Abstract
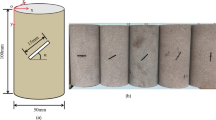
Landslides, as the most frequent geological disasters, are approximated in this study as cofacial discontinuous jointed rock masses subjected to uniaxial compression conditions. Uniaxial compression tests were carried out on 5 groups of yellow sandstone samples with prefabricated cracks from dry to saturated state. The mechanical properties and failure modes of sandstones with coplanar discontinuous joints under different water content are analyzed, combining mechanical, acoustic and digital image correlation methods. The primary findings of the research are as follows: the uniaxial compressive strength of the rock masses decreases nonlinearly with increasing moisture content. The b value of the sample with high water content fluctuates more, the cracks inside the rock are more likely to develop into macroscopic cracks, and the proportion of shear signal is reduced. Based on DIC analysis, with the increase of water content, the cohesion and internal friction angle between rock particles decreases, and more tensile failure occurs in the rock failure process. This leads to easier separation of particles in the vicinity of wing cracks, which are already created in the elastic phase of the rock, and accelerates crack extension. These observations are consistent with the increase in tensile signals from acoustic emissions and the observed failure mode of the specimens. These findings can provide a theoretical reference for slope stability assessment under the background of geological engineering.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Cheng FQ, Li ZH, Li GA, Wei Y, Yin S, Liu SJ, Kong YH (2018) Influence of prefabricated fissure angle on sandstone damage and infrared radiation temperature characteristics. J Geophys Eng 15(4):1187–1196
Ciantia MO, Castellanza R, di Prisco C (2015) Experimental study on the water-induced weakening of Calcarenites. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48(2):441–461
Davarpanah SM, Sharghi M, Tarifard A, Török A, Vásárhelyi B (2022) Studies on the mechanical properties of dry, saturated, and frozen marls using destructive and non-destructive laboratory approaches. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civil Eng 46(2):1311–1328
Duperret A, Taibi S, Mortimore RN, Daigneault M (2005) Effect of groundwater and sea weathering cycles on the strength of chalk rock from unstable coastal cliffs of NW France. Eng Geol 78(3–4):321–343
Gao R, Wang W, Xiong X, Li J, Xu C (2023) Effect of curing temperature on the mechanical properties and pore structure of cemented backfill materials with waste rock-tailings. Constr Build Mater 409:133850
Guo J, Yu L, Wen Z, Feng G, Bai J, Wen X, Qi T, Qian R, Zhu L, Guo X, Mi X (2022) Mechanical and acoustic emission characteristics of coal-like rock specimens under static direct shear and dynamic normal load. Materials 15(19)
Huang D, Li B, Ma W-Z, Cen D-F, Song Y-X (2020) Effects of bedding planes on fracture behavior of sandstone under semicircular bending test. Theor Appl Fract Mech 108
Huang K, Kang B, Zha F, Li Y, Zhang Q, Chu C (2022) Disintegration characteristics and mechanism of red-bed argillaceous siltstone under drying-wetting cycle. Environ Earth Sci 81(12)
Huang SB, Liu YZ, Guo YL, Zhang ZL, Cai YT (2019) Strength and failure characteristics of rock-like material containing single crack under freeze-thaw and uniaxial compression. Cold Reg Sci Technol 162:1–10
Ke B, Zhang CY, Liu CJ, Ding LM, Zheng Y, Li N, Wang YX, Lin H (2021) An experimental study on characteristics of impact compression of freeze-thawed granite samples under four different states considering moisture content and temperature difference. Environ Earth Sci 80(18):12
Lei RD, Zhang ZY, Berto F, Ranjith PG, Liu L (2020a) Cracking process and acoustic emission characteristics of sandstone with two parallel filled-flaws under biaxial compression. Eng Fract Mech 237:22
Lei RD, Zhang ZY, Ge ZL, Berto F, Wang G, Zhou L (2020b) Deformation localization and cracking processes of sandstone containing two flaws of different geometric arrangements. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 43(9):1959–1977
Li CM, Liu N, Liu WR (2020) Experimental investigation of mechanical behavior of sandstone with different moisture contents using the acoustic emission technique. Adv Civil Eng 2020:10
Li GH, Wang YT, Wang D, Yang XX, Yang SP, Zhang SP, Li CJ, Teng RX (2023a) An unsteady creep model for a rock under different moisture contents. Mech Time-Depend Mater 27(2):291–305
Li HR, Shen RX, Li DX, Jia HS, Li TX, Chen TQ, Hou ZH (2019) Acoustic emission multi-parameter analysis of dry and saturated sandstone with cracks under uniaxial compression. Energies 12(10):18
Li S, Lin H, Lin Q-b, Wang Y-x, Zhao Y-l, Hu H-h (2023b) Mechanical behavior and failure characteristics of double-layer composite rock-like specimens with two coplanar joints under uniaxial loading. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 33(9):2815–2831
Li SN, Huang ZH, Liang Q, Liu J, Luo SL, Zhou WQ (2022) Evolution mechanism of mesocrack and macrocrack propagation in carbonaceous mudstone under the action of dry-wet cycles. Geofluids 2022
Liu B, Sun YD, Wang B, Han YH, Zhang RH, Wang JX (2020a) Effect of water content on mechanical and electrical characteristics of the water-rich sandstone during freezing. Environ Earth Sci 79(10):14
Liu B, Sun YD, Wang J, Zhang G (2020b) Characteristic analysis of crack initiation and crack damage stress of sandstone and mudstone under low-temperature condition. J Cold Reg Eng 34(3):10
Luo ZY, Zhang YF, Du SG, Huang M, Lyu Y (2023) Experimental study on shear performance of saw-tooth rock joint with weak interlayer under different moisture contents and filling degrees. Front Earth Sci 10:10
Miao S, Pan P-Z, Konicek P, Yu P, Liu K (2021) Rock damage and fracturing induced by high static stress and slightly dynamic disturbance with acoustic emission and digital image correlation techniques. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 13(5):1002–1019
Pan J, Tang Y, Yuan W, Luo J, Chen Y, Lin H (2024) A method for automatically identifying the shape of locking sections in slopes. Environ Earth Sci 83(8):243
Sabbagh-Yazdi SR, Misaghian M (2017) Effect of water infiltration through concrete block spillways on the slope stability of earth overflow dams. Eur J Environ Civ Eng 21(9):1114–1127
Shao X, Tian C, Li C, Fang Z, Zhao B, Xu B, Ning J, Li L, Tang R (2022) The experimental investigation on mechanics and damage characteristics of the Aeolian sand paste-like backfill materials based on acoustic emission. Materials 15(20)
Shen RX, Li TX, Li HR, He S, Zhao EL, Hou ZH, Chen TQ (2021) Study on the effect of water on electromagnetic radiation characteristics of fractured sandstone under load. Environ Earth Sci 80(3):14
Shi ZM, Li JT, Wang J (2022) Effect of the upper limit stress on the fatigue properties and crack propagation processes of sandstones containing pre-existing crack under fatigue-creep interaction. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 45(5):1391–1405
Su Y, Dong L, Pei Z (2022) Non-destructive testing for cavity damages in automated machines based on acoustic emission tomography. Sensors 22(6)
Tan H, Li J, Shi Z, Wang M, Wang J, Li J (2023) Damage evolution and failure characteristics of red sandstone with prefabricated crack under coupled dry-wet cycle-fatigue loading. Int J Fatigue 175
Tang Y, Lin H, Cao RH, Sun SW, Zha WH (2023) Role of rock sections in intermittent joints in controlling rock mass strength and failure modes. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56(7):5203–5221
Tang Y, Lin H, Li S, Chen Y, Ou K, Xie L (2024) Numerical study of rock bridge shape identification and rock bridge damage mechanism. Comput Part Mech
Tomor AK, Nichols JM, Orbán Z (2024) Evaluation of the loss of uniaxial compressive strength of sandstones due to moisture. Int J Archit Heritage 18(5):771–787
Wang HL, Xu WY, Jia CJ, Cai M, Meng QX (2016) Experimental research on permeability evolution with microcrack development in sandstone under different fluid pressures. J Geotech Geoenviron 142(6)
Wang WN, Yao QL, Tang CJ, Li HT, Liu HY, Shan CH (2022) Mechanical properties damage, fracture evolution, and constitutive model of siltstone under the effect of moisture content. Geofluids 2022:18
Wang ZY, Lin H, Yang CY (2024) Fatigue-thermal damage characteristics of red sandstone with a hole under high-temperature cyclic loading coupling and microstructural degradation. J Mater Res Technol 33:3250–3263
Xu RC (2019) Influence of flaw inclination angle on cracking behavior of rock-like materials under uniaxial compression. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2019:10
Yu Z, Zhang L, Jiang P, Papelis C, Li Y (2015) Study on water-rock interactions of trace elements in groundwater with leaching experiments. Groundwater 53:95–102
Zha F, Huang K, Kang B, Sun X, Su J, Li Y, Lu Z (2022) Deterioration characteristic and constitutive model of red-bed argillaceous siltstone subjected to drying-wetting cycles. Lithosphere 2022(1)
Zhang C, Bai QS, Han PH, Wang L, Wang XJ, Wang FT (2023) Strength weakening and its micromechanism in water-rock interaction, a short review in laboratory tests. Int J Coal Sci Technol 10(1):15
Zhao K, Liu Z, Zeng P, Gong C, Li Y (2022) Fracture process analysis and acoustic emission response of cemented tailings backfill with different sizes under uniaxial compression. Materials 15(22)
Zhao K, Ran SH, Zeng P, Yang DX, Teng TY (2021) Effect of moisture content on characteristic stress and acoustic emission characteristics of red sandstone. Rock Soil Mech 42(4):899–908
Zheng WH, Shi TW, Pan YS, Luo H, Lü XF (2022a) Effects of water content on the charge induced signal of rock. Rock Soil Mech 43(3):659–668
Zheng Z, Zhou Z, Wang Y, Su Y (2022b) The prediction of evacuation efficiency on metro platforms based on passengers’ decision-making capability. Appl Sci 12(18):8992
Zhou ZL, Cai X, Ma D, Cao WZ, Chen L, Zhou J (2018) Effects of water content on fracture and mechanical behavior of sandstone with a low clay mineral content. Eng Fract Mech 193:47–65
Zhu J, Deng JH, Huang YM, He ZL (2019) Influence of water on the fracture process of marble with acoustic emission monitoring. KSCE J Civ Eng 23(7):3239–3249
Funding
This paper gets its funding from Projects (42277175) supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2023JJ30657) supported by Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China; Guizhou Provincial Major Scientific and Technological Program (2023–425); Hunan Provincial Department of natural resources geological exploration project (2023ZRBSHZ056); The First National Natural Disaster Comprehensive Risk Survey in Hunan Province (2022–70).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Methodology, H.L.; Validation, S.Y.C., H.L. and X.Z; Formal analysis, S.Y.C. and K.O.; Writing—original draft, S.Y.C., H.L. and C.Y.Y.; Writing—review & editing, X.Z., C.Y.Y., and K.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: Hassan Babaie
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Lin, H., Ou, K. et al. Mechanical properties and failure modes of discontinuous jointed considering water softening effects. Earth Sci Inform 18, 196 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-025-01694-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-025-01694-3