Abstract
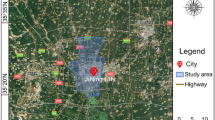
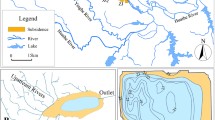
Land subsidence has become a widespread engineering geological problem due to human-induced causes such as the withdrawal of groundwater and the extraction of coal and ores. There is a relative lack of research on land subsidence under the coupling effect of groundwater and coal mining. This paper uses numerical and theoretical computational models to study land subsidence under the coupling effect of groundwater and coal mining. The study area is a coal mine in Jining City from 2000 to 2020. Numerical results show that groundwater withdrawal induces substantial land subsidence over a long period and that the rate of land subsidence decreases over time. The maximum land subsidence was 128 mm in 2010. Due to coal extraction (2015), the area induces significant land subsidence in the short term. The maximum land subsidence in 2016 was 305 mm. Based on the stochastic medium theory, this paper establishes a theoretical model for land subsidence under the coupling effect of groundwater and coal mining. And based on the numerical results, the theoretical subsidence equation applicable to the area is calculated. By comparing the theoretical results with the actual measurement results, the analysis proves that the equation can better calculate the land subsidence of the model.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidin HZ, Andreas H, Gumilar I, Fukuda Y, Pohan YE, Deguchi T (2011) Land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) and its relation with urban development. Nat Hazards 59(3):1753–1771
Alejano L, Ramirez-Oyanguren P, Taboada J (1999) FDM predictive methodology for subsidence due to ¯at and inclined coal seam mining. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 36(4):475–491
Cabral-Cano E, Dixon TH, Miralles-Wilhelm F, Diaz-Molina O, Sanchez-Zamora O, Carande RE (2008) Space geodetic imaging of rapid ground subsidence in Mexico City. Geol Soc Am Bull 120(11–12):1556–1566
Calderhead AI, Therrien R, Rivera A, Martel R, Garfias J (2011) Simulating pumping-induced regional land subsidence with the use of InSAR and field data in the Toluca Valley. Mex Adv Water Resour 34(1):83–97
Cao G, Han D, Moser J (2013) Groundwater exploitation management under land subsidence constraint: empirical evidence from the Hangzhou–Jiaxing–Huzhou plain. China Environ Manag 51(6):1109–1125
Cao S, Song W, Deng D, Lei Y, Lan J (2016) Numerical simulation of land subsidence and verification of its character for an iron mine using sublevel caving. Int J Min Sci Technol 26(2):327–332
Castellazzi P, Garfias J, Martel R, Brouard C, Rivera A (2017) InSAR to support sustainable urbanization over compacting aquifers: the case of Toluca Valley, Mexico. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 63:33–44
Ceccatelli M, Del Soldato M, Solari L, Fanti R, Mannori G, Castelli F (2021) Numerical modelling of land subsidence related to groundwater withdrawal in the Firenze-Prato-Pistoia basin (Central Italy). Hydrogeol J 29(2):629–649
Chang M, Upomo TC, Huang R, Wu P, Su P (2020) Evaluation on the behavior and contributing factors of subsidence in the intersection area of Expwy 78 and Taiwan high speed rail based on in situ monitoring and numerical simulations. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79(6):2971–2995
Chatterjee RS, Fruneau B, Rudant JP, Roy PS, Frison P, Lakhera RC, Dadhwal VK, Saha R (2006) Subsidence of Kolkata (Calcutta) City, India during the 1990s as observed from space by differential synthetic aperture radar interferometry (D-InSAR) technique. Remote Sens Environ 102(1–2):176–185
Chaussard E, Amelung F, Abidin H, Hong S (2013) Sinking cities in Indonesia: ALOS PALSAR detects rapid subsidence due to groundwater and gas extraction. Remote Sens Environ 128:150–161
Chen B, Deng K, Fan H, Hao M (2013) Large-scale deformation monitoring in mining area by D-InSAR and 3D laser scanning technology integration. Int J Min Sci Technol 23(4):555–561
Conway BD (2016) Land subsidence and earth fissures in south-central and southern Arizona, USA. Hydrobiol J 24(3):649–655
Ding P, Jia C, Di S, Wang L, Bian C, Yang X (2020) Analysis and prediction of land subsidence along significant linear engineering. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79(10):5125–5139
Dixon TH, Amelung F, Ferretti A, Novali F, Rocca F, Dokka R, Sella G, Kim SW, Wdowinski S, Whitman D (2006) Space geodesy: subsidence and flooding in New Orleans. Nature 441(7093):587–588
Dong S, Samsonov S, Yin H, Ye S, Cao Y (2014) Time-series analysis of subsidence associated with rapid urbanization in Shanghai, China measured with SBAS InSAR method. Environ Earth Sci 72(3):677–691
Fan H, Lu L, Yao Y (2018) Method combining probability integration model and a small baseline subset for time series monitoring of mining subsidence. Remote Sens 10(9):1444
Fiaschi S, Tessitore S, Bonì R, Di Martire D, Achilli V, Borgstrom S, Ibrahim A, Floris M, Meisina C, Ramondini M, Calcaterra D (2017) From ERS-1/2 to Sentinel-1: two decades of subsidence monitored through A-DInSAR techniques in the Ravenna area (Italy). GISci Remote Sens 54(3):305–328
Galloway DL, Hoffmann J (2007) The application of satellite differential SAR interferometry-derived ground displacements in hydrogeology. Hydrogeol J 15(1):133–154
Garg S, Motagh M, Indu J, Karanam V (2022) Tracking hidden crisis in India’s capital from space: implications of unsustainable groundwater use. Sci Rep 12(1)
Guzy A, Malinowska A (2020a) State of the art and recent advancements in the modelling of land subsidence induced by groundwater withdrawal. Water 12(7):2051
Guzy A, Malinowska AA (2020b) Assessment of the impact of the spatial extent of land subsidence and aquifer system drainage induced by underground mining. Sustainability 12(19):7871
Guzy A, Witkowski WT (2021) Land subsidence estimation for aquifer drainage induced by underground mining. Energies 14(15):4658
Haghshenas Haghighi M, Motagh M (2019) Ground surface response to continuous compaction of aquifer system in Tehran, Iran: results from a long-term multi-sensor InSAR analysis. Remote Sens Environ 221:534–550
Herrera-García G, Ezquerro P, Tomás R, Béjar-Pizarro M, López-Vinielles J, Rossi M, Mateos RM, Carreón-Freyre D, Lambert J, Teatini P, Cabral-Cano E, Erkens G, Galloway D, Hung W, Kakar N, Sneed M, Tosi L, Wang H, Ye S (2021) Mapping the global threat of land subsidence. Sci (Am Assoc Adv Sci) 371(6524):34–36
Howladar MF, Hasan K (2014) A study on the development of subsidence due to the extraction of 1203 slice with its associated factors around Barapukuria underground coal mining industrial area, Dinajpur. Bangladesh Environ Earth Sci 72(9):3699–3713
Hu RL, Yue ZQ, Wang LC, Wang SJ (2004) Review on current status and challenging issues of land subsidence in China. Eng Geol 76(1–2):65–77
Jianjun S, Chunjian H, Ping L, Junwei Z, Deyuan L, Minde J, Lin Z, Jingkai Z, Jianying S (2012) Quantitative prediction of mining subsidence and its impact on the environment. Int J Min Sci Technol 22(1):69–73
Jin W, Luo Z, Wu X (2016) Sensitivity analysis of related parameters in simulation of land subsidence and ground fissures caused by groundwater exploitation. Bull Eng Geol Environ 75(3):1143–1156
Kadiyan N, Chatterjee RS, Pranjal P, Agrawal P, Jain SK, Angurala ML, Biyani AK, Sati MS, Kumar D, Bhardwaj A, Champati Ray PK (2021) Assessment of groundwater depletion–induced land subsidence and characterisation of damaging cracks on houses: a case study in Mohali-Chandigarh area, India. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80(4):3217–3231
Knothe S (1957, April) Observations of surface movements under influence of mining and their theoretical interpretation. In Proceedings of the European congress on ground movement, Leeds, UK, p 9–12
Li Z, Luo Z, Wang Q, Du J, Lu W, Ning D (2019) A three-dimensional fluid-solid model, coupling high-rise building load and groundwater abstraction, for prediction of regional land subsidence. Hydrogeol J 27(4):1515–1526
Liu B, Yang J (1999) Stochastic media model for the prediction of pumped ground settlement. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 05:13–15
Liu H, Deng K, Lei S, Bian Z (2015) Mechanism of formation of sliding ground fissure in loess hilly areas caused by underground mining. Int J Min Sci Technol 25(4):553–558
Liu L, Liu X (2017) Future groundwater extraction scenarios based on COMSOL multiphysics for the confined aquifer at Linfen basin, Shanxi Province. China Cogent Eng 4(1):1404178
Liu X, Wang Y, Yan S (2018) Interferometric SAR time series analysis for ground subsidence of the abandoned mining area in north Peixian using sentinel-1A TOPS data. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 46(3):451–461
Mahmoudpour M, Khamehchiyan M, Nikudel MR, Ghassemi MR (2016) Numerical simulation and prediction of regional land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation in the southwest plain of Tehran. Iran Eng Geol 201:6–28
Malinowska A, Hejmanowski R, Dai H (2020) Ground movements modeling applying adjusted influence function. Int J Min Sci Technol 30(2):243–249
Minderhoud P, Erkens G, Pham VH, Bui VT, Erban L, Kooi H, Stouthamer E (2017) Impacts of 25 years of groundwater extraction on subsidence in the Mekong delta. Vietnam Environ Res Lett 12(6):64006
Osmanoğlu B, Dixon TH, Wdowinski S, Cabral-Cano E, Jiang Y (2011) Mexico City subsidence observed with persistent scatterer InSAR. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 13(1):1–12
Qiao S (2006) Study on deformation failure criterion of stochastic medium and its applications. Dissertation, Central South University
Qin H, Andrews CB, Tian F, Cao G, Luo Y, Liu J, Zheng C (2018) Groundwater-pumping optimization for land-subsidence control in Beijing plain. China Hydrogeol J 26(4):1061–1081
Qu F, Lu Z, Zhang Q, Bawden GW, Kim J, Zhao C, Qu W (2015) Mapping ground deformation over Houston–Galveston, Texas using multi-temporal InSAR. Remote Sens Environ 169:290–306
Rosen P, Hensley S, Joughin I, Li F, Madsen S, Rodriguez E, Goldstein R (2000) Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Proc IEEE 88(3):333–382
Shen S, Xu Y (2011) Numerical evaluation of land subsidence induced by groundwater pumping in Shanghai. Can Geotech J 48(9):1378–1392
Sikora P, Wesołowski M (2021) Numerical assessment of the influence of former mining activities and plasticity of rock mass on deformations of terrain surface. Int J Min Sci Technol 31(2):209–214
Teatini P, Ferronato M, Gambolati G, Bertoni W, Gonella M (2005) A century of land subsidence in Ravenna. Italy Environ Geol 47(6):831–846
Tosi L, Lio C, Teatini P, Strozzi T (2018) Land subsidence in coastal environments: knowledge advance in the Venice coastland by TerraSAR-X PSI. Remote Sens 10(8):1191
Tung H, Chen H, Hu J, Ching K, Chen H, Yang K (2016) Transient deformation induced by groundwater change in Taipei metropolitan area revealed by high resolution X-band SAR interferometry. Tectonophysics
Wang Y, Wang Z, Cheng W (2019) A review on land subsidence caused by groundwater withdrawal in Xi’an, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78(4):2851–2863
Xie G, Zhang J, Yin Z (2010) Spatiotemporal model of ground deformation caused by groundwater gathering based on stochastic medium theory. Rock Soil Mech 31(01):282–286
Xu H, Liu B, Fang Z (2014) New grey prediction model and its application in forecasting land subsidence in coal mine. Nat Hazards 71(2):1181–1194
Xu Y, Shen S, Cai Z, Zhou G (2008) The state of land subsidence and prediction approaches due to groundwater withdrawal in China. Nat Hazards 45(1):123–135
Yu G, Zhang C, Pan Y, Liu F, Yuan C (2006) Space-time predicting model research of surface subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation. Rock Soil Mech (05):759–762
Yuan M, Li M, Liu H, Lv P, Li B, Zheng W (2021) Subsidence monitoring base on SBAS-InSAR and slope stability analysis method for damage analysis in mountainous mining subsidence regions. Remote Sens 13(16):3107
Zhang B, Zhang L, Yang H, Zhang Z, Tao J (2016) Subsidence prediction and susceptibility zonation for collapse above goaf with thick alluvial cover: a case study of the Yongcheng coalfield, Henan Province, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 75(3):1117–1132
Zhao Y, Wang C, Yang J, Bi J (2021) Coupling model of groundwater and land subsidence and simulation of emergency water supply in Ningbo urban area. China J Hydrol 594:125956
Zhou H, Wang Y, Yan S, Li Y, Liu X, Zhang F (2018) Monitoring of recent ground surface subsidence in the Cangzhou region by the use of the InSAR time-series technique with multi-orbit Sentinel-1 TOPS imagery. Int J Remote Sens 39(22):8113–8128
Zhu G, Xu Z, Xie C, Guo Y (2014) Study of influence functions of surface residual movement and deformation above old goaf. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 33(10):1962–1970
Zhu X, Guo G, Fang Q (2016) Coupled discrete element–finite difference method for analyzing subsidence control in fully mechanized solid backfilling mining. Environ Earth Sci 75(8)
Zhu X, Zhang W, Wang Z, Wang C, Li W, Wang C (2020) Simulation analysis of influencing factors of subsidence based on mining under huge loose strata: a case study of Heze mining area, China. Geofluids 2020:1–17
Acknowledgments
Research in this paper is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 41877239, 51379112, 51422904, 40902084, and 41772298), Fundamental Research Fund of Shandong University (grant number 2018JC044), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (grant numbers JQ201513 and 2019GSF111028).
Author contributions statement
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Chen Hong. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Chen Hong. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Data availability statement (DAS)
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to the confidential nature of the data but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
Research in this paper is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 41877239, 51379112, 51422904, 40902084, and 41772298), Fundamental Research Fund of Shandong University (grant number 2018JC044), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (grant numbers JQ201513 and 2019GSF111028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Y., Chen, H., Kong, F. et al. Land subsidence calculation model under the coupling effect of groundwater and coal mining. Earth Sci Inform 15, 2689–2701 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00855-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00855-y