Abstract
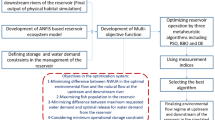
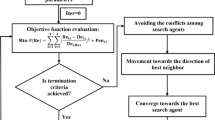
The present study proposes a novel optimization framework of the reservoir operation in terms of optimizing storage benefits while alleviating downstream environmental impacts. We utilized adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system as the habitat model to assess physical habitat loss at downstream of the reservoir. Furthermore, we applied metaheuristic algorithms including genetic algorithm, particle swarm optimization, invasive weed optimization, differential evolution algorithm, shuffled frog leaping algorithm, gravity search algorithm, atom search algorithm and bat algorithm to optimize reservoir operation. The developed objective function minimizes difference between physical habitat suitability in the natural flow and the optimal release in the simulated period. Based on the results in the case study, The Nash–Sutcliffe model efficiency coefficient demonstrated that the proposed ANFIS model is reliable to assess physical habitats. Hence, it could be used in a coupled simulation-optimization framework to optimize environmental flow regime downstream of a reservoir. Moreover, decision-making system indicated that gravity search algorithm is the best solution for optimization in terms of reliability, vulnerability and mean absolute error. The proposed method can be a robust framework to minimize physical habitat loss at downstream of the reservoirs.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acreman MC, Dunbar MJ (2004) Defining environmental river flow requirements? A review
Afshar A, Haddad OB, Mariño MA, Adams BJ (2007) Honey-bee mating optimization (HBMO) algorithm for optimal reservoir operation. J Frankl Inst 344(5):452–462
Afshar A, Shafii M, Haddad OB (2011) Optimizing multi-reservoir operation rules: an improved HBMO approach. J Hydroinf 13(1):121–139
Almeida RM, Hamilton SK, Rosi EJ, Arantes JD, Barros N, Boemer G, Gripp A, Huszar VL, Junger PC, Lima M, Pacheco F (2019) Limnological effects of a large Amazonian run-of-river dam on the main river and drowned tributary valleys. Sci Rep 9(1):1–11
Altinbilek D (2002) The role of dams in development. Water Sci Technol 45(8):169–180
Amiri B, Fathian M, Maroosi A (2009) Application of shuffled frog-leaping algorithm on clustering. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 45(1–2):199–209
Arunkumar R, Jothiprakash V (2012) Optimal reservoir operation for hydropower generation using non-linear programming model. J Inst Eng(India): Series A 93(2):111–120
Asgari HR, Bozorg Haddad O, Pazoki M, Loáiciga HA (2016) Weed optimization algorithm for optimal reservoir operation. J Irrig Drain Eng 142(2):04015055
Cai W, Zhang L, Zhu X, Zhang A, Yin J, Wang H (2013) Optimized reservoir operation to balance human and environmental requirements: a case study for the three gorges and Gezhouba dams, Yangtze River basin, China. Eco Inform 18:40–48
Chai T, Draxler RR (2014) Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?–arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci Model Dev 7(3):1247–1250
Chen CT (2000) Extensions of the TOPSIS for group decision-making under fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Sets Syst 114(1):1–9
Choi SU, Im D, Kim SK (2018) Physical habitat simulation with ANFIS method. EPiC Eng 3:456–459
Datta B, Burges SJ (1984) Short-term, single, multiple-purpose reservoir operation: importance of loss functions and forecast errors. Water Resour Res 20(9):1167–1176
Dokeroglu T, Sevinc E, Kucukyilmaz T, Cosar A (2019) A survey on new generation metaheuristic algorithms. Comput Ind Eng 137:106040
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In proceedings of the IEEE international conference on neural networks (Vol. 4, pp. 1942-1948). Citeseer
Ehteram M, Karami H, Mousavi SF, Farzin S, Kisi O (2018a) Evaluation of contemporary evolutionary algorithms for optimization in reservoir operation and water supply. J Water Supply Res Technol AQUA 67(1):54–67
Ehteram M, Karami H, Mousavi SF, Farzin S, Celeste AB, Shafie AE (2018b) Reservoir operation by a new evolutionary algorithm: kidney algorithm. Water Resour Manag 32(14):4681–4706
Haddad OB, Karimirad I, Seifollahi-Aghmiuni S, Loáiciga HA (2015a) Development and application of the bat algorithm for optimizing the operation of reservoir systems. J Water Resour Plan Manag 141(8):04014097
Haddad OB, Moravej M, Loáiciga HA (2015b) Application of the water cycle algorithm to the optimal operation of reservoir systems. J Irrig Drain Eng 141(5):04014064
Haddad OB, Hosseini-Moghari SM, Loáiciga HA (2016) Biogeography-based optimization algorithm for optimal operation of reservoir systems. J Water Resour Plan Manag 142(1):04015034
Harby A, Baptist M, Dunbar MJ, Schmutz S (2004) State-of-the-art in data sampling, modelling analysis and applications of river habitat modelling. In COST action (Vol. 626, pp. 1-313)
Hashimoto T, Stedinger JR, Loucks DP (1982) Reliability, resiliency, and vulnerability criteria for water resource system performance evaluation. Water Resour Res 18(1):14–20
Hecht JS, Lacombe G, Arias ME, Dang TD, Piman T (2019) Hydropower dams of the Mekong River basin: a review of their hydrological impacts. J Hydrol 568:285–300
Horne A, Kaur S, Szemis J, Costa A, Webb JA, Nathan R, Stewardson M, Lowe L, Boland N (2017) Using optimization to develop a “designer” environmental flow regime. Environ Model Softw 88:188–199
Im D, Choi SU, Choi B (2018) Physical habitat simulation for a fish community using the ANFIS method. Eco Inform 43:73–83
Jahandideh-Tehrani M, Bozorg-Haddad O, Loáiciga HA (2019) Application of non-animal–inspired evolutionary algorithms to reservoir operation: an overview. Environ Monit Assess 191(7):439
Jorde K, Schneider M, Peter A, Zoellner F (2001) Fuzzy based models for the evaluation of fish habitat quality and instream flow assessment. In Proceedings of the 3rd international symposium on environmental hydraulics (Vol. 3, pp. 27-28)
Jowett IG (1997) Instream flow methods: a comparison of approaches. Regulated Rivers: Research & Management: An International Journal Devoted to River Research and Management 13(2):115–127
Kim K, Park J (2009) A survey of applications of artificial intelligence algorithms in eco-environmental modelling. Environ Eng Res 14(2):102–110
Labadie JW (2004) Optimal operation of multireservoir systems: state-of-the-art review. J Water Resour Plan Manag 130(2):93–111
Lamouroux N, Capra H, Pouilly M (1998) Predicting habitat suitability for lotic fish: linking statistical hydraulic models with multivariate habitat use models. Regula Rivers: Res Manage14(1):1–11
Maavara T, Chen Q, Van Meter K, Brown LE, Zhang J, Ni J, Zarfl C (2020) River dam impacts on biogeochemical cycling. Nature Reviews Earth Env1(2):103–116
McCuen RH, Knight Z, Cutter AG (2006) Evaluation of the Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency index. J Hydrol Eng 11(6):597–602
Mehrabian AR, Lucas C (2006) A novel numerical optimization algorithm inspired from weed colonization. Eco Inform 1(4):355–366
Nandalal KDW, Bogardi JJ (2007) Dynamic programming based operation of reservoirs: applicability and limits. Cambridge university press, Cambridge
Needham JT, Watkins DW Jr, Lund JR, Nanda SK (2000) Linear programming for flood control in the Iowa and Des Moines rivers. J Water Resour Plan Manag 126(3):118–127
Noack M, Schneider M, Wieprecht S (2013) The habitat modelling system CASiMiR: a multivariate fuzzy-approach and its applications. In: Ecohydraulics: An Integrated Approach. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, pp 75–92
Ponnambalam K, Vannelli A, Unny TE (1989) An application of Karmarkar's interior-point linear programming algorithm for multi-reservoir operations optimization. Stoch Hydrol Hydraul 3(1):17–29
Qin AK, Huang VL, Suganthan PN (2008) Differential evolution algorithm with strategy adaptation for global numerical optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 13(2):398–417
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-Pour H, Saryazdi S (2009) GSA: a gravitational search algorithm. Inf Sci 179(13):2232–2248
Reed PM, Hadka D, Herman JD, Kasprzyk JR, Kollat JB (2013) Evolutionary multiobjective optimization in water resources: The past, present, and future. Adv Waters 51:438–456
Schöngart J, Wittmann F, Faria de Resende A, Assahira C, de Sousa Lobo G, Rocha Duarte Neves J, da Rocha M, Biem Mori G, Costa Quaresma A, Oreste Demarchi L and Weiss Albuquerque B (2021) The shadow of the Balbina dam: a synthesis of over 35 years of downstream impacts on floodplain forests in Central Amazonia. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems
Sedighkia M, Abdoli A (2021) Efficiency of coupled invasive weed optimization-adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system method to assess physical habitats in streams. SN Appl Sci 3(2):1–13
Stalnaker CB (1994) The instream flow incremental methodology: a primer for IFIM (Vol. 29). National Ecology Research Center, National Biological Survey
Stedinger JR, Sule BF, Loucks DP (1984) Stochastic dynamic programming models for reservoir operation optimization. Water Resour Res 20(11):1499–1505
Waddle T (2001) PHABSIM for windows user's manual and exercises (no. 2001-340)
Whitley D (1994) A genetic algorithm tutorial. Stat Comput 4(2):65–85
Yang, X.S. and Gandomi, A.H., 2012. Bat algorithm: a novel approach for global engineering optimization. Engineering computations
Yaseen ZM, Allawi MF, Karami H, Ehteram M, Farzin S, Ahmed AN, Koting SB, Mohd NS, Jaafar WZB, Afan HA, El-Shafie A (2019) A hybrid bat–swarm algorithm for optimizing dam and reservoir operation. Neural Comput & Applic 31(12):8807–8821
Yin XA, Yang ZF, Petts GE (2012) Optimizing environmental flows below dams. River Res Appl 28(6):703–716
Zhao Y, Zhou J, Bi S, Zhang H (2013) Application of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for physical habitat simulation. In 2013 10th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD) (pp. 349-353). IEEE
Zhao W, Wang L, Zhang Z (2019) A novel atom search optimization for dispersion coefficient estimation in groundwater. Futur Gener Comput Syst 91:601–610
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sedighkia, M., Datta, B. & Abdoli, A. Optimizing reservoir operation to avoid downstream physical habitat loss using coupled ANFIS- metaheuristic model. Earth Sci Inform 14, 2203–2220 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00671-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00671-w