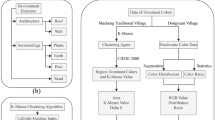
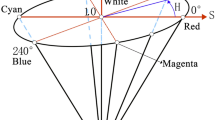
Abstract
The landscape color of an urban park is the carrier of urban culture and the embodiment of urban style since it is an advanced form resulting from urban growth. It is expected to offer some theoretical references for the color design of urban parks to quantify the color features of urban parks in various seasons and the variations in people’s perceptions of parks. This study used People’s Park and Huanhuanxi Park in Chengdu as research objects. It used the K-means clustering algorithm to quantify the seasonal characteristics of spatial color changes of different landscape types, and it used the SD. method to examine how people perceived the landscape color in the two parks during various seasons. The findings indicate that N (no color) and G (green) are People’s Park’s and Huanhuaxi Park’s base colors. Architectural landscapes’ use of color exhibits a trend toward medium saturation and medium-high brightness. Low saturation and low brightness are characteristics of the color of the pavement landscape. The landscape color in the sketch demonstrates the traits of wide hue dispersion, consistent saturation distribution, and brightness distribution. Seasonal change considerably impacts plant color, according to the color analysis of the natural landscape. According to the SD. evaluation results, spring had the most excellent crowd perception score, followed by summer and winter. Autumn had the highest crowd perception score. The landscape color recommendation chromatography of two urban parks is then put forth in conjunction with quantitative data and population perception evaluation, offering some reference guidelines for creating urban parks.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Chang CR, Li MH (2014) Effects of urban parks on the local urban thermal environment. Urban For Urban Green 13(4):672–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2014.08.001
Chang Chien Y-M, Carver S, Comber A (2021) An exploratory analysis of expert and nonexpert-based land-scape aesthetics evaluations: a case study from Wales. Land 10:192. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10020192
Chen TW, Chen YL, Chien SY (2008) Fast image segmentation based on K-Means clustering with histograms in HSV color space. 2008 IEEE 10th Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, IEEE, pp 322–325. https://doi.org/10.1109/MMSP.2008.4665097
Cheng Y, Tan M (2018) The quantitative research of landscape color: a study of Ming Dynasty City Wall in Nanjing. Color Res Appl 43(3):436–448. https://doi.org/10.1002/col.22203
Eroğlu E, Müderrisoğlu H, Kesim GA (2012) The effect of seasonal change of plants compositions on visual perception. J Environ Eng Landsc Manage 20(3):196–205. https://doi.org/10.3846/16486897.2011.646007
Frackiewicz M, Mandrella A, Palus H (2019) Fast color quantization by K-means clustering combined with image sampling. Symmetry 11(8):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11080963
Güneş E, Olguntürk N (2020) Color-emotion associations in interiors. Color Res Appl 45(1):129–141. https://doi.org/10.1002/col.22443
Han X, Sun T, Cao T (2021) Study on landscape quality assessment of urban forest parks: take Nanjing Zijinshan National forest park as an example. Ecol Ind 120:106902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106902
Han W, Zhang C, Wang C, Yin L (2023) Constructing a forest color palette and the effects of the color patch index on human eye recognition accuracy. Forests 14(3):627. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030627
Hsiao H (2021) Evaluation of park management based on installation-management permission in TEN-SHIBA, Tennoji Park, Osaka City: focus on park users and financial effects. Landscape Ecol Eng 17(2):119–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11355-020-00441-8
Huang ASH, Lin YJ (2020) The effect of landscape colour, complexity and preference on viewing behaviour. Landsc Res 45(2):214–227. https://doi.org/10.1080/01426397.2019.1593336
Jahani A, Saffariha M (2020) Aesthetic preference and mental restoration prediction in urban parks: an application of environmental modeling approach. Urban For Urban Green 54:126775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2020.126775
Jain AK (2010) Data clustering: 50 years beyond K-means. Pattern Recognit Lett 31(8):651–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2009.09.011
Jeon JY, Hong JY (2015) Classification of urban park soundscapes through perceptions of the acoustical environments. Landsc Urban Plann 141:100–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2015.05.005
Jianhua C (2022) Evaluation of urban park landscape quality from a territorial perspective: a case study of Huanhuaxi Park in Chengdu. J Cent South Univ Forestry Technol 42(6):152–159. https://doi.org/10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2022.06.017. (in Chinese)
Jingjing Z, Guang H, Mufeng L (2022) Applications of plant color configurations in urban parks based on the LIM analysis—a case of Quyuanfenghe Park of West Lake in Hangzhou. J Nanjing Forestry Univ (Natural Sci Edition) 46(4):230–238. https://doi.org/10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202101010. (in Chinese)
Kaili Z, Xiaohong T, Yutong Z, Bowen H, Lijuan H, Minyi L, Erdan L, Yuxin L, Tian J, Lingqing Z, Yuhan W, Jiangjun W (2022) Differing perceptions of the youth and the elderly regarding cultural ecosystem services in urban parks: An exploration of the tour experience. Sci Total Enviro 821:153388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153388
Kong L, Liu Z, Pan X, Wang Y, Guo X, Wu J (2022) How do different types and landscape attributes of urban parks affect visitors’ positive emotions? Landsc Urban Plann 226:104482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2022.104482
Li Z, Yong X (2021) Chengdu Yearbook. Chengdu Yearbook Association, pp 3–4. https://cdstats.chengdu.gov.cn/cdstjj/c155008/2023-02/20/content_bf74875536b74398b98067db58a97f58.shtml. Accessed 2022-10-1
Li Z, Han X, Wang L (2020a) Feature extraction and image Retrieval of Landscape images based on image Processing. Traitement Du Signal 37(6):1009–1018. https://doi.org/10.18280/ts.370613
Li C, Shen S, Ding L (2020b) Evaluation of the winter landscape of the plant community of urban park green spaces based on the scenic beauty esitimation method in Yangzhou, China. PLoS ONE 15(10):e0239849. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0239849
Liu WY, Tsao C, Lin CC (2023) Tourists’ preference for colors of forest landscapes and its implications for forest landscape planning policies. For Policy Econ 147:102887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forpol.2022.102887
Luo Y, He J, Long Y, Xu L, Zhang L, Tang Z, Li C, Xiong X (2023) The relationship between the Color Landscape Characteristics of Autumn Plant Communities and Public Aesthetics in Urban Parks in Changsha, China. Sustainability 15(4):3119. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043119
Ma B, Hauer RJ, Xu C (2020) Effects of design proportion and distribution of Color in Urban and Suburban Green Space Planning to Visual aesthetics Quality. Forests 11(3):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11030278
Mu Y, Lin W, Diao X, Zhang Z, Wang J, Lu Z, Guo W, Wang Y, Hu C, Zhao C (2022) Implementation of the visual aesthetic quality of slope forest autumn color change into the configuration of tree species. Sci Rep 12:1034. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-04317-1
Rapuano M, Ruotolo F, Ruggiero G (2022) Spaces for relaxing, spaces for recharging: how parks affect people’s emotions. J Environ Psychol 81:101809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2022.101809
Schloss KB, Nelson R, Parker L, Heck IA, Palmer SE (2017) Seasonal variations in color preference. Cogn Sci 41(6):1589–1612. https://doi.org/10.1111/cogs.12429
Shao J, Qiu Q, Qian Y, Tang L (2020) Optimal visual perception in land-use planning and design based on landsenses ecology. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 27:233–239. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2020.1727990
Shen S, Yao Y, Li C (2022) Quantitative study on landscape colors of plant communities in urban parks based on natural color system and M-S theory in Nanjing, China. Color Res Appl 47(1):152–163. https://doi.org/10.1002/col.22713
Sodjinou SG, Mohammadi V, Mahama ATS (2022) A deep semantic segmentation-based algorithm to segment crops and weeds in agronomic color images. Inform Process Agric 9(3):355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2021.08.003
Stoklasa J, Talášek T, Stoklasová J (2019) Semantic differential for the twenty-first century: scale relevance and uncertainty entering the semantic space. Qual Quant 53:435–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-018-0762-1
Tan C, Yang S (2021) Automatic extraction of Color features from Landscape images based on image Processing. Trait Du Signal 38(3):747–755. https://doi.org/10.18280/ts.380322
Thompson S, Celebi ME, Buck KH (2020) Fast color quantization using MacQueen’s k-means algorithm. J Real-Time Image Proc 17:1609–1624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-019-00914-6
Wang D (2021) Seasonal color matching method of ornamental plants in urban landscape construction. Open Geosci 13(1):594–605. https://doi.org/10.1515/geo-2020-0261
Wang Y, Qu H, Bai T, Chen Q, Li X, Luo Z, Lv B, Jiang M (2021) Effects of variations in Color and Organ of Color Expression in Urban Ornamental Bamboo Landscapes on the physiological and psychological responses of College Students. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(3):1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031151
Wang Z, Sun H, Li J (2023) Research on architectural color and visual comfort in historic landscape areas. Buildings 13(4):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13041004
Witzel C (2019) Misconceptions about colour categories. Rev Philos Psychol 10(3):499–540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13164-018-0404-5
Wu L, Luo S, Li D, Chen Q, Li J, Wen J (2023) Effects of deciduous forests on adolescent Emotional Health in Urban areas: an Example from the autumn Ginkgo Forest in Chengdu. Forests 14(6):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14061099
Xiaan W, Leiqing X, Liang Z (2020) Key indicators of 15-minute life Circle in the Standard for Urban Residential Area Planning and Design. Planners 36(8):33–40. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2020.08.005. (in Chinese)
Xingcheng S, Ting Z, Junjun F et al (2020) Evaluation of spring leaf color of Japanese red maple. J Nanjing Forestry Univ (Natural Sci Edition) 44(06):213–220. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.201703113
Xudie C, Hongyu L, Zhang X, Ruiming Y, Chao D, Fan Z (2019) The Integration of Urban Context and Park Landscape Design—A Case Study of Chengdu Park. Urban Archit 16(4):143–146. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-0232.2019.04.031
Yang M (2020) Investigating seasonal color change in the environment by color analysis and information visualization. Color Res Appl 45(3):503–511. https://doi.org/10.1002/col.22484
Yang T, Wang XR (2021) Evaluation of the plant landscape suitability in mountain parks based on principal component analysis: a case study of Guiyang City. Agron J 113(2):760–773. https://doi.org/10.1002/agj2.20463
Yang J, Wang X, Zhao Y (2022) Leaf color attributes of urban colored-leaf plants. Open Geosci 14(1):1591–1605. https://doi.org/10.1515/geo-2022-0433
Yangting J, Yanni L, Wei C, Chenyang L, Yanyun L (2016) Evaluation on waterfront plantscape of Urban Park in Chengdu. J Northwest Forestry Univ 31(3):291–297. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2016.03.51. (in Chinese)
Yu H, Chenghui Y, Dexue Q et al (2022) Quantitative study on Autumn Color of the plants in Urban Park—A Case Study of Suzhou Industrial Zone. J Norehwest Forestry Univ 37(4):266–272. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2022.04.36. (in Chinese)
Zhang Z, Qie G, Wang C, Jiang S, Li X, Li M (2017) Relationship between forest color characteristics and scenic beauty: case study analyzing pictures of mountainous forests at sloped positions in Jiuzhai Valley, China. Forests 8(3):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8030063
Zhao Y, Sheppard S, Sun Z (2022) Soundscapes of urban parks: an innovative approach for ecosystem monitoring and adaptive management. Urban For Urban Green 71:127555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2022.127555
Funding
This research was supported by the Research Fund of Sichuan Provincial Key Research Base of Social Sciences (GJGY2023-YB002) and Sichuan Landscape and Recreation Research Center Project (JGYQ2020028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jingyang Feng and Zhihong Xu was responsible for the experiment process and original article writing.
Jingyang Feng was responsible for data collection and revision to the manuscript.
Kai Zhang was responsible for literature research and revision to a part of the manuscript.
Chenfan Du was responsible for modifying the article format and prepared Fig. 2.
Xiaohong Tang was responsible for experimental guidance.
Lingqing Zhang was responsible for the guidance of methods and ideas.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, J., Zhang, K., Xu, Z. et al. Quantitative study on color characteristics of urban park landscapes based on K-means clustering and SD. method. Earth Sci Inform 17, 999–1012 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01235-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01235-4