Abstract
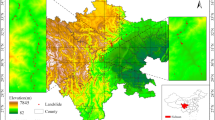
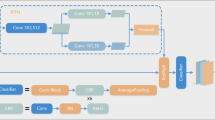
Rapid identification and detection of landslides is of significance for disaster damage assessment and post-disaster relief. However, U-net for rapid landslide identification and detection suffers from semantic gap and loss of spatial information. For this purpose, this paper proposed the U-net with a progressive Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM-U-net) for landslide boundary identification and extraction from high-precision aerial imagery. Firstly, 109 high-precision aerial landslide images were collected, and the original database was extended by data enhancement to strengthen generalization ability of models. Subsequently, the CBAM-U-net was constructed by introducing spatial attention module and channel attention module for each down-sampling process in U-net. Meanwhile, U-net, FCN and DeepLabv3 + are used as comparison models. Finally, 6 evaluation metrics were used to comprehensively assess the ability of models for landslide identification and segmentation. The results show that CBAM-U-net exhibited better recognition and segmentation accuracies compared to other models, with optimal values of average row correct, dice coefficient, global correct, IoU and mean IoU of 98.3, 0.877, 95, 88.5 and 90.2, respectively. U-net, DeepLab V3 + , and FCN tend to confuse bare ground and roads with landslides. In contrast, CBAM-U-net has stronger ability of feature learning, feature representation, feature refinement and adaptation.The proposed method can improve the problems of semantic gap and spatial information loss in U-net, and has better accuracy and robustness in recognizing and segmenting high-precision landslide images, which can provide certain reference value for the research of rapid landslide recognition and detection.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Anand V, Gupta S, Koundal D, Singh K (2023) Fusion of U-Net and CNN model for segmentation and classification of skin lesion from dermoscopy images. Expert Syst Appl 213:119230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119230
Argyrou A, Agapiou A (2022) A review of artificial intelligence and remote sensing for archaeological research. Remote Sens 14(23):6000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236000
Bai S, Tang P, Miao C, Jin C, Zhao B, Wan H (2024) Landslide extraction based on high-resolution remote sensing imagery and improved U-Net model - A case study of Wenchuan area. Remote Sensing of Natural Resources 1–12. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/10.1759.P.20240125.1645.018. (in Chinese)
Ball JE, Anderson DT, Chan CS (2017) Comprehensive survey of deep learning in remote sensing: theories, tools, and challenges for the community. J Appl Remote Sens 11(4):042609–042609. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JRS.11.042609
Bukhari MH, da Silva PF, Pilz J, Istanbulluoglu E, Görüm T, Lee J, Haque U (2023) Community perceptions of landslide risk and susceptibility: A multi-country study. Landslides 20(6):1321–1334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-023-02027-5
Chen H, He Y, Zhang L, Yao S, Yang W, Fang Y, Gao B (2023) A landslide extraction method of channel attention mechanism U-Net network based on Sentinel-2A remote sensing images. Int J Digit Earth 16(1):552–577. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2023.2177359
Chen H, He Y, Zhang L, Yang W, Liu Y, Gao B, Lu J (2023) A Multi-Input Channel U-Net Landslide Detection Method Fusing SAR Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. IEEE J Select Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3339294
Cheng L, Li J, Duan P, Wang M (2021) A small attentional YOLO model for landslide detection from satellite remote sensing images. Landslides 18(8):2751–2765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01694-6
CRED (Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters) (2019) Emergency Events Database (EM-DAT). https://www.emdat.be/. Accessed 10 Sept 2020
Dai K, Li Z, Xu Q, Tomas R, Li T, Jiang L, Wang H (2023) Identification and evaluation of the high mountain upper slope potential landslide based on multi-source remote sensing: The Aniangzhai landslide case study. Landslides 20(7):1405–1417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-023-02044-4
Ghorbanian A, Ahmadi SA, Amani M, Mohammadzadeh A, Jamali S (2022) Application of artificial neural networks for mangrove mapping using multi-temporal and multi-source remote sensing imagery. Water 14(2):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14020244
Ghorbanzadeh O, Meena SR, Abadi HSS, Piralilou ST, Zhiyong L, Blaschke T (2020) Landslide mapping using two main deep-learning convolution neural network streams combined by the Dempster-Shafer model. IEEE J Select Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 14:452–463. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3043836
Ghorbanzadeh O, Xu Y, Zhao H, Wang J, Zhong Y, Zhao D, Ghamisi P (2022) The outcome of the 2022 landslide4sense competition: Advanced landslide detection from multisource satellite imagery. IEEE J Select Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 15:9927–9942. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3220845
Göktürkler G, Balkaya Ç, Erhan Z (2008) Geophysical investigation of a landslide: The Altındağ landslide site, İzmir (western Turkey). J Appl Geophys 65(2):84–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2008.05.008
Guo M, Liu H, Xu Y, Huang Y (2020) Building extraction based on U-Net with an attention block and multiple losses. Remote Sens 12(9):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091400
Guzzetti F, Reichenbach P, Ardizzone F, Cardinali M, Galli M (2006) Estimating the quality of landslide susceptibility models. Geomorphology 81(1–2):166–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.04.007
Han Z, Fang Z, Li Y, Fu B (2023) A novel Dynahead-Yolo neural network for the detection of landslides with variable proportions using remote sensing images. Front Earth Sci 10:1077153. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2022.1077153
Hinton GE, Osindero S, Teh YW (2006) A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput 18(7):1527–1554. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527
Hussain Y, Schlögel R, Innocenti A, Hamza O, Iannucci R, Martino S, Havenith HB (2022) Review on the geophysical and UAV-based methods applied to landslides. Remote Sens 14(18):4564. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184564
Jia J, Ye W (2023) Deep Learning for Earthquake Disaster Assessment: Objects, Data, Models, Stages, Challenges, and Opportunities. Remote Sensing 15(16):4098. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164098
Jia L, Wang J, Gao S, Fang L, Wang D (2023) Landslide risk evaluation method of open-pit mine based on numerical simulation of large deformation of landslide. Sci Rep 13(1):15410. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-42736-4
Jiang W, Xi J, Li Z, Zang M, Chen B, Zhang C, Zhu W (2022) Deep learning for landslide detection and segmentation in high-resolution optical images along the Sichuan-Tibet transportation corridor. Remote Sens 14(21):5490. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215490
Jiang G, Wang J, Li K, Xu C, Li H, Jing Z, Liu J (2023a) Consistency Analysis and Accuracy Evaluation of Multi-Source Land Cover Data Products in the Eastern European Plain. Remote Sens 15(17):4254. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174254
Jiang W, Xi J, Li Z, Ding M, Yang L, Xie D (2023b) Mask R-CNN landslide segmentation recognition for simulating difficult samples. J Wuhan Univ (Information Science Edition) (12):1931–1942. https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13203/j.whugis20200692. (in Chinese)
Li D, Tang X, Tu Z, Fang C, Ju Y (2023) Automatic Detection of Forested Landslides: A Case Study in Jiuzhaigou County. China Remote Sensing 15(15):3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153850
Li Z, Shi A, Li X, Dou J, Li S, Chen T, Chen T (2024) Deep Learning-Based Landslide Recognition Incorporating Deformation Characteristics. Remote Sens 16(6):992. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16060992
Lucas S, Johannessen JA, Cancet M, Pettersson LH, Esau I, Rheinlænder JW, Donlon C (2023) Knowledge Gaps and Impact of Future Satellite Missions to Facilitate Monitoring of Changes in the Arctic Ocean. Remote Sens 15(11):2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112852
Mao Z, Yu H, Ma X, Liang W, Gao G, Tian Y, Shi S (2024) Refinement analysis of landslide risk assessment for wide area based on UAV-acquired high spatial resolution images. Stoch Env Res Risk A 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-024-02688-1
Martins VS, Kaleita AL, Gelder BK, da Silveira HL, Abe CA (2020) Exploring multiscale object-based convolutional neural network (multi-OCNN) for remote sensing image classification at high spatial resolution. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 168:56–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.08.004
Mohan A, Singh AK, Kumar B, Dwivedi R (2021) Review on remote sensing methods for landslide detection using machine and deep learning. Transact Emerg Telecommun Technol 32(7):e3998. https://doi.org/10.1002/ett.3998
NASA Landslide Viewer (2023) Global landslide sites and landslide areas dataset (1915–2021) national glacial permafrost desert science data center (http://www.ncdc.ac.cn), 2021. https://doi.org/10.12072/ncdc.nieer.db2700.2023. (in Chinese)
National Bureau of Statistics in the People’s Republic of China (2024) Geologic hazards and prevention in China (from 2019-2022). https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01
Oktay O, Schlemper J, Folgoc LL, Lee M, Heinrich M, Misawa K, Rueckert D (2018) Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arxiv preprint arxiv:1804.03999. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv preprint arxiv:1804.03999
Qi J, Chen H, Chen F (2022) Extraction of landslide features in UAV remote sensing images based on machine vision and image enhancement technology. Neural Comput Appl 34(15):12283–12297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06523-4
Shen M, Cheng G, Zhu L, Du X, Hu J (2020) Content-based multi-source encrypted image retrieval in clouds with privacy preservation. Futur Gener Comput Syst 109:621–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.04.089
Song AG, Wang G, Yin YP, Jiang Y, Wang GZ, Yang SY, Dai JA (2014) Dynamic analysis and field investigation of a fluidized landslide in Guanling, Guizhou, China. Eng Geol 181:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.07.022
Wang Q, Zhang J (2021) A method for landslide texture feature extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology (04):547–556. https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.16355/j.cnki.issn1007-9432tyut.2021.04.006. (in Chinese)
Wang X, Wang L, Zhong X, Bai C, Huang X, Zhao R, Xia M (2021) PaI-Net: A modified U-Net of reducing semantic gap for surgical instrument segmentation. IET Image Proc 15(12):2959–2969. https://doi.org/10.1049/ipr2.12283
Wang J, Chen G, Jaboyedoff M, Derron MH, Fei L, Li H, Luo X (2023) Loess landslides detection via a partially supervised learning and improved Mask-RCNN with multi-source remote sensing data. CATENA 231:107371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2023.107371
Wang Y, Yang L, Liu X, Yan P (2024) An improved semantic segmentation algorithm for high-resolution remote sensing images based on DeepLabv3+. Sci Rep 14(1):9716. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60375-1
Xu C, Xu X, Shyu JBH, Gao M, Tan X, Ran Y, Zheng W (2015) Landslides triggered by the 20 April 2013 Lushan, China, Mw 6.6 earthquake from field investigations and preliminary analyses. Landslides 12:365–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-014-0546-1
Yin L, Wang L, Li T, Lu S, Tian J, Yin Z, Zheng W (2023) U-Net-LSTM: time series-enhanced lake boundary prediction model. Land 12(10):1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12101859
Zeng C, Cao Z, Su F, Zeng Z, Yu C (2022) High-precision aerial imagery and interpretation dataset of landslide and debris flow disaster in Sichuan and surrounding areas. China Sci Data 7(2):195–205. https://doi.org/10.11922/sciencedb.j00001.00222
Zhang S, Zhang C (2023) Modified U-Net for plant diseased leaf image segmentation. Comput Electron Agric 204:107511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2022.107511
Zhang S, Qiu L, Jing C (2024) Normalized auto-encoder based on biased walk for network representation learning. Eng Appl Artif Intell 130:107265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107265
Funding
This work was supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. KJZD-M202301205, KJQN202001218, KJQN202301260, KJQN202101206, KJQN202201238), the Research development and application of “big data intelligent prediction and early warning cloud service platform for geological disasters in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area” of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. HZ2021012), the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (Grant No. CSTB2023NSCQ-MSX0433), the Chongqing Engineering Research Center of Disaster Prevention & Control for Banks and Structures in Three Gorges Reservoir Area (Grant No. SXAPGC21ZD01, SXAPGC24XC20, SXAPGC23XC02), the Science and technology innovation project of Chongqing Wanzhou District Bureau of science and technology (Grant No. wzstc20230303) and 2024 Graduate Student Research and Innovation Program at Chongqing Three Gorges College (Grant No. YJSKY24049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lin was primarily responsible for conceptualizing the entire article and writing the introduction and methods; Li and Qiang were mainly responsible for obtaining funding for the article and proofreading the article; Xu is primarily responsible for using the software; Liang was responsible for writing Sections "Study area profiles and Data sources, Results and Analysis , Discussions and Conclusions"; Chen, Yang and Zhang were responsible for collecting research data and drawing all tables and pictures for the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: Hassan Babaie
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, H., Li, L., Qiang, Y. et al. A method for landslide identification and detection in high-precision aerial imagery: progressive CBAM-U-net model. Earth Sci Inform 17, 5487–5498 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01465-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01465-6