Abstract
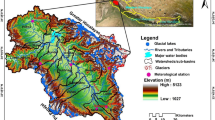
As global warming intensifies, the changes of glacial lakes in Xizang need to be carefully examined. Because of their special geographical location and physical characteristics, it is extremely liable to occur Glacial Lake Outburst Flood, which poses a serious threat to the surrounding residents, infrastructure and ecological environment. However, our knowledge about the specific distribution of glacial lakes across the region and their potential risks is still limited. Therefore, by using GIS spatial analysis and the parametric optimal geodetector method, we analyzed the spatio-temporal changes of glacial lakes in Xizang from 1990 to 2015, and the extent to which the annual total precipitation, annual average temperature, annual relative humidity and glacier area change factors affected the changes of glacial lakes. The statistics and analysis show that from 1990 to 2015, the growth rates of glacial lakes in quantity and area were 2.57% and 6.32%, respectively, while the number and area of moraine lakes increased by 18.96% and 28.45%, respectively. Through the analysis of the optimal parameter geographic detector, it is found that the change of glacier area has the greatest influence on the area and number of glacial lakes, with the q value 0.5006 and 0.1696, respectively. In the interaction detection, the interaction between temperature and glacier area change has the strongest explanatory power to the change of glacial lake area. The interaction of the precipitation and the glacier area change has the strongest explanatory power relative to the change of glacier lake number, and the relationship is non-linear. The change of glacial lake is the result of the interaction of various factors. This paper puts forward the quantitative evaluation of various factors and their interactions by using geographic detectors, and reveals the spatio-temporal distribution rule of glacial lakes in Xizang and its influencing factors. On the one hand, it can provide a scientific basis for the early warning and prevention of outbursts of flood from glacial lakes, and help to reduce disaster losses. On the other hand, this study also provides an important reference for the evolution of glacial lakes in the context of global climate change.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Bhuiyan MAH, Kumamoto T, Suzuki S (2015) Application of remote sensing and GIS for evaluation of the recent morphological characteristics of the lower Brahmaputra-Jamuna River, Bangladesh [J]. Earth Sci Inf 8(3):551–568
Bolch T, Buchroithner MF, Peters J et al (2008) Identification of glacier motion and potentially dangerous glacial lakes in the Mt. Everest region/Nepal using spaceborne imagery. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 8(6):1329–1340. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-8-1329-2008
Chen L, Wang Q (2021) Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of land use in tibetan region: 1995–2025. Earth Sci Inf 14(4):1821–1832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00627-0
Chernos M, Koppes M, Moore RD (2016) Ablation from calving and surface melt at lake-terminating Bridge Glacier, British Columbia, 1984–2013. Cryosphere 10(1):87–102. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-10-87-2016
Fujita K, Sakai A, Takenaka S et al (2013) Potential flood volume of Himalayan glacial lakes. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 13(7):1827–1839. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-13-1827-2013
He YP, Hu KH, Wei FQ et al (2001) Characteristics of debris Flow in Polongzangbu Basin of Sichuan-Tibet Highway. J Soil Water Conserv 0376–80. https://doi.org/10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2001.03.021
He XQ, Wang ZF, Wang CW et al (2022) A method for estimating the probability of glacial lake outburst floods based on logistic regression and geodetector: a case study of the himalayan region. Earth Sci Inf 15(1):649–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00738-8
Li ZG (2014) Glacier and Lake Changes across the Tibetan Plateau during the past 50 years of Climate Change. J Resour Ecol 5(2):123–131. https://doi.org/10.5814/j.issn.1674-764X.2014.02.004
Li Linfeng L (2019) Study on the relationship between glacier change and topographic factors in the Shiyang River Basin [J]. J Glaciology Geocryology 41(5):1026–1035
Liang LQ, Cuo L, Liu Q (2018) The energy and mass balance of a continental glacier: Dongkemadi Glacier in central tibetan Plateau. Sci Rep 8(1):12788. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31228-5
Linsbauer A, Frey H, Haeberli W et al (2016) Modelling glacier-bed overdeepenings and possible future lakes for the glaciers in the Himalaya-Karakoram region. Ann Glaciol 57(71):119–130. https://doi.org/10.3189/2016AoG71A627
Liu J, Yao XJ, Gao YP et al (2019a) Glacial lake variation and hazard assessment of glacial lakes outburst in the Parlung Zangbo River Basin. J Lake Sci 31(04):1132–1143. https://doi.org/10.18307/2019.0420
Liu JK, Zhang JJ, Gao B et al (2019b) An overview of glacial lake outburst flood in Tibet, China. J Glaciology Geocryology 41(06):1335–1347. https://doi.org/10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2019.0073
Liu Jiali Z, Tiancai Y Huan, Dynamics and driving forces of lake changes in Tibet during the past 25 years [J]. J Yangtze River Sci Res Inst 2018, 35 (2):145–150
Nie Y, Sheng YW, Liu Q et al (2017) A regional-scale assessment of Himalayan glacial lake changes using satellite observations from 1990 to 2015. Remote Sens Environ 189:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.11.008
Nie Y, Pritchard HD, Liu Q et al (2021) Glacial change and hydrological implications in the Himalaya and Karakoram. Nat Reviews Earth Environ 2(2):91–106. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-020-00124-w
Peng JB, Cui P, Zhuang JQ (2020) Challenges to engineering geology of Sichuan—Tibet railway Chinese. J Rock Mech Eng 39(12):2377–2389. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0446
Qiu J (2008) China: the third Pole. Nature 454(7203):393–396. https://doi.org/10.1038/454393a
Shugar DH, Clague JJ, McSaveney MJ (2018) Late holocene activity of Sherman and Sheridan glaciers, Prince William Sound, Alaska. Q Sci Rev 194:116–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.07.016
Shugar DH, Burr A, Haritashya UK et al (2020) Rapid worldwide growth of glacial lakes since 1990. Nat Clim Change 10(10):939–945. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-020-0855-4
Stuart-Smith RF, Roe GH, Li S et al (2021) Increased outburst flood hazard from Lake Palcacocha due to human-induced glacier retreat. Nat Geosci 14(2):85–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-021-00686-4
Wang J, Xu C (2017) Geodetector: principle and prospective. Acta Geogr Sin 72(1):116–134
Wang X, Liu SY, Guo WQ et al (2009) Hazard Assessment of Moraine-dammed Lake Outburst Floods
Wang X, Liu SY, Guo WQ, et al (2009) Hazard Assessment of Moraine-dammed Lake Outburst Floods in the Himalayas, China Acta Geogr Sin 64(07): 782–790. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2009.07.002
Wang WC, Yao TD, Yang XX (2011) Variations of glacial lakes and glaciers in the Boshula mountain range, southeast Tibet, from the 1970s to 2009. Ann Glaciol 52(58):9–17. https://doi.org/10.3189/172756411797252347
Wang X, Liu S, Ding Y et al (2012) An approach for estimating the breach probabilities of moraine-dammed lakes in the Chinese himalayas using remote-sensing data. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 12(10):3109–3122. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-12-3109-2012
Wang SJ, Che YJ, Ma XG (2020) Integrated risk assessment of glacier lake outburst flood (GLOF) disaster over the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau (QTP). Landslides 17(12):2849–2863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01443-1
Wang SJ, Qin DH, Xiao CD (2015) Moraine-dammed lake distribution and outburst flood risk in the Chinese Himalaya. J Glaciol 61(225):115–126. https://doi.org/10.3189/2015JoG14J097
Wang Zhoufeng F, Shangjie W, Yujun et al Research on influencing factors of glacier area change in Sichuan based on geographic detectors [J]. J Geomatics 2023, 48 (2):97–101
Watson CS, Kargel JS, Shugar DH et al (2020) Mass loss from calving in Himalayan Proglacial Lakes. Front Earth Sci 7:342. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2019.00342
Ye QH, Zhong ZW, Kang SC et al (2009) Monitoring Glacier and Supra-glacier lakes from space in Mt. Qomolangma Region of the Himalayas on the Tibetan Plateau in China. J Mt Sci 6(3):211–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-009-1016-4
Yongsheng Y, Xin W, Shiyin L et al Characteristics and influence factors of the glacial lake changes in China from 1990 to 2020 [J]. J Lake Sci 2023, 35(1):358–367
Zhang GQ, Yao TD, Xie HJ et al (2015) An inventory of glacial lakes in the third Pole region and their changes in response to global warming. Glob Planet Change 131:148–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2015.05.013
Zhang TG, Wang WC, Gao TG et al (2022) An integrative method for identifying potentially dangerous glacial lakes in the Himalayas. Sci Total Environ 806:150442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150442
Zhang Ruojing C, Yuehong Z (2021) Spatial-temporal pattern and driving factors of flash flood disasters in Jiangxi Province analyzed by optimal parameters-based geographical detector [J]. Geogr Geo-Information Sci 37(4):72–80
Zheng GX, Allen SK, Bao AM et al (2021a) Increasing risk of glacial lake outburst floods from future third Pole deglaciation. Nat Clim Change 11(5):411–417. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-021-01028-3
Zheng GX, Bao AM, Allen S et al (2021b) Numerous unreported glacial lake outburst floods in the third Pole revealed by high-resolution satellite data and geomorphological evidence. Sci Bull 66(13):1270–1273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2021.01.014
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFF0414359), Sichuan Science and Technology Program(2023YFS0406), Chongqing Municipal Construction Science and Technology Plan Project (City Sci-Tech Code 2023 No. 1-4) and Innovative Experimental Programme for Higher Educational Institutions in Sichuan Province ‘Innovative Experiment on Disaster Risk Assessment of Energy Pipeline Networks and Dual Carbon Monitoring’ (2023-44).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Data curation, conceptualization, investigation, software, methodology, and writing—original draft were done by Zhoufeng Wang; resources, supervision, and writing—review and editing were done by Bo Zheng; conceptualization, supervision—review and editing were performed by Xinggang Ma; supervision, investigation—review and editing were done by Longjie Zhu and Liu Wei. Every author reviewed and gave their approval to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Informed consent
Not applicable for studies not involving humans.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable for studies not involving humans or animals.
Additional information
Communicated by: Hassan Babaie
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Liu, W., Zheng, B. et al. A regional-scale distribution changes and influencing factors of glacial lakes in Xizang autonomous region. Earth Sci Inform 18, 103 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01638-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01638-3