Abstract
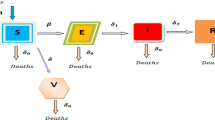
This work applies a novel geometric criterion for nonlinear autonomous differential equations developed by Lu and Lu (NARWA 36:20–43, 2017) to a nonlinear SEIVS epidemic model with temporary immunity and achieves its threshold dynamics. Specifically, global-stability problems for the SEIVS model of Cai and Li (AMM 33:2919–2926, 2009) are effectively solved. The corresponding optimal control system with vaccination, awareness campaigns and treatment is further established and four different control strategies are compared by numerical simulations to contain hepatitis B. It is concluded that joint implementation of these measures can minimize the numbers of exposed and infectious individuals in the shortest time, so it is the most efficient strategy to curb the hepatitis B epidemic. Moreover, vaccination for newborns plays the core role and maintains the high level of population immunity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krämer, A., Kretzschmar, M., Krickeberg, K.: Modern infectious disease epidemiology: concepts, methods, mathematical models, and public health. Springer, Berlin, Germany (2010)
WHO, Immunization coverage, 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/immunization-coverage Accessed 7 December 2020
Cai, L.M., Li, X.Z.: Analysis of a SEIV epidemic model with a nonlinear incidence rate. Appl. Math. Model. 33(7), 2919–2926 (2009)
Sahu, G.P., Dhar, J.: Analysis of an SVEIS epidemic model with partial temporary immunity and saturation incidence rate. Appl. Math. Model. 36(3), 908–923 (2012)
Cai, L.M., Li, Z.Q., Song, X.Y.: Global analysis of an epidemic model with vaccination. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 57(1), 605–628 (2018)
Lahrouz, A., Omari, L., Kiouach, D., Belmaâtic, A.: Complete global stability for an SIRS epidemic model with generalized non-linear incidence and vaccination. Appl. Math. Comput. 218(11), 6519–6525 (2012)
Li, T., Zhang, F.Q., Liu, H.W., Chen, Y.M.: Threshold dynamics of an SIRS model with nonlinear incidence rate and transfer from infectious to susceptible. Appl. Math. Lett. 70, 52–57 (2017)
Liu, W.M., Levin, S.A., Iwasa, Y.: Influence of nonlinear incidence rates upon the behavior of SIRS epidemiological models. J. Math. Biol. 23(2), 187–204 (1986)
Lu, M., Huang, J.C., Ruan, S.G., Yu, P.: Bifurcation analysis of an SIRS epidemic model with a generalized nonmonotone and saturated incidence rate. J. Differ. Equ. 267(3), 1859–1898 (2019)
Capasso, V., Serio, G.: A generalization of the Kermack–McKendrick deterministic epidemic model. Math. Biosci. 42, 43–61 (1978)
Xiao, D.M., Ruan, S.G.: Global analysis of an epidemic model with a nonlinear incidence rate. Math. Biosci. 208(2), 419–429 (2007)
Khan, M.A., Ullah, S., Khan, Y., Farhan, M.A.: Modeling and scientific computing for the transmission dynamics of avian influenza with half-saturated incidence. Int. J. Model Simul. Sci. Comput. 11(4), 2050035 (2020)
Anderson, R.M., May, R.M.: Infectious diseases of humans: dynamics and control. Oxford University Press, London (1991)
Lu, G.C., Lu, Z.Y.: Geometric approach to global asymptotic stability for the SEIRS models in epidemiology. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 36, 20–43 (2017)
Lu, G.C., Lu, Z.Y.: Global asymptotic stability for the SEIRS models with varying total population size. Math. Biosci. 296, 17–25 (2018)
Li, M.Y., Muldowney, J.S.: A geometric approach to the global-stability problems. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 27(4), 1070–1083 (1996)
Li, M.Y., Graef, J.R., Wang, L.C., Karsai, J.: Global dynamics of a SEIR model with varying total population size. Math. Biosci. 160, 191–213 (1999)
Li, M.Y., Muldowney, J.S.: Dynamics of differential equations on invariant manifolds. J. Differ. Equ. 168, 295–320 (2000)
Doungmo Goufo, E.F., Khan, Y., Chaudhry, Q.A.: HIV and shifting epicenters for COVID-19, an alert for some countries. Chaos Solitons Fractals 139, 110030 (2020)
Khan, M.A., Khan, Y., Islam, S.: Complex dynamics of an SEIR epidemic model with saturated incidence rate and treatment. Phys. A 493, 210–227 (2018)
Khan, M.A., Khan, R., Khan, Y., Islam, S.: A mathematical analysis of Pine Wilt disease with variable population size and optimal control strategies. Chaos Solitons Fractals 108, 205–207 (2018)
Khan, M.A., Iqbal, N., Khan, Y., Alzahrani, E.: A biological mathematical model of vector-host disease with saturated treatment function and optimal control strategies. Math. Biosci. Eng. 17(4), 3972–3997 (2020)
Arino, J., Cooke, K.L., van den Driessche, P., Velasco-Hernndez, J.: An epidemiology model that includes a leaky vaccine with a general waning function. Discrete Cont. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 4(2), 479–495 (2004)
Huo, J.J., Zhao, H.Y., Zhu, L.H.: The effect of vaccines on backward bifurcation in a fractional order HIV model. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 26, 289–305 (2015)
WHO: Global tuberculosis report 2020, (2020). Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240013131 Accessed 7 December 2020
Wang, L.W., Liu, Z.J., Xu, D.S., Zhang, X.A.: Global dynamics and optimal control of an influenza model with vaccination, media coverage and treatment. Int. J. Biomath. 10, 1750068 (2017)
Graber-Stiehl, I.: The silent epidemic killing more people than HIV, malaria or TB. Nature 564(7734), 24–26 (2018)
Lazarus, J.V., Picchio, C., Dillon, J.F., Rockstroh, J.K., Weis, N., Buti, M.: Too many people with viral hepatitis are diagnosed late-with dire consequences. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol Hepatol 16, 451–452 (2019)
Pontryagin, L., Boltyanskii, V., Gramkrelidze, R., Mischenko, E.: The mathematical theory of optimal processes. Wiley, New York (1962)
Fleming, W.H., Rishel, R.W.: Deterministic and stochastic optimal control. Springer, Berlin (1975)
Pang, L.Y., Ruan, S.G., Liu, S.H., Zhao, Z., Zhang, X.A.: Transmission dynamics and optimal control of measles epidemics. Appl. Math. Comput. 256, 131–147 (2015)
Wang, X.W., Peng, H.J., Shi, B.Y., Jiang, D.H., Zhang, S., Chen, B.S.: Optimal vaccination strategy of a constrained time-varying SEIR epidemic model. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 67, 37–48 (2019)
Yang, J.Y., Modnak, C., Wang, J.: Dynamical analysis and optimal control simulation for an age-structured cholera transmission model. J. Franklin. I 356, 8438–8467 (2019)
Lv, W., Ke, Q., Li, K.Z.: Dynamic stability of an SIVS epidemic model with imperfect vaccination on scale-free networks and its control strategy. J. Franklin. I 357, 7092–7121 (2020)
Djidjou Demasse, R., Tewa, J.J., Bowong, S., Emvudu, Y.: Optimal control for an age-structured model for the transmission of hepatitis B. J. Math. Biol. 73(2), 305–333 (2016)
Melesse, D.Y., Gumel, A.B.: Global asymptotic properties of an SEIRS model with multiple infectious stages. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 366, 202–217 (2010)
Khan, M.A., Khan, Y., Khan, T.W.: Dynamical system of a SEIQV epidemic model with nonlinear generalized incidence rate arising in biology. Int. J. Biomath. 10(7), 1750096 (2017)
Liu, J.L., Zhang, T.L.: Global stability for a tuberculosis model. Math. Comput. Model. 54, 836–845 (2011)
van den Driessche, P., Watmough, J.: Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 180, 29–48 (2002)
LaSalle, J.P.: The stability of dynamical systems, in: regional conference series in Applied Mathematics. SIAM, Philadephia (1976)
Tian, Y.N., Liu, X.N.: Global dynamics of a virus dynamical model with general incidence rate and cure rate. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 16, 17–26 (2014)
Bi, K.M., Chen, Y.Y., Wu, C.H.J., Ben-Arieh, D.: A memetic algorithm for solving optimal control problems of Zika virus epidemic with equilibriums and backward bifurcation analysis. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 84, 105176 (2020)
World Health Statistics 2020 visual summary. Available from: https://www.who.int/data/gho/whs-2020-visual-summary Accessed 7 December 2020
Pang, J., Cui, J.A., Zhou, X.: Dynamical behavior of a hepatitis B virus transmission model with vaccination. J. Theor. Biol. 265(4), 572–578 (2010)
Edmunds, W.J., Medley, G.F., Nokes, D.J.: The transmission dynamics and control of hepatitis B virus in the Gambia. Stat. Med. 15, 2215–2233 (1996)
Zou, L., Zhang, W.N., Ruan, S.G.: Modeling the transmission dynamics and control of hepatitis B virus in China. J. Theor. Biol. 262, 330–338 (2010)
Liu, W.M., Hethcote, H.W., Levin, S.A.: Dynamical behavior of epidemiological models with nonlinear incidence rates. J. Math. Biol. 25, 359–380 (1987)
Khan, Y., Faraz, N., Kumar, S., Yildirim, A.: A coupling method of homotopy perturbation and laplace transformation for fractional models. U.P.B. Sci. Bull. Series A 74(1), 57–68 (2012)
Khan, Y., Faraz, N., Yildirim, A., Wu, Q.B.: Fractional variational iteration method for fractional initial-boundary value problems arising in the application of nonlinear science. Comput. Math. Appl. 62, 2273–2278 (2011)
Khan, Y., Wu, Q.B., Faraz, N., Yildirim, A., Madanie, M.: A new fractional analytical approach via a modified Riemann-Liouville derivative. Appl. Math. Lett. 25, 1340–1346 (2012)
Khan, Y., Latifizadeh, H.: Application of new optimal homotopy perturbation and adomian decomposition methods to the MHD non-Newtonian fluid flow over a stretching sheet. Int. J. Numer. Method H. 24, 124–136 (2012)
Khan, Y.: A method for solving nonlinear time-dependent drainage model. Neural Comput. Appl. 23, 411–415 (2013)
Khan, Y., Vázquez-Leal, H., Wu, Q.: An efficient iterated method for mathematical biology model. Neural Comput. Appl. 23, 677–682 (2013)
Khan, Y., Wu, Q.B.: Homotopy perturbation transform method for nonlinear equations using He’s polynomials. Comput. Math. Appl. 61, 1963–1967 (2011)
Khan, Y.: Two-dimensional boundary layer flow of chemical reaction MHD fluid over a shrinking sheet with suction and injection. J. Aerosp. Eng. Trans. ASCE 27, 04014019 (2014)
Khan, Y., Vázquez-Leal, H., Faraz, N.: An auxiliary parameter method using adomian polynomials and laplace transformation for nonlinear differential equations. Appl. Math. Model. 37, 2702–2708 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Nos. 2019CFB241, 2019CFB773) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11871201,11961023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Liu, Z., Wang, L. et al. An application of a novel geometric criterion to global-stability problems of a nonlinear SEIVS epidemic model. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 67, 707–730 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-020-01487-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-020-01487-5