Abstract
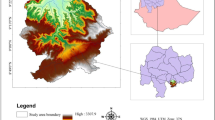
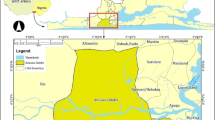
In this paper, we analyse the applicability and effectiveness of satellite-retrieved Land Surface Temperature (LST) for monitoring and spatial analysis of forest fires using pre- and post-fire Landsat 8 and Aster satellite images. Firstly, LST was used for pre-fire analysis, along with other meteorological parameters to evaluate fire risk, and the results showed that the LST was highly correlated with all parameters. Besides, Google Earth Engine platform was used to evaluate forest-fire susceptibility in the region. For post-fire analysis, LST was used to monitor, analyse, and map post-fire disturbances using different image spectral transformations, and correlation analysis was performed to evaluate the strength of relationships between the parameters. High correlation coefficients were obtained between LST and selected spectral indices; and the highest correlation (0.90) was found between Difference Land Surface Temperature (dLST) – Difference Normalized Burn Ratio (dNBR). Spatial analysis done for dLST and slope showed that the post-fire LST increased in areas with a slope range of 42—55%. Then, spatial relation analysis between dLST and other indices was performed and a high correlation was found between dLST – dNBR, dLST – DI (Disturbance Index), and dLST – NDMI (Normalized Difference Moisture Index). Finally, for 4 categorical variables (namely CORINE Land Cover (CLC) map, dLST, Burn severity and Slope), the areal extent of burnt forest areas was calculated and most burnt areas were found to be related a certain degree with each category (i.e. coniferous forest class, -2 and 0.5 °C, medium–low burning intensity, 29–42% slope range, respectively).










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Akkaş ME, Bucak C, Boza Z, Eronat H, Bekereci A, Erkan A, Cebeci C (2006) Büyük orman yangınlarının meteorolojik verilerin ışığında incelenmesi. [The investigation of the great wild fires based on meteorological data.] Ege Forestry Research Institute Technical Bulletin, 36. https://www.cem.gov.tr/erozyon/files/erozyon/yardop.../yangin_meteoroloji_iliskisi_2.doc. Accessed 15 March 2019
Alexander C (2020) Normalised difference spectral indices and urban land cover as indicators of Land Surface Temperature (LST). Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 86:102013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2019.102013
Baig MH, Zhang L, Shuai T, Tong Q (2014) Derivation of a Tasselled Cap transformation based on Landsat 8 At-Satellite reflectance. Remote Sensing Letters 5:423–431. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2014.915434
Barraza V, Grings F, Franco M, Douna V, Entekhabi D, Restrepo-Coupe N et al (2019) Estimation of latent heat flux using satellite land surface temperature and a variational data assimilation scheme over a eucalypt forest savanna in Northern Australia. Agric for Meteorol 268(15):341–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.01.032
Chaparro D, Vall-llossera M, Piles M, Champs A, Rüdiger C, Riera-Tatche R (2016) Predicting the extent of wildfires using remotely sensed soil moisture and temperature trends. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 9(6):2818–2829. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2571838
Chen W, Cao C, Koyama L (2012) Detection of forest disturbance in the Greater Hinggan Mountain of China based on Landsat time-series data. Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), 2012 IEEE International. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6351993
Chen W, Moriya K, Sakai T, Koyama L, Cao C (2014) Monitoring of post-fire forest recovery under different restoration modes based on time series Landsat data. European Journal of Remote Sensing 47:153–168. https://doi.org/10.5721/EuJRS20144710
Chen S, Wen Z, Jiang H, Zhao Q, Zhang X, Chen Y (2015) Temperature Vegetation Dryness Index estimation of soil moisture under different tree species. Sustainability 7:11401–11417. https://doi.org/10.3390/su70911401
Chen W, Zhang S, Li R, Shahabi H (2018) Performance evaluation of the GIS-based data mining techniques of best-first decision tree, random forest, and naïve Bayes tree for landslide susceptibility modeling. Sci Total Environ 644:1006–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.389
Chowdhury EH, Hassan QK (2015) Operational perspective of remote sensing-based forest fire danger forecasting systems. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 104:224–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.03.011
Chuvieco E, Aguado I, Yebra M, Nieto H, Salas J, Martin MP et al (2010) Development of a framework for fire risk assessment using remote sensing and Geographic Information System technologies. Ecol Model 221:46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2008.11.017
Cristobal J, Jimenez-Munoz JC, Prakash A, Mattar C, Skokovic D, Sobrino JA (2018) An improved Single-Channel method to retrieve land surface temperature from the Landsat-8 thermal band. Remote Sensing 10:431. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030431
Copernicus Climate Change Service (2021) Surface air temperature anomaly for July 2021. https://climate.copernicus.eu/surface-air-temperature-july-2021 Accessed 7 August 2021
Çolak E, Sunar AF (2018) Remote sensing and GIS integratıon for monitoring the areas affected by forest fires: A case study in Izmir, Turkey. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens Spatial Inf Sci, XLII-3/W4, 165–170. 10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-3-W4-165-2018
Çolak E, Sunar F (2020a) Spatial pattern analysis of post-fire damages in the Menderes district of Turkey. Frontiers of Earth Science 14:446–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-019-0786-4
Çolak E, Sunar F (2020b) Evaluation of forest fire risk in the Mediterranean Turkish forests: A case study of Menderes region. Izmir Int J Disaster Risk Reduction 45:101479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.101479
Çolak E, Sunar F (2020c) The importance of ground-truth and crowdsourcing data for the statistical and spatial analyses of the NASA FIRMS active fires in the Mediterranean Turkish forests. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment 19:100327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2020.100327
Du H, Cai W, Xu Y, Wang Z, Wang Y, Cai Y (2017) Quantifying the cool island effects of urban green spaces using remote sensing data. Urban Forestry and Urban Greening 27:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2017.06.008
Ertuğrul M, Varol T, Ozel HB, Cetin M, Sevik H (2021) Influence of climatic factor of changes in forest fire danger and fire season length in Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 193(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08800-6
Esri (2018) How to perform spatial analysis. https://www.esri.com/arcgis-blog/products/product/analytics/how-to-perform-spatial-analysis/ Accessed 6 August 2021
Flannigan MD, Stocks BJ, Wotton BM (2000) Climate change and forest fires. Sci Total Environ 262:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00524-6
Fraser R H, Li Z, Cihlar J (2000) Hotspot and NDVI Differencing Synergy (HANDS): a new technique for burned area mapping over boreal forest. Remote Sens Environ 74(3):362–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(00)00078-X
Galiano GSG (2012) Assessment of vegetation indexes from remote sensing: theoretical basis. Otions Méditerranéennes. Series b: Studies and Research 67:65–75
Ghulam A (2009) How to calculate reflectance and temperature using ASTER data. Center for Environmental Sciences at Saint Louis University. http://www.pancroma.com/downloads/ASTER%20Temperature%20and%20Reflectance.pdf Accessed 20 April 2019
Giannakopoulos C, Le Sager P, Bindi M, Moriondo M, Kostopoulou E, Goodess CM (2009) Climatic changes and associated impacts in the Mediterranean resulting from a 2 °C global warming. Global Planet Change 68:209–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2009.06.001
Giri C, Long J, Abbas S, Murali RM, Qamer FM, Pengra B et al (2015) Distribution and dynamics of mangrove forests of South Asia. J Environ Manage 148:101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.01.020
Gonçalves AC, Sousa AMO (2017) The fire in the Mediterranean Region: a case study of forest fires in Portugal. In: Fuerst-Bjeliš B (ed) Mediterranean identities - environment, society, culture. InTech. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.69410
Guangmeng G, Mei Z (2004) Using MODIS Land Surface Temperature to evaluate forest fire risk of northeast China. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 1:98–100. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2004.826550
Hengl T, Heuvelink GBM, Perčec Tadić M, Pebesma EJ (2012) Spatio-temporal prediction of daily temperatures using time-series of MODIS LST images. Theor Appl Climatol 107:265–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-011-0464-2
Hernandez-Leal PA, Arbelo M, Gonzalvez-Calvo A (2006) Fire risk assessment using satellite data. Adv Space Res 37:741–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2004.12.053
Holden ZA, Smith AMS, Morgan P, Rollins MG, Gessler PE (2005) Evaluation of novel thermally enhanced spectral indices for mapping fire perimeters and comparisons with fire atlas data. Int J Remote Sens 26:4801–4808. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160500239008
Hu X, Ren H, Tansey K, Zheng Y, Ghent D, Liu X et al (2019) Agricultural drought monitoring using European Space Agency Sentinel 3A land surface temperature and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index imageries. Agric for Meteorol 279:107707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.107707
Huang C, Wylie BK, Yang L, Homer C, Zylstra G (2010) Derivation of a Tasseled Cap transformation based on Landsat 7 At-Satellite reflectance. Int J Remote Sens 23:1741–1748. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160110106113
Jimenez-Munoz JC, Cristobal J, Sobrino JA, Soria G, Ninyerola M, Pons X (2009) Revision of the Single-Channel algorithm for land surface temperature retrieval from Landsat thermal-infrared data. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 47:339–349. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2008.2007125
Jin S, Sader SA (2004) Comparison of time series Tasseled Cap wetness and the Normalized Difference Moisture Index in detecting forest disturbances. Remote Sens Environ 94:364–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.10.012
Kayet N, Chakrabarty A, Pathak K (2020) Comparative analysis of multi-criteria probabilistic FR and AHP models for forest fire risk (FFR) mapping in Melghat Tiger Reserve (MTR) forest. J for Res 31:565–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0826-z
Key CH, Benson NC (2005) Landscape assessment (LA) sampling and analysis methods. In book: FIREMON: Fire Effects Monitoring and Inventory System. Edition: Gen. Tech. Rep. RMRS-GTR-164. Publisher: USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Ogden, UT. (Editors: D.C. Lutes, R.E. Keane, J.F. Caratti, C.H. Key, N.C. Benson, S. Sutherland, L.J. Gangi). https://www.fs.fed.us/postfirevegcondition/documents/publicati ons/FIREMON_LandscapeAssessment.pdf Accessed 16 April 2019
Laneve G, Pampanoni V, Uddien Shaik R (2020) The daily fire hazard index: A fire danger rating method for Mediterranean areas. Remote Sensing 12(15):2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12152356
Li ZL, Duan SB (2018) Land surface temperature. Comprehensive Remote Sensing 5:264–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409548-9.10375-6
Kursah MB (2017) GIS and correlation analysis of geo-environmental variables influencing malaria prevalence in the Saboba district of Northern Ghana. Ghana Journal of Geography 9(3):112–131
Macarof P, Groza S, Statescu F (2018) Investigating Correlation LST and vegetation indices using Landsat images for the warmest month: A case study of Iasi County. Annals of Valahia University of Targoviste, Geographical Series 18(1):33–40. https://doi.org/10.2478/avutgs-2018-0004
Manzo-Delgado L, Sánchez-Colón S, Álvarez R (2009) Assessment of seasonal forest fire risk using NOAA-AVHRR: A case study in central Mexico. Int J Remote Sens 30:4991–5013. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160902852796
Mason PJ (2005) Encyclopedia of Geology. Elsevier Academic Press, Oxford
Matin MA, Chitale VS, Murthy MSR, Uddin K, Bajracharya B, Pradhan S (2017) Understanding forest fire patterns and risk in Nepal using remote sensing, Geographic Information System and historical fire data. Int J Wildland Fire 26:276–286. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF16056
Midekisa A, Holl F, Savory DJ, Andrade-Pacheco R, Gething W, Bennett A et al (2017) Mapping land cover change over continental Africa using Landsat and Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing. PLoS ONE 12:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184926
Moriondo M, Good P, Durao R, Bindi M, Giannakopoulos C, Corte-Real J (2006) Potential impact of climate change on fire risk in the Mediterranean area. Climate Res 31:85–95
Ndossi MI, Avdan U (2016) Inversion of Land Surface Temperature (LST) using Terra ASTER Data: A comparison of three algorithms. Remote Sensing 8:993. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8120993
Norton J (2008) The use of remote sensing indices to determine wildland burn severity in semiarid sagebrush steppe rangelands using landsat ETM + and SPOT 5. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/4233/597fb51c5a29b4c282381081fa0a223a7341.pdf?_ga=2.222787999.589094426.15332235001622772386.1533223500
Oğuz H (2015) A software tool for retrieving land surface temperature from ASTER imagery. Journal of Agricultural Sciences 21:471–482
Parastatidis D, Mitraka Z, Chrysoulakis N, Abrams M (2017) Online global land surface temperature estimation from Landsat. Remote Sens 9(12):1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121208
Parks SA, Holsinger LM, Voss MA, Loehman RA, Robinson NP (2018) Mean composite fire severity metrics computed with Google Earth Engine offer improved accuracy and expanded mapping potential. Remote Sensing 10(6):879. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060879
Rahman S, Chang H, Magill C, Tomkins K, Hehir W (2018) Forest fire occurrence and modeling in southeastern Australia. In Forest Fire, InTechOpen 95-109. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.76072
Razali SM, Nuruddin AA, Ismail AM, Norizan P (2010) Forest fire hazard rating assessment in peat swamp forest using Landsat Thematic Mapper image. J Appl Remote Sens 4:043531. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.3430040
Sajib MQU, Wang T (2020) Estimation of land surface temperature in an agricultural region of Bangladesh from Landsat 8: Intercomparison of four algorithms. Sensors 20(6):1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061778
Seidl R, Thom D, Kautz M, Martin-Benito D, Peltoniemi M, Vacchiano G, Wild J, Ascoli D, Petr M, Honkaniemi J, Lexer M J, Trotsiuk V, Mairota P, Svoboda M, Fabrika M, Nagel TA, Reyer CPO (2017) Forest disturbances under climate change. Nat Clim Chang 7(6):395‒402. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate330
Sputnik (2021). Orman yangınlarıyla yıllık ortalamanın 9 katı alan kül oldu. [Forest fires destroyed 9 times the annual average]. https://tr.sputniknews.com/20210806/orman-yanginlariyla-yillik-ortalamanin-9-kati-alan-kul-oldu-1045176242.html Accessed 7 August 2021
Sunar F, Ozkan C, Ok AO, Osmanoglu B, Avci ZDU, Berberoglu S (2017) Dijital görüntü işleme. Anadolu University. [Digital image processing], Eskişehir
Teillet PM, Stanez K, William DJ (1997) Effects of spectral, spatial, and radiometric characteristics on remote sensing vegetation indices of forested regions. Remote Sens Environ 61:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(96)00248-9
Tran BN, Tanase MA, Bennett LT, Aponte C (2018) Evaluation of spectral indices for assessing fire severity in Australian temperate forests. Remote Sensing 10(11):1680. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111680
Tucker CJ (1979) Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens Environ 8:127–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(79)90013-0
U.S. Geological Survey (2016) Landsat 8 (L8) data users handbook. https://landsat.usgs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/Landsat8DataUs ersHandbook.pdf Accessed 16 March 2019
Venkatramanan S, Viswanathan PM, Chung SY (2019) GIS and geostatistical techniques for groundwater science. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Veraverbeke S, Verstraeten WW, Lhermitte S, Van de Kerchove R, Goossens R (2012) Assessment of post-fire changes in land surface temperature and surface albedo, and their relation with fire-burn severity using multitemporal MODIS imagery. Int J Wildland Fire 21:243–256
Vidal A, Pinglo F, Durand H, Devaux-Ros C, Maillet A (1994) Evaluation of a temporal fire risk index in Mediterranean forests from NOAA thermal IR. Remote Sens Environ 49:296–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(94)90024-8
Vlassova L, Pérez-Cabello F, Mimbrero MR, Llovería RM, García-Martín A (2014) Analysis of the relationship between land surface temperature and wildfire severity in a series of Landsat images. Remote Sensing 6:6136–6162. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6076136
Wang M, Zhang Z, Hu T, Liu X (2019) A practical Single-Channel algorithm for land surface temperature retrieval: Application to Landsat series data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 124:299–316. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD029330
Wang L, Lu Y, Yao Y (2020) Comparison of three algorithms for the retrieval of land surface temperature from Landsat 8 Images. Sensors 19(22):5049. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19225049
World Meteorological Organization (WMO) (2021) New climate predictions increase likelihood of temporarily reaching 1.5 °C in next 5 years. https://public.wmo.int/en/media/press-release/new-climate-predictions-increase-likelihood-of-temporarily-reaching-15-%C2%B0c-next-5 Accessed 6 August 2021
Yarbrough LD, Easson G, Kuszmaul JS (2005) Using at-sensor radiance and reflectance Tasseled Cap transforms applied to change detection for the ASTER sensor. IEEE International Workshop on the Analysis of Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Images, Biloxi, MS, USA. https://doi.org/10.1109/AMTRSI.2005.1469857
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Emre Çolak: Writing—original draft, Methodology, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Data curation. Filiz Sunar: Supervision, Writing—review & editing, Methodology.
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Emre Çolak and Filiz Sunar. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Emre Çolak and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
Not applicable
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Communicated by H. Babaie.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Çolak, E., Sunar, F. Investigating the usefulness of satellite-retrieved land surface temperature (LST) in pre- and post-fire spatial analysis. Earth Sci Inform 16, 945–963 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00883-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00883-8