Abstract
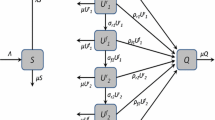
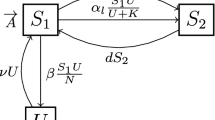
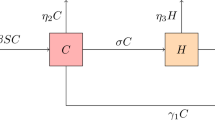
In this paper, a synthetic drugs transmission model with treatment is formulated based on the principles of mathematical epidemiology. The model considers that relapse can occur among those individuals who have a history of drug abuse and we distinguish the addiction rates of susceptible individuals who have a history of drug abuse and those who have not. The global dynamics of this model are determined by the basic reproduction number, \(R_{0}\), under certain conditions. If \(R_{0}<1\), the drug-free equilibrium is globally exponentially stable for a special case and the exponential convergence rate can be unveiled, and if \(R_{0}>1\), the drug-addiction equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable under certain conditions. Sensitivity analysis is performed to seek for effective control measures for drug abuse. Numerical simulations are also carried out to confirm the analytical results.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castellani, B., Wedgeworth, R., Wootton, E., Rugle, L.: A bi-directional theory of addiction: examining coping and the factors related to substance relapse. Addict. Behav. 22(1), 139 (1997)
Cui, J.A., Tao, X., Zhu, H.: An SIS infection model incorporating media coverage. Rocky Mt. J. Math. 38(2008), 1323–1334 (2008)
Fang, B., Li, X., Martcheva, M., Cai, L.: Global stability for a heroin model with two distributed delays. Discrete Contin. Dyn. B 19(3), 715–733 (2017)
Grunbaum, J.A., Tortolero, S., Weller, N., Gingiss, P.: Cultural, social, and intrapersonal factors associated with substance use among alternative high school students. Addict. Behav. 25, 145–151 (2000)
Heffernan, K., Cloitre, M., Tardiff, K., Marzuk, P.M., Portera, L., Leon, A.C.: Childhood trauma as a correlate of lifetime opiate use in psychiatric patients. Addict. Behav. 25(5), 797 (2000)
Huang, G., Liu, A.: A note on global stability for a heroin epidemic model with distributed delay. Appl. Math. Lett. 26(7), 687–691 (2013)
Huo, H., Dang, S., Li, Y.: Stability of a two-strain tuberculosis model with general contact rate. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2010(6), 759–786 (2010)
Huo, H., Zhu, C.: Influence of relapse in a giving up smoking model. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2013, 123–185 (2013)
Kalula, A.S., Nyabadza, F.: A theoretical model for substance abuse in the presence of treatment. S. Afr. J. Sci. 108(3/4), 96–107 (2012)
Katerndahl, D.A., Realini, J.P.: Relationship between substance abuse and panic attacks. Addict. Behav. 24(5), 731–736 (1999)
LaSalle, J.P.: The stability of dynamical systems. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 27(11), 1121–1130 (1976)
López-Torrecillas, F., Godoy García, J.F., Pérez, G.M., Godoy, I.D., Sánchez-Barrera, M.B.: Variables modulating stress and coping that discriminate drug consumers from low or nondrug consumers. Addict. Behav. 25(1), 161–165 (2000)
Ma, M., Liu, S., Li, J.: Does media coverage influence the spread of drug addiction? Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 50, 169–179 (2017)
Mulone, G., Straughan, B.: A note on heroin epidemics. Math. Biosci. 218(2), 138 (2009)
Mushanyu, J., Nyabadza, F., Stewart, A.G.R.: Modelling the trends of inpatient and outpatient rehabilitation for methamphetamine in the Western Cape province of South Africa. BMC Res. Notes 8(1), 1–13 (2015)
Nyabadza, F., Hovemusekwa, S.D.: From heroin epidemics to methamphetamine epidemics: modelling substance abuse in a South African province. Math. Biosci. 225(2), 132–140 (2010)
Nyabadza, F., Njagarah, J.B.H., Smith, R.J.: Modelling the dynamics of crystal meth (Tik) abuse in the presence of drug-supply chains in South Africa. Bull. Math. Biol. 75(1), 24–48 (2013)
Obot, I.S., Anthony, J.C.: Association of school dropout with recent and past injecting drug use among African American adults. Addict. Behav. 24(5), 701 (1999)
Sahu, G.P., Dhar, J.: Dynamics of an SEQIHRS epidemic model with media coverage, quarantine and isolation in a community with pre-existing immunity. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 421(2), 1651–1672 (2015)
Samanta, G.P.: Dynamic behaviour for a nonautonomous heroin epidemic model with time delay. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 35(1–2), 161–178 (2011)
Sun, C., Yang, W., Arino, J., Khan, K.: Effect of media-induced social distancing on disease transmission in a two patch setting. Math. Biosci. 230(2), 87–95 (2011)
Tchuenche, J.M., Dube, N., Bhunu, C.P., Smith, R.J., Bauch, C.T.: The impact of media coverage on the transmission dynamics of human influenza. BMC Public Health 11(Suppl 1), S5 (2011)
van den Driessche, P., Watmough, J.: Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 180(1–2), 29 (2002)
Wang, X., Yang, J., Li, X.: Dynamics of a heroin epidemic model with very population. Appl. Math. 2(6), 732–738 (2011)
White, E., Comiskey, C.: Heroin epidemics, treatment and ODE modelling. Math. Biosci. 208(1), 312 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11601405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Zhang, L. & Xing, Y. Modelling and stability of a synthetic drugs transmission model with relapse and treatment. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 60, 465–484 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-018-01223-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-018-01223-0