Abstract
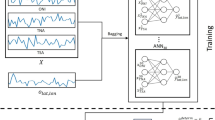
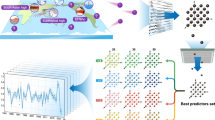
Excessive rainfall and droughts harshly impact India's social and economic growth. Though several statistical methods have been used in literature to predict Indian monsoons, uncertainties cannot be ruled out. The accuracy prediction of ISMR (Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall) is scientifically demanding. From this perspective, it is essential to explore exploiting machine learning techniques. In this paper, a novel De-correlated Regularized Random Vector Functional Link Neural Network Ensemble (DRRNE) prediction approach was proposed using Climate Predictors such as Southern Oscillation Index (SOI), Sea Surface Temperature Anomaly (SST), El-Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), and Dipole Mode Index (DMI) to predict ISMR. The proposed work has also investigated the predictability of climate above predictors using the DRRNE approach to predict ISMR. In addition to the predictors above, the data for an 8-year training window time series for June to September is combined and analyzed for four predictors (ENSO, DMI, SOI, and SST) to derive another predictor, ENSO-DMI-SOI-SST (EDSS). It is found that the combination of these four predictors- the EDSS- produces better accuracy than using any of the individual predictors in this study. Among the individual predictors (ENSO, DMI, SOI, and SST), the DMI predictor has shown the best predictability for ISMR prediction. Thus, the suggested study concludes that the DRRNE technique with negative correlation learning may be a suitable tool for predicting the ISMR using the combined outcome of the four climate predictors as mentioned above.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Acharya N, Chattopadhyay S, Kulkarni MA, Mohanty UC (2012) A neurocomputing approach to predict monsoon rainfall in monthly scale using SST anomaly as a predictor. Acta Geophys 60:260–279
Adya M, Collopy F (1998) How effective are neural networks at forecasting and prediction? A review and evaluation. J Forecast 17:481–495
Alhamdoosh M, Wang D (2014) Fast decorrelated neural network ensembles with random weights. Inf Sci 264:104–117
Arcomano T et al (2022) A hybrid approach to atmospheric modeling that combines machine learning with a physics-based numerical model. J Adv Model Earth Syst 14:e2021MS002712
Ashok K, Guan Z, Saji NH, Yamagata T (2004) Individual and combined influences of the ENSO and Indian Ocean dipole on the Indian summer monsoon. J Clim 17:3141–3155
Ashok K, Guan Z, Yamagata T (2001) Impact of the Indian Ocean dipole on the relationship between the Indian monsoon rainfall and ENSO. Geophys Res Lett 28:4499–4502
Azad S, Rajeevan M (2016) Possible shift in the ENSO-Indian monsoon rainfall relationship under future global warming. Sci Rep 6:20145
Rosen BE (1996) Ensemble learning using decorrelated neural networks. Connect Sci 8(3/4):373–383
Bach E, Ghil M (2023) A multi-model ensemble Kalman filter for data assimilation and forecasting. J Adv Model Earth Syst 15:e2022MS003123
Bach E, Krishnamurthy V, Mote S et al (2024) Improved subseasonal prediction of South Asian monsoon rainfall using data-driven forecasts of oscillatory modes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 121(15):e2312573121. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2312573121
Behera SK, Yamagata T (2003) Influence of the Indian Ocean dipole on the Southern Oscillation. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 81:169–177
Bhalme HN, Jadhav SK, Mooley DA, Ramana Murty BV (1986) Forecasting of monsoon performance over India. Int J Climatol 6:347–354
Blanford HF (1884) On the connection of the Himalayan snowfall with dry winds and seasons of draughts in India. Proc R Soc Lond 37:3–22
Brown G, Wyatt JL, Tinˇo P (2005) Managing diversity in regression ensembles. J Mach Learn Res 6:1621–1650
Chattopadhyay G, Chattopadhyay S, Jain R (2010) Multivariate forecast of winter monsoon rainfall in India using SST anomaly as a predictor: neurocomputing and statistical approaches. CR Geosci 342:755–765
Chattopadhyay M, Chattopadhyay S (2016) Elucidating the role of topological pattern discovery and support vector machine in generating predictive models for Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Theor Appl Climatol 126:93–104
Chen H, Yao X (2009) Regularized negative correlation learning for neural network ensembles. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 20(12):1962–1979
Dash Y, Mishra SK, Panigrahi BK (2017) NEMR predictability assessment over Indian peninsula using ELM. Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Climate Informatics: CI 2017, NCAR Technical Note NCAR/TN-536+PROC, pp.77–80.
Dash Y, Mishra SK, Panigrahi BK (2017) Rainfall prediction of a maritime state (Kerala), India using SLFN and ELM techniques,” 2017 ICICICT, Kannur, India, IEEE Xplore Digital Library, pp. 1714- 1718
Dash Y, Mishra SK, Panigrahi BK (2018) Rainfall Prediction for Kerala state of India using artificial intelligence approaches. Comput Electr Eng 70:66–73
Dash Y, Mishra SK, Panigrahi BK (2018) Predictability assessment of northeast monsoon rainfall in India using sea surface temperature anomaly through statistical and machine learning techniques. Environmetrics 30:e2533
Dash Y, Mishra SK, Panigrahi BK (2019) Neural Network Based Approaches for Prediction of the Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall. 2019 2nd ICICICT, Kannur, Kerala, India, IEEE Xplore Digital Library, pp. 550–554
Dash Y, Mishra SK, Panigrahi BK (2019a) Prediction of Southwest Monsoon Rainfall for Kerala, India using ε-SVR Model. 2019 2nd ICICICT, Kannur, Kerala, India, IEEE Xplore Digital Library, pp. 746–748.
Dash Y, Mishra SK, Sahany S, Panigrahi BK (2018) Indian summer monsoon rainfall prediction: a comparison of iterative and non-iterative approaches. Appl Soft Comput 70:1122–1134
Dash Y, Kumar N, Raj M, Abraham A (2024) Deep Learning Approach for Predicting Monsoon Dynamics of Regional Climate Zones of India. Applied Computing and Geosciences, 100176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acag.2024.100176
Gadgil S, Rajeevan M, Nanjundiah R (2005) Monsoon prediction-why yet another failure? Curr Sci 88:1389–1400
Hadley Centre SST data set (HadSST3). Available at: https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/hadobs/hadsst3/.
He S et al (2022) Learning and dynamical models for sub-seasonal climate forecasting: Comparison and collaboration. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell 36:4495–4503
Hornik K, Stinchcombe M, White H (1989) Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Netw 2(5):359–366
Igelnik B, Pao Y-H (1995) Stochastic choice of basis functions in adaptive function approximation and the functional-link net. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 6(6):1320–1329
Igelnik B, Pao Y-H, LeClair S, Shen CY (1999) The ensemble approach to neural-network learning and generalization. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(1):19–30
IITM Data Archival (2016). Available online at: http://www.tropmet.res.in/.
Irrgang C et al (2021) Towards neural Earth system modelling by integrating artificial intelligence in Earth system science. Nat Mach Intell 3:667–674
Kashinath K et al (2021) Physics-informed machine learning: Case studies for weather and climate modelling. Philos Trans R Soc a: Math Phys Eng Sci 379:20200093
Kennedy JJ, Rayner NA, Smith RO, Saunby M, Parker DE (2011) Reassessing biases and other uncertainties in sea-surface temperature observations since 1850 part 1: measurement and sampling errors. J Geophys Res 116:D14103
Kennedy JJ, Rayner NA, Smith RO, Saunby M, Parker DE (2011) Reassessing biases and other uncertainties in sea-surface temperature observations since 1850 part 2: biases and homogenisation. J Geophys Res 116:D14104
Kripalani RH, Kulkarni A (1997) Climate impact of El- Nino/La- Nina on the Indian monsoon: a new perspective. Weather 52:39–46
Kumar PK, Kumar R, Rajeevan M, Sahai AK (2007) On the recent strengthening of the relationship between ENSO and northeast monsoon rainfall over south Asia. Clim Dyn 28:649–660
Leshno M, Schocken S (1993) Multilayer feedforward networks with a nonpolynomial activation function can approximate any function. Neural Netw 6:6861–867
Liu Y, Yao X (1997) Negatively correlated neural networks can produce best ensembles. Aust J Intell Inform Process Syst 4(3/4):176–185
Liu Y, Yao X (1999) Simultaneous training of negatively correlated neural networks in an ensemble. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern-Part b: Cybern 29(6):716–725
Liu Y, Yao X (1999) Ensemble learning via negative correlation. Neural Netw 12(10):1399–1404
Liu Y, Yao X, Higuchi T (2000) Evolutionary ensembles with negative correlation learning. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 4(4):380–387
Loschnigg J, Meehl GA, Webster PJ, Arblaster JM, Compo GP (2003) The Asian monsoon, the tropospheric biennial oscillation and the Indian Ocean dipole in the NCAR CSM. J Clim 16:2138–2158
Navone HD, Ceccatto HA (1994) Predicting Indian monsoon rainfall: a neural network approach. Clim Dyn 10:305–312
Pao Y-H, Takefuji Y (1992) Functional-link net computing: theory, system architecture, and functionalities. Comput Mag 25(5):76–79
Park J, Sandberg IW (1991) Universal approximation using radial-basis-function networks. Neural Comput 3(2):246–257
Rajeevan M, Pai DS (2007) On the El Niño-Indian monsoon predictive relationships. Geophys Res Lett 34 . L04704_1-L04704_4. ISSN 0094–8276
Rajeevan M, Pai DS, Kumar RA, Lal B (2007) New statistical models for long-range forecasting of southwest monsoon rainfall over India. Clim Dyn 28:813–828
Rao CR, Mitra SK (1971) Generalized Inverse of Matrices and Its Applications. Wiley, New York
Rasmusson EM, Carpenter TH (1983) The Relationship between Eastern Equatorial Pacific Sea Surface Temperature and Rainfall over India and Sri Lanka. Mon Weather Rev 111:517–528
Rayner NA et al (2003) Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J Geophys Res 108:4407
Ren Y, Suganthan PN, Srikanth N, Amaratunga G (2016) random vector functional link network for short-term electricity load demand forecasting. Inform Sci 367:1078–1093
Sahai AK, Soman MK, Satyan V (2000) All India summer monsoon rainfall prediction using an artificial neural network. Clim Dyn 16:291–302
Sahai AK et al (2021) Multi-model multi-physics ensemble: A futuristic way to extended range prediction system. Front Clim 3:655919
Saji NH, Goswami BN, Vinayachandran PN, Yamagata T (1999) A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 401:360–363
Schmidt W, Kraaijveld M, Duin R (1992) Feedforward neural networks with random weights, in: Proceedings of 11th IAPR International Conference on Pattern Recognition Methodology and Systems, pp. 1–4
Shukla J, Mooley DA (1987) Empirical prediction of the summer monsoon rainfall over India. Mon Weather Rev 115:695–703
Singh P, Borah B (2013) Indian summer monsoon rainfall prediction using artificial neural network. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 27:1585–1599
Statistical Year Book, Chapter 34 Rainfall, Ministry of statistics and programme implementation. Available at: mospi.nic.in/Mospi_New/upload/SYB2015/CH-34-RAINFALL/Rainfall.pdf. Accessed on 15 Jun 2016.
The NOAA ESRL Physical Sciences Division (PSD). www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/.
Torchinsky JL, Stechmann S (2023) Mitigating model error via a multimodel method and application to tropical intraseasonal oscillations. SIAM J Appl Dyn Syst 22:3025–3058
Walker GT (1908) Correlation in seasonal variation of climate (Introduction). Mem India Meteorol Dep 20:117–124
Walker GT (1910) On the meteorological evidence for supposed changes of climate in India. Mem India Meteorol Dep 21:1–21
Webster P, Magana VO, Palmer T, Shukla J, Thomas R, Yanai M, Yasunari T (1998) Monsoons: Processes, predictability, and prospects for prediction. J Geophys Res 1031:14451–14510
Webster PJ, Yang S (1992) Monsoon and ENSO: Selectively interactive systems. Quart J Roy Meteor Soc 118:877–926
Xie J, Hsu PC, Hu Y, Ye M, Yu J (2023) Skillful extended-range forecast of rainfall and extreme events in east China based on deep learning. Weather Forecast 38:467–486
Yamagata T, Behera SK, Rao SA, Guan Z, Ashok K, Saji NH (2003) Comments on Dipoles, temperature gradient, and tropical climate anomalies. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 84:1418–1422
Zhang L, Suganthan PN (2016) A Comprehensive Evaluation of Random Vector Functional Link Networks. Inform Sci 367:1094–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2015.09.025
Zhang L, Suganthan PN (2016) A Survey of Randomized Algorithms for Training Neural Networks. Inform Sci 364:146–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2016.01.039
Funding
No funding is received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yajnaseni Dash has implemented and written the manuscript. Ajith Abraham, Dileep Kumar Yadav, Naween Kumar, and Neha Singhal have contributed to reviewing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: Hassan Babaie
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dash, Y., Abraham, A., Kumar, N. et al. Climate predictors in Indian summer monsoon forecasting: a novel De-correlated RVFL ensemble strategy. Earth Sci Inform 18, 134 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01532-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01532-y