Abstract
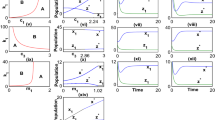
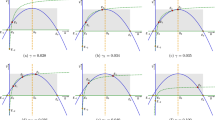
Empirical studies have shown that animals often focus on short-term benefits under conditions of predation risk, which increases the likelihood that they will co-operate with others. With this motivation, we propose and analyze a predator and two prey model with the assumption that during predation the members of both prey make a team to reduce risk of predation. We incorporate Monod–Haldane and Holling type II functional response to model the interaction with predator. Firstly, we discuss conditions which ensure that model system has a unique positive solution. We investigate stability and Hopf bifurcation conditions to explore dynamics of system around positive equilibrium. We also derive Kolmogorov conditions for the parametric restriction of the system. Secondly, we present numerical solution which substantiate our analytical results. In numerical simulation, we observe period doubling and period halving cascade which explore the dynamical complexity of predator-prey system. Finally, we conclude that partial co-operation and low defense may lead to extinction of prey species.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, T., Saleem, M.: Complex dynamics in a ratio-dependent two-predator one-prey model. Comput. Appl. Math. 34(1), 265–274 (2014)
Andrews, J.F.: A mathematical model for the continuous culture of micro-organisms utilizing inhibitory substrate. Biotecnhnol. Bioeng. 10, 700–723 (1968)
Ali, N., Jafar, M.: Global dynamics of a modified Leslie–Gower predator-prey model with Crowley–Martin functional responses. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 13, 271–293 (2013)
Agrawal, R., Jana, D., Upadhayay, R., Rao, V.S.H.: Complex dynamics of sexually reproductive generalist predator and gestation delay in a food chain model: double Hopf-bifurcation to Chaos. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 55, 513–547 (2017)
Beddington, J.R.: Mutual interference between parasites or predators and its effect on searching efficiency. J. Anim. Ecol. 44, 331–340 (1975)
Cramer, N., May, R.: Interspecific competition, predation and species diversity: a comment. J. Theor. Biol. 34, 280–292 (1972)
De Angelis, D.L., Goldstein, R.A., ONeill, R.V.: A model for tropic interaction. Ecology 56, 881–892 (1975)
Dubey, B., Upadhyay, R.K.: Persistence and extinction of one-prey and two- predators system. Nonlinear Anal. 9, 307–329 (2004)
Dugatkin, L.A.: Co-operation Among Animals: A Evolutionary Prospective. Oxford University Press, New York (1997)
Freedman, H.I.: Hopf bifurcation in three species food chain models with group defense. Math. Biosci. 111, 73–87 (1992)
Freedman, H.I., Hongshun, Q.: Interaction leading to persistence in predator-prey systems with group defense. Bull. Math. Biol. 50, 517–530 (1988)
Freedman, H.I.: Deterministic Mathematical Models in Population Ecology. M. Dekker, New York (1980)
Gause, G.F.: Struggle for Existence. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore (1934)
Hasting, A., Powell, T.: Chaos in a three-species food chain. Ecology 72, 896–903 (1991)
Holmes, J.C., Bethel, W.M.: Modification of intermediate host behavior parasites. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 51, 123–49 (1972)
Holling, C.: The functional response of predators to prey density and its role in mimicry and population regulation. Memo. Entom. Soc. Can. 97, 5–60 (1965)
Hwang, Z.W.: Global analysis of the predator-prey system with Beddington–DeAngelis functional response. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 281, 395–401 (2003)
Kot, M.: Elements of Mathematical Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Kuang, Y., Freedman, H.I.: Uniqueness of limit cycles in Gause-type models of predator-prey systems. Math. Biol. 88, 67–84 (1988)
Klebanoff, A., Hastings, A.: Chaos in one-predator, two-prey models: general results from bifurcation theory. Math. Biol. 122, 221–233 (1994)
Kolmogorov, A.N.: Sulla Teoria di Voltera della Lotta per IEsisttenza. Giorn. Instituto Ital. Attuari. 7, 74–80 (1936)
Lotka, A.: Elements of Mathematical Biology. Dover Publications, New York (1956)
Martin, M.M., Mitani, J.C.: Conflict and co-operation in wild life chimpanzees. Adv. Study Behav. 35, 275–331 (2005)
Mischaikow, K., Wolkowicz, G.S.: A predator-prey system involving group defense: a connection matrix approach. Nonlinear. Anal. 14, 955–969 (1990)
May, R.M.: Limit cycles in predator-prey communities. Science 177, 900–902 (1972)
Murray, J.D.: Mathematical Biology I: An Introduction. Springer, New Delhi (2002)
Pal, R., Basu, D., Banerjee, M.: Modelling of phytoplankton allelopathy with Monod–Haldane type functional response–a mathematical study. Biosystems 95, 243–253 (2009)
Pasquet, A., Krafft, B.: Cooperation and prey capture efficiency in a social spider, Anelosimus eximius (Araneae, Theridiidae). Ethology 90, 121–133 (1992)
Raw, S.N., Mishra, P., Kumar, R., Thakur, S.: Complex behavior of prey-predator system exhibiting group defense: a mathematical modeling study. Chaos. Soli. Frac. 100, 74–90 (2017)
Sokol, J., Howell, J.A.: Kinetics of phenol oxidation by washed cell. Biotecnhnol. Bioeng. 23, 203–249 (1980)
Shen, C.: Permanence and global attractivity of the food-chain system with Holling IV type functional response. Appl. Math. Comput. 194(1), 179–185 (2007)
Strogatz, S.H.: Non-linear Dyanmics and Chaos with Applications to Physics, Bilogy, Chemistry, and Engineering. Westview Press, Colorado (2001)
Tripathi, J.P., Abbas, S., Thankur, M.: Local and global stability analysis of a two prey one predator model with help. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19, 3284–3297 (2014)
Tener, J.S.: Muskoxen. Queens Printer, Ottawa (1965)
Upadhyay, R.K., Raw, S.N.: Complex dynamics of a three species food-chain model with Holling type IV functional response. Nonlinear Anal. Model Control 16, 353–374 (2011)
Upadhyay, R.K., Naji, R.K., Raw, S.N., Dubey, B.: The role of top predator interference on the dynamics of a food chain model. Commun. Nonlinear. Sci. Numer. Simul. 18, 757–768 (2013)
Volterra, V.: Fluctuations in the abundance of a species considered mathematically. Nature 118, 558–560 (1926)
Wang, W., Wang, H., Li, Z.: The dynamic complexity of a three-species Beddington-type food chain with impulsive control strategy. Chaos. Soli. Frac. 32, 1772–1785 (2007)
Wiggins, S.: Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical System and Chaos, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2003)
Wolkowicz, G.S.K.: Bifurcation analysis of a predator-prey system involving group defense. SIAM. J. Appl. Math. 48, 592–606 (1988)
Zhao, M., Songjuan, L.V.: Chaos in a three-species food chain model with a Beddington–DeAngelis functional response. Chaos. Soli. Frac. 40, 2305–2316 (2009)
Zhang, S.W., Tan, D.J., Chen, L.S.: Chaos in periodically forced Holling type IV predator-prey system with impulsive perturbations. Chaos. Soli. Frac. 27, 980–90 (2006)
Acknowledgements
The work done in this paper is supported by a grant (File No. ECR/2017/000141) under Early Career Research (ECR) Award, Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, to the corresponding author (SNR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, P., Raw, S.N. Dynamical complexities in a predator-prey system involving teams of two prey and one predator. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 61, 1–24 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-018-01236-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-018-01236-9