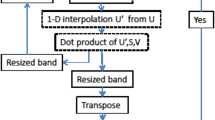
Abstract
This paper discusses the development of PyGeoRS, a Python-based QGIS plugin designed to automate remote sensing tasks for environmental mapping using Landsat 8 and 9 data. PyGeoRS simplifies complex processes using data from Landsat 8 and 9 satellites, facilitating tasks such as Principal and Independent Component Analysis, band ratios, indices calculation, false-color image generation, and Optimum Index Factor calculation. A key advantage of PyGeoRS is its ability to significantly enhance processing speed, offering a 40–60% improvement compared to other remote sensing software, which optimizes workflow efficiency. Additionally, as an open-access tool, PyGeoRS broadens the availability of advanced remote sensing capabilities to users with varying levels of access to technology. While this version supports only Landsat data, future expansions are planned to include additional sensors, further extending PyGeoRS’s applicability in remote sensing and mapping tasks.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Abrams MJ, Ashley RP, Rowan LC, Goetz AF, Kahle AB (1977) Mapping of hydrothermal alteration in the Cuprite mining district, Nevada, using aircraft scanner images for the spectral region 0.46 to 2.36 µm. Geology 5(12):713–718. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1977)5713:mohait2.0.co;2
An K, Kim S, Chae T, Park D (2018) Developing an accessible landslide susceptibility model using open-source resources. Sustainability, 10(2):293.
Chai B, Li P (2023) An ensemble method for monitoring land cover changes in urban areas using dense landsat time series data. ISPRS J Photogrammetry Remote Sens 195:29–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2022.11.002
Chavez PS, GL, B., LB S (1982) Statistical method for selecting Landsat MSS ratios
Comon P (1994) Independent component analysis, a new concept? Sig Process 36(3):287–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1684(94)90029-9
Congedo L (2021) Semi-automatic classification Plugin: a Python tool for the download and processing of remote sensing images in QGIS. J Open Source Softw 6(64):3172. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03172
Drury SA (1987) Image Interpretation in Geology (London: Allen &Unwin). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-9393-4
Duarte L, Silva P, Teodoro AC (2018) Development of a QGIS plugin to obtain parameters and elements of plantation trees and vineyards with aerial photographs. ISPRS Int J Geo-Information 7(3):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7030109
Ellsäßer F, Röll A, Stiegler C, Hölscher D (2020) Introducing QWaterModel, a QGIS plugin for predicting evapotranspiration from land surface temperatures. Environ Model Softw 130:104739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2020.104739
Endsley KA (2019) The unmixing library: Interactive tools for spectral mixture analysis of multispectral raster data in Python v0.2.4.dev. Zenodo. https://zenodo.org/record/3585979
Gao BC (1996) NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sens Environ 58(3):257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(96)00067-3
GDAL/OGR contributors D (2020) GDAL/OGR geospatial data abstraction software library. Open Source Geospatial Foundation
Gillies S, Ward B, Petersen AS, Rasterio (2013) Geospatial Raster I/O for Python Programmers. https://github.com/rasterio/rasterio
Green AA, Berman M, Switzer P, Craig MD (1988) A transformation for ordering multispectral data in terms of image quality with implications for noise removal. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 26(1):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.3001
Guo Z, Torra O, Hürlimann M, Abancó C, Medina V (2022) FSLAM: a QGIS plugin for fast regional susceptibility assessment of rainfall-induced landslides. Environ Model Softw 150:105354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2022.105354
Hall DK, Riggs GA, Salomonson VV (1995) Development of methods for mapping global snow cover using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer data. Remote Sens Environ 54(2):127–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(95)00137-p
Hansen MC, Loveland TR (2012) A review of large area monitoring of land cover change using landsat data. Remote Sens Environ 122:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.08.024
Harris CR, Millman KJ, Van Der Walt SJ, Gommers R, Virtanen P, Cournapeau D, Oliphant TE (2020) Array programming with NumPy. Nature 585(7825):357–362. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2649-2
Huete A, Didan K, Miura T, Rodriguez EP, Gao X, Ferreira LG (2002) Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens Environ 83(1–2):195–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(02)00096-2
Ihlen V, Zanter K (2019) Landsat 8 data users handbook. US Geological Survey: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 55
Jakimow B, Janz A, Thiel F, Okujeni A, Hostert P, van der Linden S (2023) EnMAP-Box: imaging spectroscopy in QGIS. SoftwareX 23:101507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2023.101507
Jung M (2013) LecoS-A QGIS plugin for automated landscape ecology analysis. https://doi.org/10.7287/peerj.preprints.116v1
Kaufmann H (1988) Mineral exploration along the Aqaba-Levant structure by use of TM-data. Concepts, processing and results. Int J Remote Sens (Print) 9(10–11):1639–1658. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431168808954966
Key CH, Benson NC (1999) June Measuring and remote sensing of burn severity. In Proceedings joint fire science conference and workshop (Vol. 2, p. 284). University of Idaho and International Association of Wildland Fire Moscow, ID
Mandeng EPB, Bidjeck LMB, Wambo JDT, Taku A, Betsi TB, Ipan AS, Dieudonné LB (2018) Lithologic and structural mapping of the abiete–Toko gold district in southern Cameroon, using landsat 7 ETM+/SRTM. Comptes Rendus Géoscience 350(3):130–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crte.2017.11.003
Marzouki A, Dridri A (2022) Normalized difference enhanced Sand Index for desert sand dunes detection using Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 OLI data, application to the north of Figuig, Morocco. J Arid Environ 198:104693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2021.104693
Marzouki A, Dridri A (2023) Lithological discrimination and structural lineaments extraction using landsat 8 and ASTER data: a case study of Tiwit (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Environ Earth Sci 82(5):125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10831-4
Nguyen CT, Chidthaisong A, Kieu Diem P, Huo LZ (2021) A modified bare soil index to identify bare land features during agricultural fallow-period in southeast Asia using landsat 8. Land 10(3):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10030231
Nielsen A, Bolding K, Hu F, Trolle D (2017) An open source QGIS-based workflow for model application and experimentation with aquatic ecosystems. Environ Model Softw 95:358–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2017.06.032
Nijmeijer R, de Haas A, Dost RJJ, Budde PE (2001) ILWIS 3.0 Academic: user’s guide
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, Duchesnay É (2011) Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J Mach Learn Res 12:2825–2830
Pour AB, Hashim M, Hong JK, Park Y (2019) Lithological and alteration mineral mapping in poorly exposed lithologies using Landsat-8 and ASTER satellite data: North-eastern Graham Land, Antarctic Peninsula. Ore Geol Rev 108:112–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.07.018
Qi J, Chehbouni A, Huete AR, Kerr YH, Sorooshian S (1994) A modified soil adjusted vegetation index. Remote Sens Environ 48(2):119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(94)90134-1
Rocklin M (2015), July Dask: Parallel computation with blocked algorithms and task scheduling. In SciPy (pp. 126–132). ROI: https://doi.org/10.25080/majora-7b98e3ed-013
Rossetto R, Cisotto A, Dalla Libera N, Braidot A, Sebastiani L, Ercoli L, Borsi I (2022) ORGANICS: a QGIS Plugin for simulating one-dimensional transport of dissolved substances in Surface Water. Water 14(18):2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182850
Rouse JW Jr, Haas RH, Schell JA, Deering DW (1973), December Paper a 20. In Third Earth Resources Technology Satellite-1 Symposium: The Proceedings of a Symposium Held by Goddard Space Flight Center at Washington, DC on (Vol. 351, p. 309)
Sabins FF (1999) Remote sensing for mineral exploration. Ore geology reviews. 14(3–4):157–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-1368(99)00007-4
Segal D (1982) Theoretical basis for differentiation of ferric-iron bearing minerals, using Landsat MSS data. In Proceedings of Symposium for Remote Sensing of Environment, 2nd Thematic Conference on Remote Sensing for Exploratory Geology, Fort Worth, TX (pp. 949–951)
Souza Jr CM, Shimbo Z, Rosa J, Parente MR, Alencar LLA, Rudorff A, Azevedo BF, T (2020) Reconstructing three decades of land use and land cover changes in Brazilian biomes with landsat archive and earth engine. Remote Sens 12(17):2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12172735
Titti G, Sarretta A, Lombardo L, Crema S, Pasuto A, Borgatti L (2022) Mapping susceptibility with open-source tools: a new plugin for QGIS. Frontiers in Earth Science 10:842425.
Wasser L, Joseph MB, McGlinchy J, Palomino J, Korinek N, Holdgraf C, Head T (2019) EarthPy: a Python package that makes it easier to explore and plot raster and vector data using open source Python tools. J Open Source Softw 4(43):1886. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.01886
Wold S, Esbensen K, Geladi P (1987) Principal component analysis. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 2(1–3):37–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-7439(87)80084-9
Xu H (2006) Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int J Remote Sens 27(14):3025–3033. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160600589179
Zha Y, Gao J, Ni S (2003) Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from TM imagery. Int J Remote Sens 24(3):583–594. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160304987
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to Mr. Riad MARZOUKI for his invaluable technical assistance during the development of PyGeoRS. His support and expertise greatly contributed to the successful completion of this project.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AM: conceptualization, methodology, software, data curation, writing – original draft. AD: supervision, writing – review & editing, validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing process
During the preparation of this work the authors used ChatGPT in order to check for grammatical / spelling errors and to further enhance the text. After using this tool, the authors reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Hassan Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Marzouki, A., Dridri, A. PyGeoRS: a QGIS plugin for automating landsat data processing in environmental mapping. Earth Sci Inform 18, 58 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01522-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01522-0