Abstract
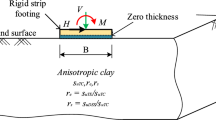
This study employs a two-dimensional plane strain finite element limit analysis method to evaluate the seismic bearing capacity of a planar caisson in anisotropic and non-homogeneous clay. The anisotropic behavior of the clay is simulated using the Anisotropic Undrained Shear (AUS) failure criterion in the finite element limit analysis (FELA). A rigid caisson has a depth (L) and a width (B). A comprehensive parametric analysis is executed to evaluate the non-dimensional seismic bearing capacity factor (Nce) in terms of the adhesion factor (α), anisotropic strength ratio (re), horizontal seismic coefficient (kh), depth to diameter ratio (L/D), and shear strength gradient ratio (ρB/suc0). The relationship between these parameters to the seismic bearing capacity factor is investigated, and the influence of these parameters on the potential failure mechanisms is discussed in detail. Moreover, an equation for predicting the seismic bearing capacity factor is developed through a machine learning regression approach called the Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model, which practitioners can extensively employ in the field. These correlation functions fit well with those obtained from FELA, with a value of R2 = 99.43%.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data associated with the study are present in the manuscript itself.
References
Andersen KH, Dyvik R, Schroder K, Hansteen OE, Bysveen S (1993) Field test of anchors in clay II: Predictions and interpretation. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 119:1532–1549. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1993)119:10(1532
Beygi M, Keshavarz A, Abbaspour M, Vali R, Saberian M, Li J (2022) Finite element limit analysis of the seismic bearing capacity of strip footing adjacent to excavation in c-ϕ soil. Geomech Geoengin 17:246–259. https://doi.org/10.1080/17486025.2020.1728396
Bhattacharya P, Kumar J (2013) Seismic pullout capacity of vertical anchors in sand. Geomech Geoengin 8:191–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/17486025.2012.714475
Bishop AW (1966) The strength of soils as engineering materials. Géotechnique 16:89–128. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1966.16.2.91
Bransby MF, Yun G (2009) The undrained capacity of skirted strip foundations under combined loading. Géotechnique 59:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2007.00098
Brinkgreve R, Vermeer PA (2019) PLAXIS 2D reference manual CONNECT edition V20. Delft University
Cauble DF (1996) Experimental measurements for a model suction caisson [Ph.D. thesis]. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, USA. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784479087.070
Chakraborty D, Kumar J (2014) Uplift resistance of long pipelines in the presence of seismic forces. J Pipeline Syst Eng Pract 5:06014003. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)ps.1949-1204.0000172
Chen W, Sarir P, Bui XN, Nguyen H, Tahir MM, Jahed Armaghani D (2020) Neuro-genetic, neuro-imperialism and genetic programing models in predicting ultimate bearing capacity of pile. Eng Comput 36:1101–1115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00752-x
Clukey EC, Morrison MJ (1993) A Centrifuge and analytical study to evaluate suction caissons for TLP applications in gulf of Mexico. Design and performance of deep foundations: Piles and piers in soil and soft rock, ASCE 141–156
Deng Y, Zhang Y, Luo X, Lytton RL (2022) Development of equivalent stationary dynamic loads for moving vehicular loads using artificial intelligence-based finite element model updating. Eng Comput 38:2955–2974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01306-w
Dyvik R, Andersen KH, Hansen SB, Christophersen HP (1993) Field test of anchors in clay I: Description. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 119:1515–1531. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9410(1993)119:10(1515)
Esmaeili M, Osanloo M, Rashidinejad F, Aghajani Bazzazi A, Taji M (2014) Multiple regression, ANN and ANFIS models for prediction of backbreak in the open pit blasting. Eng Comput 30:549–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-012-0298-2
Gao W, Raftari M, Rashid ASA, Mu’azu MA, Jusoh WAW (2020) A predictive model based on an optimized ANN combined with ICA for predicting the stability of slopes. Eng Comput 36:325–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00702-7
Garson GD (1991) Interpreting neural network connection weights. AI Expert 6:46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107481
Geer M (1996) Analysis of pile and suction caisson behavior in axial loading. [Ph.D. thesis]. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, USA
Gevrey M, Dimopoulos I, Lek S (2003) Review and comparison of methods to study the contribution of variables in artificial neural network models. Ecol Modell 160:249–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3800(02)00257-0
Ghaleini EN, Koopialipoor M, Momenzadeh M, Sarafraz ME, Mohamad ET, Gordan B (2019) A combination of artificial bee colony and neural network for approximating the safety factor of retaining walls. Eng Comput 35:647–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-018-0625-3
Gordan B, Jahed Armaghani D, Hajihassani M, Monjezi M (2016) Prediction of seismic slope stability through combination of particle swarm optimization and neural network. Eng Comput 32:85–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-015-0400-7
Gourvenec S (2008) Effect of embedment on the undrained capacity of shallow foundations under general loading. Géotechnique 58:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2008.58.3.177
Gourvenec S, Barnett S (2011) Undrained failure envelope for skirted foundations under general loading. Géotechnique 61:263–270. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.9.t.027
Harandizadeh H, Jahed Armaghani D, Khari M (2021) A new development of ANFIS–GMDH optimized by PSO to predict pile bearing capacity based on experimental datasets. Eng Comput 37:685–700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00849-3
Jaiswal S, Chauhan VB (2021) Assessment of seismic bearing capacity of a strip footing resting on reinforced earth bed using pseudo-static analysis Civ Environ Eng Rep 31: 117-137. https://doi.org/10.2478/ceer-2021-0023
Jaiswal S, Chauhan VB (2022) Influence of secondary reinforcement layers to enhance the stability of steep soil slope under earthquake loading. Arab J Geosci 15:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10366-1
Jearsiripongkul T, Keawsawasvong S, Thongchom C, Ngamkhanong C (2022a) Prediction of the stability of various tunnel shapes based on Hoek-Brown failure criterion using Artificial Neural Network (ANN). Sustainability 14:4533. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084533
Jearsiripongkul T, Lai VQ, Keawsawasvong S, Nguyen TS, Van CN, Thongchom C, Nuaklong P (2022b) Prediction of uplift capacity of cylindrical caissons in anisotropic and inhomogeneous clays using multivariate adaptive regression splines. Sustainability 14:4456. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084456
Jin Z, Yin ZY, Kotronis P, Ji YF (2019) Numerical investigation on evolving failure of caisson foundation in sand using the combined Lagrangian-SPH method. Mar Georesour Geotechnol 37:23–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119x.2018.1425311
Keawsawasvong S (2021) Bearing capacity of conical footings on clays considering combined effects of anisotropy and non-homogeneity. Ships and Offshore Structures 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/17445302.2021.1987110
Keawsawasvong S, Lawongkerd J (2021a) Influences of anisotropic undrained shear strengths of clays on pullout capacity of planar caissons. Sci Technol Asia 26:90–98
Keawsawasvong S, Ukritchon B (2016) Finite element limit analysis of uplift capacity of planar caissons in clay. Comput Geotech 75:12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.01.015
Keawsawasvong S, Ukritchon B (2022) Design equation for stability of a circular tunnel in an anisotropic and heterogeneous clay. Underground Space 7:76–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.undsp.2021.05.003
Keawsawasvong S, Yoonirundorn K, Senjuntichai T (2021) Uplift capacity factor for cylindrical suction caissons in anisotropic clays based on Anisotropic Uundrained Shear failure criterion. Transp Infrastruct Geotechnol 8:629–644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-021-00154-x
Keawsawasvong S, Lawongkerd J (2021b) Influences of anisotropic undrained shear strengths of clays on pullout capacity of planar caissons. Sci Technol Asia 26:90–98
Khajehzadeh M, Keawsawasvon S, Nehdi ML (2022) Effective hybrid soft computing approach for optimum design of shallow foundations. Sustainability 14:1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031847
Khandelwal M, Marto A, Fatemi SA, Ghoroqi M, Armaghani DJ, Singh TN, Tabrizi O (2018) Implementing an ANN model optimized by genetic algorithm for estimating cohesion of limestone samples. Eng Comput 34:307–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-017-0541-y
Koopialipoor M, Fahimifar A, Ghaleini EN, Momenzadeh M, Armaghani DJ (2020) Development of a new hybrid ANN for solving a geotechnical problem related to tunnel boring machine performance. Eng Comput 36:345–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00701-8
Krabbenhoft K, Lyamin A, Krabbenhoft J (2020) Optum computational engineering <www.Optumce.Com>.” www.optumce.com. Last accessed on 31 07 2023
Krabbenhoft K, Galindo-Torres SA, Zhang X, Krabbenhøft J (2019) AUS: Anisotropic undrained shear strength model for clays. Int J Numer Anal Meth Geomech 43:2652–2666. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2990
Krabbenhoft K, Lyamin AV (2015) Generalised Tresca criterion for undrained total stress analysis. Geotech Lett 5:313–317. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgele.15.00120
Kumar J, Rao VBKM (2002) Seismic bearing capacity factors for spread foundations. Geotechnique 52(2):79–88. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2002.52.2.79
Ladd CC (1991) Stability evaluations during stage construction. J Geotech Eng 117:540–615. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9410(1991)117:4(540)
Ladd CC, DeGroot DJ (2003) Recommended practice for soft ground site characterization. Arthur Casagrande Lecture. In: Proceedings of the 12th Panamerican Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Cambridge, MA USA. June 22 – 25, 2003
Lai VQ, Banyong B, Keawsawasvong S (2022a) Stability of limiting pressure behind soil gaps in contiguous pile walls in anisotropic clays. Eng Fail Anal 134:106049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106049
Lai VQ, Lai F, Yang D, Shiau J, Yodsomjai W, Keawsawasvong S (2022b) Determining seismic bearing capacity of footings embedded in cohesive soil slopes using multivariate adaptive regression splines. Int J Geosynth Ground Eng 8:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40891-022-00390-2
Lai VQ, Shiau J, Keawsawasvong S, Tran DT (2022c) Bearing capacity of ring foundations on anisotropic and heterogenous clays ~ FEA, NGI-ADP, and MARS. Geotech Geol Eng 40:3929–3941. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02117-6
Lai VQ, Nguyen DK, Banyong B, Keawsawasvong S (2022d) Limit analysis solutions for stability factor of unsupported conical slopes in clays with heterogeneity and anisotropy. Int J Comput Mater Sci Eng 11:2150030. https://doi.org/10.1142/s2047684121500305
Lai VQ, Jitchaijaroen W, Keawsawasvong S, Chavda JT, Sae-Long W, Limkatanyu S (2023a) Application of ANN and FELA for predicting bearing capacity of shell foundations on sand. Int J Geosynth Ground Eng 9(2):18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40891-023-00437-y
Lai VQ, Kounlavong K, Chavda JT, Jamsawang P, Keawsawasvong S (2023b) Stability analysis of buried pipelines under combined uplift and lateral forces using FELA and ANN. Appl Ocean Res 135:103568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2023.103568
Li AJ, Lyamin AV, Merifield RS (2009) Seismic rock slope stability charts based on limit analysis methods. Comput Geotech 36:135–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2008.01.004
Li AJ, Qian Z, Jiang JC, Lyamin A (2019) Seismic slope stability evaluation considering rock mass disturbance varying in the slope. KSCE J Civ Eng 23:1043–1054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-019-0963-8
Liu L, Moayedi H, Rashid ASA, Rahman SSA, Nguyen H (2020) Optimizing an ANN model with genetic algorithm (GA) predicting load-settlement behaviours of eco-friendly raft-pile foundation (ERP) system. Eng Comput 36:421–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00767-4
López I, Aragonés L, Villacampa Y, Compañ P (2018) Artificial neural network modeling of cross-shore profile on sand beaches: the coast of the province of Valencia (Spain). Mar Georesour Geotechnol 36:698–708. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119x.2017.1385666
Luo W, Zhao M, Xiao Y, Zhang R, Peng W (2019) Seismic bearing capacity of strip footings on cohesive soil slopes by using adaptive finite element limit analysis. Adv Civ Eng 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4548202
Mana DSK, Gourvenec S, Martin CM (2013) Critical skirt spacing for shallow foundations under general loading. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 139:1554–1566. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gt.1943-5606.0000882
Moayedi H, Moatamediyan A, Nguyen H, Bui XN, Bui DT, Rashid ASA (2020a) Prediction of ultimate bearing capacity through various novel evolutionary and neural network models. Eng Comput 36:671–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00723-2
Moayedi H, Mosallanezhad M, Rashid ASA, Jusoh WAW, Muazu MA (2020b) A systematic review and meta-analysis of artificial neural network application in geotechnical engineering: theory and applications. Neural Comput Appl 32:495–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04109-9
Momeni E, Armaghani DJ, Fatemi SA, Nazir R (2018) Prediction of bearing capacity of thin-walled foundation: a simulation approach. Eng Comput 34:319–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-017-0542-x
Nguyen DK, Nguyen TP, Keawsawasvong S, Lai VQ (2022) Vertical uplift capacity of circular anchors in clay by considering anisotropy and non-homogeneity. Transp Infrastruct Geotech 9:653–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-021-00191-6
Ozyildirim BM, Kiran M (2021) Levenberg–Marquardt multi-classification using hinge loss function. Neural Netw 143:564–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2021.07.010
Park YS, Lek S (2016) Artificial neural networks: multilayer perceptron for ecological modeling. Dev Environ Model 28:123–140
Petchkaew P, Keawsawasvong S, Tanapalungkorn W, Likitlersuang S (2021) 3D stability analysis of unsupported rectangular excavation under pseudo-static seismic body force. Geomech Geoeng 18(3):175–192. https://doi.org/10.1080/17486025.2021.2019321
Petchkaew P, Keawsawasvong S, Tanapalungkorn W, Likitlersuang S (2023) Seismic stability of unsupported vertical circular excavations in c-φ soil. Transp Infrastruct Geotech 10:165–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-021-00221-3
Randolph M, Gourvence S (2011) Offshore geotechnical engineering. Spon Press, Taylor & Francis, New York
Sahoo JP, Kumar J (2012) Seismic stability of a long unsupported circular tunnel. Comput Geotech 44:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2012.03.015
Sahoo JP, Kumar J (2014) Stability of a circular tunnel in presence of pseudostatic seismic body forces. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 42:264–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2014.03.003
Samadi M, Afshar MH, Jabbari E, Sarkardeh H (2021) Prediction of current-induced scour depth around pile groups using MARS CART and ANN approaches. Mar Georesour Geotechnol 39:577–588. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119x.2020.1731025
Sharma LK, Singh R, Umrao RK, Sharma KM, Singh TN (2017) Evaluating the modulus of elasticity of soil using soft computing system. Eng Comput 33:497–507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0486-6
Shiau J, Lai VQ, Keawsawasvong S (2022) Multivariate adaptive regression splines analysis for three-dimensional slope stability in anisotropic and heterogenous clay. J Rock Mech Geotechn Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.05.016
Sirimontree S, Keawsawasvong S, Ngamkhanong C, Seehavong S, Sangjinda K, Jearsiripongkul T, Nuaklong P (2022) Neural network-based prediction model for the stability of unlined elliptical tunnels in cohesive-frictional soils. Buildings 12:444
Sloan SW (2013) Geotechnical stability analysis. Géotechnique 63:531–572. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12040444
Srivastava A, Chauhan VB (2021) Parametric studies using finite element modeling for the evaluation of the performance of tiered MSE walls under seismic loading. Innov Infrastruct Solut 6:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-021-00537-6
Srivastava A, Chauhan VB (2020) Numerical studies on two-tiered MSE walls under seismic loading. SN Appl Sci 2:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03414-6
Ukritchon B, Keawsawasvong S (2016) Undrained uplift capacity of cylindrical suction caissons by finite element limit analysis. Comput Geotech 80:301–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.08.019
Ukritchon B, Wongtoythong P, Keawsawasvong S (2018) New design equation for undrained uplift capacity of suction caissons considering combined effects of caisson aspect ratio, adhesion factor at interface, and linearly increasing strength. Appl Ocean Res 75:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2018.03.007
Wang Z, Li A, Wang L, Zhou X, Wu B (2021) Aerodynamic coefficients modeling using Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm and network. Aircr Eng Aerosp Technol. https://doi.org/10.1108/aeat-03-2021-0073
Yodsomjai W, Keawsawasvong S, Senjuntichai T (2021) Undrained stability of unsupported conical slopes in anisotropic clays based on AUS failure criterion. Transp Infrastruct Geotechnol 8:557–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-021-00153-y
Yodsomjai W, Lai VQ, Banyong B, Chauhan VB, Thongchom C, Keawsawasvong S (2022) A machine learning regression approach for predicting basal heave stability of braced excavation in non-homogeneous clay. Arab J Geosci 15:873. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10161-y
Yun G, Bransby MF (2007) The undrained vertical bearing capacity of skirted foundations. Soils Found 47:493–505. https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf.47.493
Zhang Z, Pan Q, Yang Z, Yang X (2023) Physics-informed deep learning method for predicting tunnelling-induced ground deformations. Acta Geotech 18:4957–4972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-023-01874-9
Zhang N, Zhou A, Pan Y, Shen SL (2021) Measurement and prediction of tunnelling-induced ground settlement in karst region by using expanding deep learning method. Measurement 183:109700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109700
Zhang R, Xiao Y, Zhao M, Jiang J (2020) Seismic bearing capacity of strip footings placed near c-ϕ soil slopes. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 136:106221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2020.106221
Zhao Y, Noorbakhsh A, Koopialipoor M, Azizi A, Tahir MM (2020) A new methodology for optimization and prediction of rate of penetration during drilling operations. Eng Comput 36:587–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00715-2
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology (HCMUT), VNU-HCM for supporting this study.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Van Qui Lai: Data curation, Software, Methodology, Writing original draft, Project administration; Vinay Bhushan Chauhan: Data curation, Writing - review & editing , Project administration; Suraparb Keawsawasvong: Software, Validation, Writing - review and editing; Kongtawan Sangjinda: Validation, Writing - review and editing; Jitesh T. Chavda: Validation, Writing - review and editing; Lindung Zalbuin Mase: Validation, Writing - review and editing
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, V.Q., Chauhan, V.B., Keawsawasvong, S. et al. An extreme learning neural network approach for seismic bearing capacity estimation of planar caissons in nonhomogeneous clays. Earth Sci Inform 17, 251–270 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01175-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01175-5