Abstract
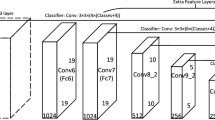
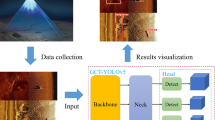
In video surveillance, real-time detection of hidden or concealed objects under the clothes of humans is a challenging task. Very few research works have been carried out on this hidden object detection and recognition with the aid of various coherent technologies namely Millimeter wave (MMW) imaging, Infrared (IR) imaging, and Terahertz (THz) imaging systems. Hidden objects that include weapons like axe, knife, gun, bomb, pistol, etc., are a major threat to security surveillance as it needs to be recognized in a few seconds irrespective of their size. This paper proposes an efficient hidden object recognition method that focuses on the detection and recognition of concealed weapons in humans using Modified Weighted You Only Look Once v5 (MWYOLOv5) model. The probable occurrence of inaccurate forecast results due to the sense of a low confidence score is mitigated by the use of the weighted boxes fusion (WBF) method. As a result, higher-confidence boxes contribute more to fused box coordinates than lower-confidence boxes. Meanwhile, it is significant to select optimal hyperparameter values for training YOLOv5 model with CSPDarknet53 based feature extractor and Path Aggregation Network (PANet) based feature aggregation procedures to predict concealed objects. To achieve this, a new crossover salp swarm algorithm (CSSA) is developed to tune the YOLO hyperparameters such as learning rate, momentum, weight decay and batch size. This provides more accuracy in recognizing hidden objects on using THz and MMW images on comparison with existing methods. The proposed hazardous weapon recognition model is trained and tested on both MMW and THz Imagery datasets and it shows that the proposed methodology is showing good results with high mAP@.5 and mAP@.5:95.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Altaher AW, Abbas S (2020) Image processing analysis of sigmoidal Hadamard wavelet with PCA to detect hidden object. TELKOMNIKA (Telecommunication Computing Electronics and Control) 18(3):1216–1223. https://doi.org/10.12928/telkomnika.v18i3.13541
Cheng Y, Zhao Z, Wang Y, Niu Y (2020) Multi-Polarization Information Fusion for Object Contour Display in Passive Millimeter-Wave and Terahertz Security Imaging. ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) 1524–1528. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9054207
Fan DP, Ji GP, Cheng MM, Shao L (2021a) Concealed object detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(10):6024–6042. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3085766
Fan L, Yang Q, Deng B, Zeng Y, Wang H (2021b) Concealed object detection for active millimeter wave imaging based CGAN data augmentation. In 2021 14th UK-Europe-China workshop on Millimetre-waves and terahertz technologies (UCMMT) 1-3 IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/UCMMT53364.2021.9569893
Feng H, An D, Tu H, Bu W, Wang W, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Meng X, Wei W, Gao B, Wu S (2020) A passive video-rate terahertz human body imager with real-time calibration for security applications. Applied Physics B 126(8):143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-020-07496-3
Hassan T, Shafay M, Akçay S, Khan S, Bennamoun M, Damiani E, Werghi N (2020) Meta-transfer learning driven tensor-shot detector for the autonomous localization and recognition of concealed baggage threats. Sensors 20(22):6450. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226450
Katsuyama Y, Sato T, Qi X, Tamesue K, Wen Z, Yu K, Tokuda K, Sato T (2021) Deep learning based concealed object recognition in active millimeter wave imaging. In2021 IEEE Asia-Pacific microwave conference (APMC) 434–436 IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/APMC52720.2021.9662033
Katsuyama Y, Sato T, Qi X, Wen Z, Yu K, Tokuda K, Sato T (2020) Radiometric Passive Imaging for Robust Concealed Object Identification. In 2020 IEEE radar conference (RadarConf20) 1-6. IEEE https://doi.org/10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266642
Khan NS, Ogura K, Cosatto E, Ariyoshi M (2023) Real-time Concealed Weapon Detection on 3D Radar Images for Walk-through Screening System. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, pp 673–681. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00074
Kovbasa M, Golenkov A, Sizov F (2020) Neural network application to the postal terahertz scanner for automated detection of concealed items. In 2020 IEEE Ukrainian microwave week (UkrMW) 870-873. IEEE https://doi.org/10.1109/UkrMW49653.2020.9252706
Li H, Wu L (2021) Active millimeter wave holographic image processing for 3D concealed object detection. In 2021 International conference on microwave and millimeter wave technology (ICMMT) 1-3. IEEE https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMMT52847.2021.9618452
Li L, Xue F, Liang D, Chen X (2021) A hard example mining approach for concealed multi-object detection of active terahertz image. Appl Sci 11(23):11241. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311241
Liang D, Xue F, Li L (2021, May 8) Active terahertz imaging dataset for concealed object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.03677. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2105.03677
Liu Y, Xu F, Pu Z, Huang X, Chen J, Shao S (2022) AC-SDBSCAN: toward concealed object detection of passive terahertz images. IET Image Process 16(3):839–851. https://doi.org/10.1049/ipr2.12390
Ma G, Yue X (2022) An improved whale optimization algorithm based on multilevel threshold image segmentation using the Otsu method. Eng Appl Artif Intell 113:104960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2022.104960
Meng Z, Zhang M, Wang H (2020) CNN with pose segmentation for suspicious object detection in MMW security images. Sensors 20(17):4974. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174974
Morozov AA, Sushkova OS (2021) Development of a publicly available terahertz video dataset and a software platform for experimenting with the intelligent terahertz visual surveillance. InProceedings of international conference on Frontiers in computing and systems 105-113. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7834-2_10
Pang L, Liu H, Chen Y, Miao J (2020) Real-time concealed object detection from passive millimeter wave images based on the YOLOv3 algorithm. Sensors 20(6):1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061678
Ramandi VY (2021) Applying SGD optimization algorithm method for detecting and localizing of concealed objects in passive millimeter-wave images. Turkish J Comput Math Educ (TURCOMAT) 12(13):4526–4533
Ruiz-Santaquiteria J, Velasco-Mata A, Vallez N, Deniz O, Bueno G (2023) Improving handgun detection through a combination of visual features and body pose-based data. Pattern Recogn 136:109252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2022.109252
Shafay M, Hassan T, Damiani E, Werghi N (2021) Temporal Fusion Based Mutli-scale Semantic Segmentation for Detecting Concealed Baggage Threats. In 2021 IEEE international conference on systems man and cybernetics (SMC) 232-237. IEEE https://doi.org/10.1109/SMC52423.2021.9658932
Si T, Miranda PB, Bhattacharya D (2022) Novel enhanced Salp swarm algorithms using opposition-based learning schemes for global optimization problems. Expert Syst Appl 207:117961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117961
Solovyev R, Wang W, Gabruseva T (2021) Weighted boxes fusion: Ensembling boxes from different object detection models. Image Vis Comput 107:104117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2021.104117
Vargas VM, Gutiérrez PA, Rosati R, Romeo L, Frontoni E, Hervás-Martínez C (2023) Deep learning-based hierarchical classifier for weapon stock aesthetic quality control assessment. Comput Ind 144:103786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2022.103786
Wang C, Shi J, Zhou Z, Li L, Zhou Y, Yang X (2020a) Concealed object detection for millimeter-wave images with normalized accumulation map. IEEE Sensors J 21(5):6468–6475. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.3040354
Wang C, Yang K, Sun X (2020b) Precise localization of concealed objects in Millimetre-wave images via semantic segmentation. IEEE Access 8:121246–121256. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3007256
Wang X, Gou S, Li J, Zhao Y, Liu Z, Jiao C, Mao S (2021) Self-paced feature attention fusion network for concealed object detection in millimeter-wave image. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Vid Technol 32(1):224–239. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3058246
Wen Z, Yu K, Qi X, Sato T, Myint SH, Tamesue K, Katsuyama Y, Dobashi H, Murakami Y, Koyama I, Tokuda K (2022) AI-based W-band suspicious object detection system for moving persons: two-stage walkthrough configuration and recognition optimization. Wirel Commun Mob Comput https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3690403
Xu F, Huang X, Wu Q, Zhang X, Shang Z, Zhang Y (2021) YOLO-MSFG: toward real-time detection of concealed objects in passive terahertz images. IEEE Sensors J 22(1):520–534. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2021.3127686
Yang H, Zhang D, Qin S, Cui T, Miao J (2021) Real-Time Detection of Concealed Threats with Passive Millimeter Wave and Visible Images via Deep Neural Networks. Sensors 21(24):8456. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248456
Yang X, Guo H, Wang N, Song B, Gao X (2020a) A novel symmetry driven Siamese network for THz concealed object verification. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:5447–5456. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.2983554
Yang X, Wei Z, Wang N, Song B, Gao X (2020b) A novel deformable body partition model for MMW suspicious object detection and dynamic tracking. Signal Process 174:107627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107627
Yuan M, Zhang Q, Li Y, Yan Y, Zhu Y (2021) A suspicious multi-object detection and recognition method for millimeter wave SAR security inspection images based on multi-path extraction network. Remote Sens 13(24):4978. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13244978
Zhang B, Wang B, Wu X, Zhang L, Yang M, Sun X (2021a) Domain adaptive detection system for concealed objects using millimeter wave images. Neural Comput & Applic 33(18):11573–11588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-05847-5
Zhang L, Pang L, Miao J (2021b) Image fusion of PMMW and optical images for concealed object detection. J Phys Conf Ser 1738(1):012018. IOP publishing. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1738/1/012018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors agreed on the content of the study. JJ, KSD, SVM and SKS collected all the data for analysis. KSD agreed on the methodology. JJ, KSD, SVM and SKS completed the analysis based on agreed steps. Results and conclusions are discussed and written together. The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jayachitra, J., K, S.D., Manisekaran, S.V. et al. An optimal deep learning model for recognition of hidden hazardous weapons in terahertz and millimeter wave images. Earth Sci Inform 16, 2709–2726 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01056-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01056-x