Abstract
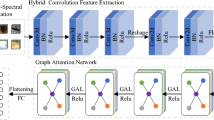
Graph convolutional networks (GCN) have attracted increasing attention in hyperspectral images (HSIs) classification because of its excellent capacities in modeling arbitrarily irregular data. The essential aim of GCN-based methods is obtaining a more reliable graph that accurately describes the similarity between graph nodes and makes its representation more discriminative. However, it is a challenging task to get a high-quality graph during the convolution process. In this paper, a novel spectral-spatial dynamic graph convolutional network (SSD-GCN) is proposed for HSIs classification, which not only can adaptively update graph according to the HSI content but also can generate the discriminative node features during the convolution process, by integrating the current spectral-spatial information of nodes and the graph embedding in the previous layers. Unlike the traditional GCN-based methods that directly convert the raw HSI into a graph in the preprocessing process, we further integrate the graph mapping into the network, to reduce the irrelevant information among spectral bands and facilitate node feature learning. In addition, an auxiliary local context-aware feature reconstruction is constructed to enhance the local representational capacities of the node features and alleviate over-smoothing. Extensive experiments compared with state-of-the-art methods on three HSIs datasets, including Pavia University, Salinas, and Kennedy Space Center, demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed SSD-GCN method, even with small-sized training data.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used and evaluated in this study are available in https://www.ehu.eus/ccwintco/index.php/Hyperspectral_Remote_Sensing_Scenes
References
Li S, Song W, Fang L, Chen Y, Ghamisi P, Benediktsson JA (2019) Deep learning for hyperspectral image classification: An overview. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57(9):6690–6709
Pu C, Huang H, Yang L (2021) An attention-driven convolutional neural network-based multi-level spectral-spatial feature learning for hyperspectral image classification. Expert Syst Appl 185:115663
Ding Y, Zhang Z, Zhao X et al (2022) Multi-feature fusion: Graph neural network and CNN combining for hyperspectral image classification. Neurocomputing 501:246–257
Bioucas-Dias JM, Plaza A, Dobigeon N, Parente M, Du Q, Gader P, Chanussot J (2012) Hyperspectral unmixing overview: Geometrical, statistical, and sparse regression-based approaches. IEEE J Sel Topic Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 5(2):354–379
Bhatti UA, Huang M, Neira-Molina H et al (2023) MFFCG-Multi feature fusion for hyperspectral image classification using graph attention network. Expert Syst Appl 229:120496
Peker M (2021) Classification of hyperspectral imagery using a fully complex-valued wavelet neural network with deep convolutional features. Expert Syst Appl 173:114708
Waske B, van der Linden S, Benediktsson JA, Rabe A, Hostert P (2010) Sensitivity of support vector machines to random feature selection in classification of hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 48(7):2880–2889
Li J, Bioucas-Dias JM, Plaza A (2010) Semisupervised hyperspectral image segmentation using multinomial logistic regression with active learning. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 48(11):4085–4098
Chen Y, Nasrabadi NM, Tran TD (2011) Hyperspectral image classification using dictionary-based sparse representation. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 49(10):3973–3985
Hang R, Liu Q, Song H, Sun Y (2015) Matrix-based discriminant subspace ensemble for hyperspectral image spatial-spectral feature fusion. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(2):783–794
Wang Y, Loe K-F, Tan T, Wu J-K (2005) A dynamic hidden markov random field model for foreground and shadow segmentation. In: 2005 Seventh IEEE Workshops on Applications of Computer Vision, IEEE, 2005, pp 474–480
Congalton RG (1991) A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens Environ 37(1):35–46
Yu L, Peng J, Chen N et al (2023) Two-branch deeper graph convolutional network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 61:1–14
Fauvel M, Benediktsson JA, Chanussot J, Sveinsson JR (2008) Spectral and spatial classification of hyperspectral data using svms and morphological profiles. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 46(11):3804–3814
Yang X, Ye Y, Li X, Lau RY, Zhang X, Huang X (2018) Hyperspectral image classification with deep learning models. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(9):5408–5423
Makantasis K, Karantzalos K, Doulamis A, Doulamis N (2015) Deep supervised learning for hyperspectral data classification through convolutional neural networks. In: 2015 IEEE International geoscience and remote sensing symposium (IGARSS), IEEE, 2015, pp 4959–4962
Yang J, Zhao Y-Q, Chan JC-W (2017) Learning and transferring deep joint spectral-spatial features for hyperspectral classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(8):4729–4742
Chen Y, Lin Z, Zhao X, Wang G, Gu Y (2014) Deep learning-based classification of hyperspectral data. IEEE J Sel Topic Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 7(6):2094–2107
Mou L, Ghamisi P, Zhu XX (2017) Deep recurrent neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(7):3639–3655
Hang R, Liu Q, Hong D, Ghamisi P (2019) Cascaded recurrent neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57(8):5384–5394
Zhou F, Hang R, Liu Q, Yuan X (2019) Hyperspectral image classification using spectral-spatial LSTMs. Neurocomputing 328:39–47
Zhou W, Kamata S, Wang H et al (2023) Multiscanning-based RNN-transformer for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 61:5512319
Gao H, Yang Y, Lei S, Li C, Zhou H, Qu X (2019) Multi-branch fusion network for hyperspectral image classification. Knowl-Based Syst 167:11–25
Hu W, Huang Y, Wei L, Zhang F (2015) Li H (2015) Deep convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. J Sens 258619(1–258619):12
Chen Y, Jiang H, Li C, Jia X, Ghamisi P (2016) Deep feature extraction and classification of hyperspectral images based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(10):6232–6251
Kipf TN, Welling M (2017) Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In: 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, OpenReview.net, 2017, pp 1–14
Qin A, Shang Z, Tian J, Wang Y, Zhang T, Tang YY (2018) Spectral-spatial graph convolutional networks for semisupervised hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 16(2):241–245
Sellars P, Aviles-Rivero AI, Schonlieb C-B (2020) Superpixel contracted graph-based learning for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 58(6):4180–4193
Xue Z, Liu Z, Zhang M (2023) DSR-GCN: Differentiated-scale restricted graph convolutional network for few-shot hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 61:1–18
Hong D, Gao L, Yao J, Zhang B, Plaza A, Chanussot J (2021) Graph convolutional networks for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 59(7):5966–5978
Wan S, Gong C, Zhong P, Du B, Zhang L, Yang J (2019) Multiscale dynamic graph convolutional network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 58(5):3162–3177
Wan S, Gong C, Zhong P, Pan S, Li G, Yang J (2020) Hyperspectral image classification with context-aware dynamic graph convolutional network. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 59(1):597–612
Alkhatib MQ, Al-Saad M, Aburaed N et al (2023) Tri-CNN: A three branch model for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sens 15(2):316
Zhang S, Xu M, Zhou J et al (2022) Unsupervised spatial-spectral cnn-based feature learning for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–17
Zhang S, Xu M, Zhou J et al (2022) Unsupervised spatial-spectral cnn-based feature learning for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–17
Moczulski M, Denil M, Appleyard J, de Freitas N (2016) ACDC: A structured efficient linear layer. In: 4th International conference on learning representations, 2016
Mironovova M, Bla J (2015) Fast fourier transform for feature extraction and neural network for classification of electrocardiogram signals. In: 2015 Fourth international conference on future generation communication technology (FGCT), IEEE, 2015, pp 1–6
Ell TA, Sangwine SJ (2006) Hypercomplex fourier transforms of color images. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(1):22–35
Frigo M, Johnson SG (2005) The design and implementation of fftw3. Proceedings of the IEEE 93(2):216–231
Hammond DK, Vandergheynst P, Gribonval R (2011) Wavelets on graphs via spectral graph theory. Appl Comput Harmon Anal 30(2):129–150
Cai Y, Zhang Z, Cai Z, Liu X, Jiang X, Yan Q (2020) Graph convolutional subspace clustering: A robust subspace clustering framework for hyperspectral image. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 59(5):4191–4202
Achanta R, Shaji A, Smith K, Lucchi A, Fua P (2012) Susstrunk S (2012) Slic superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell 34(11):2274–2282
Liu W, Gong M, Tang Z, Qin AK, Sheng K, Xu M (2021) Locality preserving dense graph convolutional networks with graph context-aware node representations. Neural Networks 143:108–120
Kipf TN, Welling M (2016) Variational graph auto-encoders. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1611.07308
Hamida AB, Benoit A, Lambert P, Amar CB (2018) 3-d deep learning approach for remote sensing image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(8):4420–4434
Gong Z, Tong L, Zhou J et al (2022) Superpixel spectral-spatial feature fusion graph convolution network for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–16
Funding
This work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62072216), the Jiangsu Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Fund (No. CX(19)3087).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Rong Chen: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Software, Investigation, Writing-Original Draft. Gua-nghui Li: Supervision, Writing-Reviewing and Editing. Chenglong Dai: Supervision, Writing-Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Consent for Publication
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, R., Li, G. & Dai, C. Spectral-spatial dynamic graph convolutional network for hyperspectral image classification. Earth Sci Inform 16, 3679–3695 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01116-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01116-2