Abstract
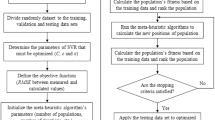
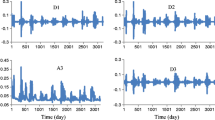
This study aimed to develop an ensemble machine learning (ML) model for multi-step ahead SSL modeling in the Katar catchment, Ethiopia. To do so, different ML models such as multilinear regression (MLR), Feed-forward Neural Network (FFNN), Support Vector Regression and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) were applied for one, two and three-step ahead SSL modeling. For this, two years of daily discharge and SSL data were used for model calibration and validation. Finally, four ensemble techniques: neuro-fuzzy ensemble (NFE), neural network ensemble (NE), weighted average ensemble (WE) and simple average ensemble (SE), were developed to improve the performance of single models. The performance of the developed models was evaluated using percent bias (PBIAS), mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE) and Nash Sutcliffe Efficiency Coefficient (NSE). The result shows that ANFIS outperformed the other individual models with a validation phase NSE value of 0.916,0.9 and 0.88 and RMSE value of 1630.5 ton/day, 1850.6 ton/day and 2026.6 ton/day, for one, two and three steps-ahead predictions, respectively. The NFE technique improved the individual model’s performance in the validation phase up to 42.17%, 49.84% and 60.66% for one, two and three-step ahead modeling. Generally, the use of ensemble techniques resulted in promising improvements in single and multi-step ahead SSL modeling.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abba SI, Linh NTT, Abdullahi J, Ali SIA, Pham QB, Abdulkadir RA, Costache R, Nam VT, Anh DT (2020) Hybrid machine learning ensemble techniques for modeling dissolved oxygen concentration. IEEE Access 8:157218–157237. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3017743
Adnan RM, Liang Z, Heddam S, Zounemat-Kermani M, Kisi O, Li B (2020) Least square support vector machine and multivariate adaptive regression splines for streamflow prediction in mountainous basin using hydro-meteorological data as inputs. J Hydrol 586(April 2019):124371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124371
Afan HA, El-Shafie A, Yaseen ZM, Hameed MM, Mohtar WHMW, Hussain A (2014) ANN based sediment prediction model utilizing different input scenarios. Water Resour Manage 29(4):1231–1245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0870-1
Aga AO, Melesse AM, Chane B (2018) Estimating the sediment flux and budget for a data limited Rift Valley Lake in Ethiopia. Hydrology 6(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology6010001
Aga AO, Melesse AM, Chane B (2020) An alternative empirical model to estimate watershed sediment yield based on hydrology and geomorphology of the basin in data-scarce rift VALLEY lake regions, Ethiopia. Geosciences (Switzerland) 10(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10010031
Aliye MA, Aga AO, Tadesse T, Yohannes P (2020) Evaluating the performance of HEC-HMS and SWAT hydrological models in simulating the rainfall-runoff process for data scarce region of Ethiopian Rift Valley Lake Basin. Open J Modern Hydrol 10(04):105–122. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojmh.2020.104007
Alizadeh MJ, Nodoushan EJ, Kalarestaghi N, Chau KW (2017) Toward multi-day-ahead forecasting of suspended sediment concentration using ensemble models. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(36):28017–28025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0405-4
Ampomah R, Hosseiny H, Zhang L, Smith V, Sample-Lord K (2020) A regression-based prediction model of suspended sediment yield in the Cuyahoga river in Ohio using historical satellite images and precipitation data. Water (Switzerland) 12(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030881
Bao Y, Xiong T, Hu Z (2014) Neurocomputing Multi-step-ahead time series prediction using multiple-output support vector regression. Neurocomputing 129:482–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2013.09.010
Bates JM, Granger CWJ (1969) The combination of forecasts. J Oper Res Soc 20:451–468
Buyukyildiz M, Kumcu SY (2017) An Estimation of the suspended sediment load using adaptive network based fuzzy inference system, support vector machine and artificial neural network models. Water Resour Manage 31(4):1343–1359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1581-1
Çaydaş U, Hasçalik A, Ekici S (2009) An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) model for wire-EDM. Expert Syst Appl 36(3 PART 2):6135–6139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.07.019
Choubin B, Darabi H, Rahmati O, Sajedi-Hosseini F, Kløve B (2018) River suspended sediment modelling using the CART model: a comparative study of machine learning techniques. Sci Total Environ 615:272–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.293
Cobaner M, Unal B, Kisi O (2009) Suspended sediment concentration estimation by an adaptive neuro-fuzzy and neural network approaches using hydro-meteorological data. J Hydrol 367(1–2):52–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.12.024
Dawson CW, Abrahart RJ, See LM (2007) HydroTest: a web-based toolbox of evaluation metrics for the standardised assessment of hydrological forecasts. Environ Model Softw 22(7):1034–1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2006.06.008
Dehghani R, Torabi Poudeh H, Younesi H, Shahinejad B (2020) Daily streamflow prediction using support vector machine-artificial flora (SVM-AF) hybrid model. Acta Geophys 68(6):1763–1778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-020-00472-7
Desta H, Fetene A (2020) Land-use and land-cover change in Lake Ziway watershed of the Ethiopian Central Rift Valley Region and its environmental impacts. Land Use Policy 96:104682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104682
Ebrahimi H, Rajaee T (2017) Simulation of groundwater level variations using wavelet combined with neural network, linear regression and support vector machine. Glob Planet Change 148:181–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2016.11.014
Elkiran G, Nourani V, Abba S (2019) Multi-step ahead modelling of river water quality parameters using ensemble artificial intelligence-based approach. J Hydrol 577(June):123962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.123962
Gelete G, Nourani V, Gokcekus H, Gichamo T (2023) Ensemble physically based semi-distributed models for the rainfall-runoff process modeling in the data-scarce Katar catchment Ethiopia. J Hydroinformatics 25(2):567. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2023.197
Ghaffari A, Abdollahi H, Khoshayand MR, Bozchalooi IS, Dadgar A, Rafiee-Tehrani M (2006) Performance comparison of neural network training algorithms in modeling of bimodal drug delivery. Int J Pharm 327(1–2):126–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.07.056
Gong Y, Zhang Y, Lan S, Wang H (2016) A comparative study of artificial neural networks, support vector machines and adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system for forecasting groundwater levels near Lake Okeechobee Florida. Water Resour Manag 30(1):375–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1167-8
Goyal MK (2014) Modeling of sediment yield prediction using M5 model tree algorithm and wavelet regression. Water Resour Manage 28(7):1991–2003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0590-6
Guo J, Zhou J, Qin H, Zou Q, Li Q (2011) Monthly streamflow forecasting based on improved support vector machine model. Expert Syst Appl 38(10):13073–13081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.04.114
Hadi SJ, Abba SI, Sammen SSH, Salih SQ, Al-Ansari N, Yaseen MZ (2019) Non-linear input variable selection approach integrated with non-tuned data intelligence model for streamflow pattern simulation. IEEE Access 7:141533–141548. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2943515
Haghiabi AH, Azamathulla HM, Parsaie A (2017) Prediction of head loss on cascade weir using ANN and SVM. ISH J Hydraul Eng 23(1):102–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/09715010.2016.1241724
Harmel RD, Smith PK, Migliaccio KW, Chaubey I, Douglas-Mankin KR, Benham B, Shukla S, Muñoz-Carpena R, Robson BJ (2014) Evaluating, interpreting, and communicating performance of hydrologic/water quality models considering intended use: a review and recommendations. Environ Model Softw 57:40–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.02.013
Himanshu SK, Pandey A, Yadav B (2017a) Ensemble wavelet-support vector machine approach for prediction of suspended sediment load using hydrometeorological data. J Hydrol Eng 22(7):05017006
Himanshu SK, Pandey A, Yadav B (2017b) Assessing the applicability of TMPA-3B42V7 precipitation dataset in wavelet-support vector machine approach for suspended sediment load prediction. J Hydrol 550:103–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.04.051
Jahani B, Mohammadi B (2019) A comparison between the application of empirical and ANN methods for estimation of daily global solar radiation in Iran. Theoret Appl Climatol 137(1–2):1257–1269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2666-3
Jang JSR (1993) ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 23(3):665–685. https://doi.org/10.1109/21.256541
Jha SK, Bombardelli FA (2011) Theoretical/numerical model for the transport of non-uniform suspended sediment in open channels. Adv Water Resour 34(5):577–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2011.02.001
Jimeno-Sáez P, Senent-Aparicio J, Pérez-Sánchez J, Pulido-Velazquez D (2018) A comparison of SWAT and ANN models for daily runoff simulation in different climatic zones of peninsular Spain. Water (Switzerland) 10(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020192
Jimeno-Sáez P, Martínez-España R, Casalí J, Pérez-Sánchez J, Senent-Aparicio J (2021) A comparison of performance of SWAT and machine learning models for predicting sediment load in a forested Basin, Northern Spain. Catena xxxx. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105953
Kalteh AM (2013) Monthly river flow forecasting using artificial neural network and support vector regression models coupled with wavelet transform. Comput Geosci 54:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2012.11.015
Keskin ME, Taylan D, Terzi Ö (2010) Adaptive neural-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) approach for modelling hydrological time series Adaptive neural-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) approach for modelling hydrological time series. Hydrol Sci J 6667:2150–3435. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.51.4.588
Kiran RN, Ravi V (2008) Software reliability prediction by soft computing techniques. J Syst Softw 81(4):576–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2007.05.005
Kisi O, Dailr AH, Cimen M, Shiri J (2012) Suspended sediment modeling using genetic programming and soft computing techniques. J Hydrol 450–451:48–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.05.031
Kisi O, Shiri J, Tombul M (2013) Modeling rainfall-runoff process using soft computing techniques. Comput Geosci 51:108–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2012.07.001
Kouziokas GN, Chatzigeorgiou A, Perakis K (2018) Multilayer feed forward models in groundwater level forecasting using meteorological data in public management. Water Resour Manage 32(15):5041–5052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2126-y
Kumar P, Nigam SP, Kumar N (2014) Vehicular traffic noise modeling using artificial neural network approach. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 40:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2014.01.006
Kumar A, Kumar P, Singh VK (2019) Evaluating different machine learning models for runoff and suspended sediment simulation. Water Resour Manage 33(3):1217–1231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2178-z
Lafdani EK, Nia AM, Ahmadi A (2013) Daily suspended sediment load prediction using artificial neural networks and support vector machines. J Hydrol 478:50–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.048
Liu Z, Zhou P, Chen G, Guo L (2014) Evaluating a coupled discrete wavelet transform and support vector regression for daily and monthly streamflow forecasting. J Hydrol 519(PD):2822–2831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.06.050
Mamdani EH, Assilian S (1975) An experiment in linguistic synthesis with a fuzzy logic controller. Int J Man Mach Stud 7(11):1–13
Melesse AM, Ahmad S, McClain ME, Wang X, Lim YH (2011) Suspended sediment load prediction of river systems: an artificial neural network approach. Agric Water Manag 98(5):855–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2010.12.012
Meshram SG, Singh VP, Kisi O, Karimi V, Meshram C (2020) Application of artificial neural networks, support vector machine and multiple Model-ANN to sediment yield prediction. Water Resour Manage 34(15):4561–4575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02672-8
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, Van Liew MW, Bingner RL, Harmel RD, Veith TL (2007) Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans ASABE 50(3):885–900. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.23153
Moriasi DN, Gitau MW, Pai N, Daggupati P (2015) Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans ASABE 58(6):1763–1785. https://doi.org/10.13031/trans.58.10715
Nourani V, Rezapour KT, Baghanam H (2014) Case studies in intelligent computing. In: Issac N, Israr B (eds) Case studies in intelligent computing. Taylor and Francis Group, New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1201/b17333
Nourani V, Andalib G (2015) Daily and monthly suspended sediment load predictions using wavelet base artificial intelligence approaches. J Mt Sci 12(1):85–100
Nourani V, Partoviyan A (2018) Hybrid denoising-jittering data pre-processing approach to enhance multi-step-ahead rainfall–runoff modeling. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 32(2):545–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-017-1400-5
Nourani V, Elkiran G, Abba SI (2018) Wastewater treatment plant performance analysis using artificial intelligence – an ensemble approach. Water Sci Technol 78(10):2064–2076. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.477
Nourani V, Molajou A, Tajbakhsh AD, Najafi H (2019a) A wavelet based data mining technique for suspended sediment load modeling. Water Resour Manage 33(5):1769–1784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02216-9
Nourani V, Elkiran G, Abdullahi J (2019b) Multi-station artificial intelligence based ensemble modeling of reference evapotranspiration using pan evaporation measurements. J Hydrol 577(June):123958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.123958
Nourani V, Elkiran G, Abdullahi J (2020a) Multi-step ahead modeling of reference evapotranspiration using a multi-model approach. J Hydrol 581(October 2019):124434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124434
Nourani V, Gökçekuş H, Umar IK (2020b) Artificial intelligence based ensemble model for prediction of vehicular traffic noise. Environ Res 180(October 2019):108852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108852
Nourani V, Gokcekus H, Gelete G (2021a) Estimation of suspended sediment load using artificial intelligence-based ensemble model. Complexity 2021(Article ID 6633760):19. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6633760
Nourani V, Gökçekuş H, Gichamo T (2021b) Ensemble data-driven rainfall-runoff modeling using multi-source satellite and gauge rainfall data input fusion. Earth Sci Inf 14(4):1787–1808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00615-4
Okkan U, Serbes ZA (2012) Rainfall-runoff modeling using least squares support vector machines. Environmetrics 23(6):549–564. https://doi.org/10.1002/env.2154
Rai AA, Pai PS, Rao BRS (2015) Prediction models for performance and emissions of a dual fuel CI engine using ANFIS. Sadhana Acad Proc Eng Sci 40(2):515–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-014-0320-z
Rajaee T, Nourani V, Zounemat-Kermani M, Kisi O (2011) River suspended sediment load prediction: application of ANN and wavelet conjunction model. J Hydrol Eng 17(5):604–614. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE
Rumelhart DE, Hinton GE, Williams RJ (1986) Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 323(6088):533–536. https://doi.org/10.1038/323533a0
Salih SQ, Sharafati A, Khosravi K, Faris H, Kisi O, Tao H, Ali M, Yaseen ZM (2020) River suspended sediment load prediction based on river discharge information: application of newly developed data mining models. Hydrol Sci J 65(4):624–637. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2019.1703186
Shamseldin AY, O’Connor KM, Liang GC (1997) Methods for combining the outputs of different rainfall-runoff models. J Hydrol 197(1–4):203–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(96)03259-3
Sharafati A, Haji Seyed Asadollah SB, Motta D,Yaseen ZM (2020) Application of newly developed ensemble machine learning models for daily suspended sediment load prediction and related uncertainty analysis. Hydrol Sci J 65(12):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2020.1786571
Sharghi E, Nourani V, Behfar N (2018) Earthfill dam seepage analysis using ensemble artificial intelligence based modeling. J Hydroinf 20(5):1071–1084. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2018.151
Sirabahenda Z, St-Hilaire A, Courtenay SC, van den Heuvel MR (2020) Assessment of the effective width of riparian buffer strips to reduce suspended sediment in an agricultural landscape using ANFIS and SWAT models. Catena 195(October 2019):104762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104762
Tabari H, Kisi O, Ezani A, Talaee PH (2012a) SVM, ANFIS, regression and climate based models for reference evapotranspiration modeling using limited climatic data in a semi-arid highland environment. J Hydrol 444–445:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.04.007
Tabari H, Kisi O, Ezani A, Hosseinzadeh Talaee P (2012b) SVM, ANFIS, regression and climate based models for reference evapotranspiration modeling using limited climatic data in a semi-arid highland environment. J Hydrol 444–445:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.04.007
Takagi T, Sugeno M (1985) Fuzzy Identification of Systems and Its Applications to Modeling and Control. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern SMC-15(1):116–132. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1985.6313399
Taylor KE (2001) Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J Geophys Res 106(D7):7183–7192. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JD900719
Tibangayuka N, Mulungu DMM, Izdori F (2022) Evaluating the performance of HBV, HEC-HMS and ANN models in simulating streamflow for a data scarce high-humid tropical catchment in Tanzania. Hydrol Sci J 67(14):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2022.2137417
Tsukamoto Y (1993) An approach to fuzzy reasoning method. In: Readings in Fuzzy Sets for Intelligent Systems, pp 523–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4832-1450-4.50055-9
Umar IK, Nourani V, Gökçekuş H (2021) A novel multi-model data-driven ensemble approach for the prediction of particulate matter concentration. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(36):49663–49677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14133-9
Wang WC, Chau KW, Cheng CT, Qiu L (2009) A comparison of performance of several artificial intelligence methods for forecasting monthly discharge time series. J Hydrol 374(3–4):294–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.06.019
Wang W, Xu D, Chau K, Chen SC (2013) Improved annual rainfall-runoff forecasting using PSO-SVM model based on EEMD. J Hydroinf 15(4):1377–1390. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2013.134
Yaseen ZM, Deo RC, Hilal A, Abd AM, Bueno LC, Salcedo-Sanz S, Nehdi ML (2018) Predicting compressive strength of lightweight foamed concrete using extreme learning machine model. Adv Eng Softw 115(April 2017):112–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2017.09.004
Yaseen ZM, Ebtehaj I, Kim S, Sanikhani H, Asadi H, Ghareb MI, Bonakdari H, Wan Mohtar WHM, Al-Ansari N, Shahid S (2019) Novel hybrid data-intelligence model for forecasting monthly rainfall with uncertainty analysis. Water (Switzerland) 11(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030502
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gebre Gelete: Conceptualization, modeling, Methodology, formal analysis, data processing, writing. Vahid Nourani: Supervision, review & editing. Huseyin Gokcekus and Tagesse Gichamo: editing:
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gelete, G., Nourani, V., Gökçekuş, H. et al. Multi-step ahead suspended sediment load modeling using machine learning– multi-model approach. Earth Sci Inform 17, 633–654 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01192-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01192-4