Abstract
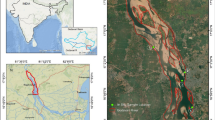
Snow cover information is essential for pursuing seasonal variation studies in Himalayan river basins. This study aims to investigate the seasonal variation of snow cover in the Sutlej river basin (Tibet to Bhakra dam in India) over three different seasons: Monsoon (June–September), winter (October-January), and summer (February-May) during the period 2010–2021. Landsat 7 and 8 Surface Reflectance (SR) data is used to develop 108 land use land cover (LULC) maps for 12 years, with three seasons per year and three machine-learning models. The study has conducted on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform, employing Random Forest (RF), Classification and Regression Trees (CART), and Support Vector Machine (SVM) models to classify the Landsat satellite data and assess the seasonal snow cover variation during the three seasons. The results show that among the three machine learning models, the RF model exhibits the highest average overall accuracy at 98.75%, followed by the CART model at 98.10%, and the SVM model with the lowest accuracy at 97.15%. In terms of snow cover area variability; there is a decline trend in summer snow cover and an increase in monsoon snow cover over the past three years (2019–2021). However, an increasing trend emerges when considering the decadal changes in all three seasons. In addition, the maximum percentages of snow cover area observed as 67.61%, 46.78%, and 30.58% in the summer period of 2013, the winter period of 2019, and the monsoon period of 2021, respectively. Similarly, the minimum percentage of snow cover is 23.22%, 11.36%, and 13.01%, observed in the summer period of 2014, the winter period of 2011, and the monsoon period of 2012, respectively. A comprehensive assessment procedure on temporal and seasonal snow cover variation in a large river basin have been presented in this work, which will help to plan and manage the sustainable water resources in study region.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Some or all data, models, or codes generated used during the study are available from the corresponding author request.
References
Acharya TD, Subedi A, Lee DH (2018) Evaluation of water indices for surface water extraction in a Landsat 8 scene of Nepal. Sensors 18(8):2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082580
Ahmad M, Alam K, Tariq S, Blaschke T (2019) Contrasting changes in snow cover and its sensitivity to aerosol optical properties in the Hindukush-Karakoram-Himalaya region. Sci Total Environ 699:134356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134356
Aman MA, Chu HJ (2023) Long-term river extent dynamics and transition detection using remote sensing: case studies of Mekong and Ganga River. Sci Total Environ 876:162774
Azizi AH, Akhtar F (2021) Analysis of spatiotemporal variation in the snow cover in the Western Hindukush-Himalaya region. Geocarto Int. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2021.1939442
Banerjee A, Chen R, Meadows ME, Sengupta D, Pathak S, Xia Z, Mal S (2021) Tracking 21st century climate dynamics of the Third Pole: an analysis of topo-climate impacts on snow cover in the central Himalaya using Google Earth Engine. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 103:102490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2021.102490
Bajracharya SR, Maharjan SB, Shrestha F, Guo W, Liu S, Immerzeel W et al (2015) The glaciers of the Hindu Kush Himalayas: Current status andobserved changes from the 1980s to 2010. Int J Water Resour Dev 31:161–173. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2015.1005731
Bhambri R, Hewitt, K, Haritashya UK, Chand P, Kumar A, Verma A et al (2022) Characteristics of surge-type tributary glaciers, Karakoram. Geomorphology 403:108161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2022.108161
Bhutiyani MR, Kale VS, Pawar NJ (2007). Long-term trends in maximum, minimum, and mean annual air temperatures across the Northwestern Himalayas during the twentieth century. Clim Chang. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9196-1, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.092
Bwangoy JB, Hansen MC, Roy DP, Grandi GD, Justice CO (2010) Wetland mapping in the Congo Basin using optical and radar remotely sensed data and derived topographical indices. Remote Sens Environ 114:73–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2009.08.004
Callaghan TV, Johansson M, Brown RD, Groisman PY, Labba N, Radionov V, Yang D (2011) The changing face of Arctic snow cover: A synthesis of observed and projected changes. Ambio 40:17–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-011-0212
Cohen J, Rind D (1991) The effect of snow cover on the climate. J Clim 4(7):689–706. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1991)
DeSousa C, Fatoyinbo L, Neigh C, Boucka F, Angoue V, Larsen T (2020) Cloud-computing and machine learning in support of country-level land cover and ecosystem extent mapping in Liberia and Gabon. PLoS ONE 15:e0227438. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0227438
Gurung DR, Kulkarni AV, Giriraj A, Aung KS, Shrestha B, Srinivasan J (2011) Changes in seasonal snow cover in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan region. The Cryosph Dis 5:755–777. https://doi.org/10.5194/tcd-5-755-2011
Hamid AT, Sharif M, Archer D (2014) Analysis of temperature trends in Sutluj River basin, India. J Earth Sci Clim Change 5(8). https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7617.1000222
Hartmann DL, Tank AMK, Rusticucci M, Alexander LV, Brönnimann S, Charabi YAR et al (2013) Climate change 2013 the physical science basis:Working group I contribution to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press. Observations: Atmosphere and surface
Hu Y, Maskey S, Uhlenbrook S (2011) Trends in temperature and rainfall extremes in the Yellow River source region, China. Clim Change https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-011-0056-2
Huang C, Davis LS, Townshend JRG (2002) An assessment of support vector machines for land cover classification. Int J Remote Sens 23:725–749. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160110040323
Immerzeel WW, van Beek LPH, Bierkens MFP (2010) Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 328:1382–1385. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1183188
Jain SK, Goswami A, Saraf AK (2009) Role of elevation and aspect in snow distribution in western Himalaya. Water Resour Manage 23:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9265-5
Keshtkar H, Voigt W, Alizadeh E (2017) Land-cover classification and analysis of Change using machine-learning classifiers and multitemporal remote sensing imagery. Arab J Geosci 10:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2899-y
Kour R, Patel N, Krishna AP (2016) Effects of terrain attributes on snow-cover dynamics in parts of Chenab basin, western Himalayas. Hydrol Sci 61(10):1861–1876. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2015.1052815
Krishnan R, Shrestha AB, Ren G, Rajbhandari R, Saeed S, Sanjay J et al (2019) Unravelling climate change in the Hindu Kush Himalaya: Rapid warmingin the mountains and increasing extremes. In: Wester P, Mishra A, Mukherji A, Shrestha AB (eds) The Hindu Kush Himalayaassessment: Mountains, climate change, sustainability and people. Springer International Publishing, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-92288-1_3
Kulkarni AV, Bahuguna IM, Rathore BP, Singh SK, Randhawa SS, Sood RK, Dhar S (2007) Glacial retreat in Himalaya using Indian remote sensing satellite data. Curr Sci 2007(92):69–74. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.694004
Lambert M-J, Traoré PCS, Blaes X, Baret P, Defourny P (2018) Estimating smallholder crops production at village level from Sentinel-2 time series in Mali’s cotton belt. Remote Sens Environ 216:647–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.06.036
Langhorst T, Pavelsky T (2023) Global observations of riverbank erosion and accretion from Landsat imagery. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 128(2):e2022JF006774
Li Y, Tao H, Su B, Kundzewicz ZW, Jiang T (2019) Impacts of 1.5 ◦C and 2◦C global warming on winter snow depth in Central Asia. Sci Total Environ 651:2866–2873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.126
Li X, Chen W, Cheng X, Wang L (2016) A comparison of machine learning algorithms for mapping complex surface-mined and agricultural landscapes using ZiYuan-3 stereo satellite imagery. Remote Sens 8:514. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060514
Lin Y, Cai T, Ju C, Cui X (2021) Applicability evaluation and improvement of different snow evaporation calculation methods in the Great Xing’an mountains. Earth Sci Inf 14(4):1809–1820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00597-3
Liu X, Chen B (2000) Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Int J Clim 20:1729–1742. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0088(20001130)
Liu C, Huang X, Li X, Liang T (2020) MODIS fractional snow cover mapping using machine learning technology in a mountainous area. Remote Sens 12(6):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12060962
Liu J, Li Y, Yu J, Yao Y (2022) Dynamic characteristics of snow frequency and its relationship with climate change on the Tibetan plateau from 2001 to 2015. Earth Sci Inf 15(2):1233–1247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00805-8
Mahdianpari M, Salehi B, Mohammadimanesh F, Motagh M (2017) Random forest wetland classification using ALOS-2 L-band, RADARSAT-2 C-band and TerraSAR-X imagery. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 130:13–31
McFeeters SK (1996) The use of the normalized differencewater index (NDWI) in the delineation of OpenWater features. Int J Remote Sens 17:1425–1432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.05.010
Midhuna TM, Kumar P, Dimri AP (2020) A new Western Disturbance Index for the Indian wintermonsoon. J Earth Syst Sci 129:59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1324-1
Millard K, Richardson M (2015) On the importance of training data sample selection in random forest image classification: a case study in peatland ecosystem mapping. Remote Sens 7:8489–8515. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70708489
Mir RA, Jain SK, Saraf AK (2015) Analysis of current trends in climatic parameters and its effect on discharge of Satluj River basin, western Himalaya. Nat Hazards 79:587–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1864-x
Moazzam MFU, Rahman G, Munawar S, Tariq A, Safdar Q, Lee B-G (2022) Trends of rainfall variability and drought monitoring using standardized precipitation index in a scarcely gauged basin of northern Pakistan. Water 14:1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071132
Nepal S, Khatiwada KR, Pradhananga S et al (2021) Future snow projections in a small basin of the western Himalayas. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148587
Nijhawan R, Raman B, Das J (2018) Meta-classifier approach with ANN, SVM, rotation forest, and random forest for snow cover mapping. In: Proceedings of 2nd international conference on computer vision & image processing: CVIP 2017, Volume 2. Springer, Singapore, pp 279–287
Notarnicola C (2020) Hotspots of snow cover changes in global mountain regions over 2000–2018. Remote Sens Environ 243:111781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.111781
Nüsser M, Schmidt S (2021) Glacier changes on the Nanga Parbat 1856–2020: a multi-source retrospective analysis. Sci Total Environ 785:147321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147321
Odry J, Boucher MA, Cantet P, Lachance-Cloutier S, Turcotte R, St-Louis PY (2020) Using artificial neural networks to estimate snow water equivalent from snow depth. Canadian Water Resources Journal/revue Canadienne Des Ressources Hydriques 45(3):252–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/07011784.2020.1796817
Olofsson P, Foody GM, Herold M, Stehman SV, Woodcock CE, Wulder MA (2014) Good practices for estimating area and assessing the accuracy of land change. Remote Sens Environ 148:42–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.02.015
Panda S, Anilkumar R, Balabantaray BK, Chutia D, Bharti R (2022) Machine Learning-Driven Snow Cover Mapping Techniques using Google Earth Engine. In: 2022 IEEE 19th India Council International Conference (INDICON). IEEE, pp 1–6
Qin J, Yang K, Liang S, Guo X (2009) The altitudinal dependence of recent rapid warming over the Tibetan Plateau. Clim Chang. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-009-9733-9
Raghubanshi S, Agrawal R, Rathore BP (2023) Enhanced snow cover mapping using object-based classification and normalized difference snow index (NDSI). Earth Sci Inform 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01077-6
Rasul A, Ningthoujam R (2021) Snow cover and vegetation greenness with leaf water content control the global land surface temperature. Environ Dev Sustain 23:14722–14748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01269-4
Rathore BP, Bahuguna IM, Singh SK, Brahmbhatt RM, Randhawa SS, Jani P, Rajawat AS (2018) Trends of snow cover in Western and West-Central Himalayas during 2004–2014. Curr Sci 800–807. https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v114/i04/800-807
Roy DP, Wulder MA, Loveland TR, Woodcock CE, Allen RG, Anderson MC, Helder D, Irons JR, Johnson DM, Kennedy R et al (2014) Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens Environ 145:154–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.02.001
Shafiq MU, Ahmed P, Islam ZU, Joshi PK, Bhat WA (2019) Snow cover area change and its relations with climatic variability in Kashmir Himalayas India. Geocarto Int 34:688–702. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1469675
Sharma V, Mishra VD, Joshi PK (2014) Topographic controls on spatiotemporal snow cover distribution in northwest Himalaya. Int J Remote Sens 35(9):3036–3056. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2014.894665
Shih HC, Stow DA, Tsai YH (2019) Guidance on and comparison of machine learning classifiers for Landsat-based land cover and land use mapping. Int J Remote Sens 40:1248–1274. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1524179
Shukla S, Kansal ML, Jain SK (2017) Snow cover area variability assessment in the upper part of the Satluj river basin in India. Geocarto Int 32(11):1285–1306. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2016.1206975
Singh DK, Gusain HS, Mishra V, Gupta N (2018) Snow cover variability in Northwest Himalayas during the last decade. Arab J Geosci 11:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3926-3
Singh P, Jain SK (2002) Snow and glacier melt in the Satluj river at Bhakra dam in the western Himalayan region. Hydrol Sci 47:93–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626660209492910
Singh SK, Rathore BP, Bahuguna IM (2014) Snow cover variability in the Himalayan-Tibetan region. Int J Climatol 34(2):446–452. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3697
Tahir AA, Adamowski JF, Chevallier P, Haq AU, Terzago S (2016) Comparative assessment of spatiotemporal snow cover changes and hydrological behavior of the Gilgit, Astore and Hunza River basins (Hindukush–Karakoram–Himalaya region, Pakistan). Meteorol Atmos Phys 128:793–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-016-0440-6
Tahir AA, Chevallier P, Arnaud Y, Ashraf M, Bhatti MT (2015) Snow cover trend and hydrological characteristics of the Astore River basin (Western Himalayas) and its comparison to the Hunza basin (Karakoram region). Sci Total Environ 505:748–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.10.065
Tamiminia H, Salehi B, Mahdianpari M, Quackenbush L, Adeli S, Brisco B (2020) Google Earth Engine for geo-big data applications: a meta-analysis and systematic review. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 164:152–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.04.001
Thanh Noi P, Kappas M (2017) Comparison of random forest, k-Nearest neighbor and support vector machine classifiers for land cover classification using Sentinel-2 imagery. Sensors 18:18. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010018
Vafakhah M, Nasiri Khiavi A, Janizadeh S, Ganjkhanlo H (2022) Evaluating different machine learning algorithms for snow water equivalent prediction. Earth Sci Inf 15(4):2431–2445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00846-z
Van Beijma S, Comber A, Lamb A (2014) Random forest classification of salt marsh vegetation habitats using quad-polarimetric airborne SAR, elevation and optical RS data. Remote Sens Environ 149:118–129
Wan B, Guo Q, Fang F, Su Y, Wang R (2015) Mapping US urban extents from MODIS data using one-class classification method. Remote Sens 7:10143–10163. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70810143
Wulder MA, White JC, Goward SN, Masek JG, Irons JR, Herold M, Cohen WB, Loveland TR, Woodcock CE (2008) Landsat continuity: Issues and opportunities for land cover monitoring. Remote Sens Environ 112:955–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2007.07.004
Yan D, Huang C, Ma N, Zhang Y (2020) Improved landsat-based water and snow indices for extracting lake and snow cover/glacier in the tibetan plateau. Water 12(5):1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051339
You Q, Wu T, Shen L, Pepin N, Zhang L, Jiang Z, Wu Z, Kang S, Agha Kouchak A (2020) Review of snow cover variation over the Tibetan Plateau and its influence on the broad climate system. Earth-Sci Rev 201:103043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.103043
Yi Y, Liu S, Zhu Y, Wu K, Xie F, Saifullah M (2021) Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of snow cover in the central and Western Karakoram Mountains based on a refined MODIS product during 2002–2018. Atmos Res 250:105402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105402
Zhu Z, Woodcock CE, Rogan J, Kellndorfer J (2012) Assessment of spectral, polarimetric, temporal and spatial dimensions for urban and peri-urban land cover classification using Landsat and SAR data. Remote Sens Environ 117:72–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.07.020
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Abhilash Gogineni: Conceptualization, Resources, Methodology, analysis, Data curation, code development, Writing an original draft. Madhusudana Rao Chintalacheruvu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing - review & editing, Validation, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gogineni, A., Chintalacheruvu, M.R. Assessing temporal snow cover variation in the Sutlej river basin using google earth engine and machine learning models. Earth Sci Inform 17, 455–473 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01161-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01161-x