 41(7):2704–2724. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2019.1697010
Xia G et al (2017) AID: a benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(7):3965–3981. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2017.2685945
Xiao Z, Long Y, Li D, Wei C, Tang G, Liu J (2017) High-resolution remote sensing image retrieval based on CNNs from a dimensional perspective. Remote Sens 9(7):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070725
Zhou W, Shao Z, Diao C, Cheng Q (2015) High-resolution remote-sensing imagery retrieval using sparse features by auto-encoder. Remote Sens Lett 6(10):775–783. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2015.1074756
Zhou W, Newsam S, Li C, Shao Z (2017) Learning low dimensional convolutional neural networks for high-resolution remote sensing image retrieval. Remote Sens 9(5):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050489
Zhou W, Newsam S, Li C, Shao Z (2018) PatternNet: a benchmark dataset for performance evaluation of remote sensing image retrieval. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 145:197–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.01.004
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the PatternNet, NWPU and AID datasets for their open access. The authors also would like to thank the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 41,701,443 and Grant 41,801,308, and in part by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant 2018YFB0505002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, D., Miao, Z., Xing, H. et al. Exploiting low dimensional features from the MobileNets for remote sensing image retrieval. Earth Sci Inform 13, 1437–1443 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00484-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00484-3