Abstract
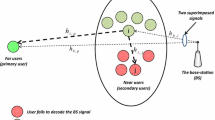
This paper investigates the performance of iterative interference alignment (IA) with spatial hole sensing in K-user multi-input multi-output (MIMO) cognitive radio (CR) networks. In the considered network, there are some unused degrees of freedom (DoF) or equivalently spatial holes in the primary network (PN) where the secondary network (SN) users communicate without causing harmful interference to the PN receivers. First, the generalized likelihood ratio test method is utilized to determine the availability of the unused DoFs; then, it is decided whether individual primary streams are present in the PN. With the aid of precoding and suppression matrices generated by an iterative IA approach, the interferences in the PN that are caused by the SN are aligned, and due to the secondary transmission, interference leakage on the kth primary receiver decreases below 10− 6. The effects of the detection threshold values and the number of transmitter and receiver antennas are investigated in terms of detection and false alarm probability. Finally, the amplify-and-forward (AF) relaying scheme in the SN is evaluated and the impact of the relaying architecture on the system performance is analyzed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaudhari S, Cabric D (2019) Power control and frequency band selection policies for underlay MIMO cognitive radio. IEEE Trans on Cognitive Commun and Netw 5(2):304–317
Li Y, Kudathanthirige D, Baduge GAA (2018) Massive MIMO relay networks with underlay spectrum sharing. IEEE Trans on Cognitive Commun and Netw 4(4):677–691
Al-Badarneh YH, Georghiades CN, Alouini MS (2019) Asymptotic performance analysis of generalized user selection for interference-limited multiuser secondary networks. IEEE Trans on Cognitive Commun and Netw 5(1):82–92
Zhang C, Jiang C, Kuang L, Jin J, He Y, Han Z (2019) Spatial spectrum sharing for satellite and terrestrial communication networks. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 55(3):1075–1089
Men H, Zhao N, Jin M, Kim JM (2015) Optimal transceiver design for interference alignment based cognitive radio networks. IEEE Commun Lett 19(8):1442–1445
Haykin S (2005) Cognitive radio: brain-empowered wireless communications. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 23(2):201–220
Mitola J, Maguire GQ (1999) Cognitive radio: making software radios more personal. IEEE Personal Commun 6(4):13–18
Biglieri E, Goldsmith AJ, Greenstein LJ, Mandayam NB, Poor HV (2013) Principles of cognitive radio. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
El Tanab M, Hamouda W (2016) Resource allocation for underlay cognitive radio networks: A survey. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 19(2):1249–1276
Liang W, Ng SX, Hanzo L (2017) Cooperative overlay spectrum access in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 19(3):1924–1944
Ali A, Hamouda W (2016) Advances on spectrum sensing for cognitive radio networks: Theory and applications. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 19(2):1277–1304
Zhao N, Yu FR, Jin M, Yan Q, Leung VC (2016) Interference alignment and its applications: A survey, research issues, and challenges. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 18(3):1779–1803
Razaviyayn M, Sanjabi M, Luo ZQ (2012) Linear transceiver design for interference alignment: Complexity and computation. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 58(5):2896–2910
Liu T, Yang C (2013) On the feasibility of linear interference alignment for MIMO interference broadcast channels with constant coefficients. IEEE Trans Sig Process 61(9):2178–2191
Gonzalez O, Beltran C, Santamaria I (2014) A feasibility test for linear interference alignment in MIMO channels with constant coefficients. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 60(3):1840–1856
Razaviyayn M, Lyubeznik G, Luo ZQ (2011) On the degrees of freedom achievable through interference alignment in a MIMO interference channel. IEEE Trans Sig Process 60(2):812–821
Zhao N, Yu FR, Sun H, Li M (2015) Adaptive power allocation schemes for spectrum sharing in interference-alignment-based cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans Veh Tech 65(5):3700– 3714
Koo B, Park D (2012) Interference alignment with cooperative primary receiver in cognitive networks. IEEE Commun Lett 16(7):1072–1075
Gomadam K, Cadambe VR, Jafar SA (2011) A distributed numerical approach to interference alignment and applications to wireless interference networks. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 57(6):3309–3322
Arzykulov S, Nauryzbayev G, Tsiftsis TA, Abdallah M (2018) On the performance of wireless powered cognitive relay network with interference alignment. IEEE Trans on Commun 66(9):3825–3836
Mosleh S, Abouei J, Aghabozorgi MR (2014) Distributed opportunistic interference alignment using threshold-based beamforming in MIMO overlay cognitive radio. IEEE Trans Veh Tech 63(8):3783–3793
Hasani-Baferani M, Abouei J, Zeinalpour-Yazdi Z (2016) Interference alignment in overlay cognitive radio femtocell networks. IET Commun 10(11):1401–1410
Zhang R, Lim TJ, Liang YC, Zeng Y (2010) Multi-antenna based spectrum sensing for cognitive radios: A GLRT approach. IEEE Trans Commun 58(1):84–88
Font-Segura J, Wang X (2010) GLRT-based spectrum sensing for cognitive radio with prior information. IEEE Trans Commun 58(7):2137–2146
Alizadeh A, Bahrami HR, Maleki M, Sastry S (2014) Spatial sensing and cognitive radio communication in the presence of a k-user interference primary network. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 33(5):741–754
Sharma SK, Chatzinotas S, Ottersten B (2013) Interference alignment for spectral coexistence of heterogeneous networks. EURASIP J Wireless Commun Netw 2013(46):1–14
Shin W, Lee N, Yang H, Lee J (2016) Relay-aided successive aligned interference cancellation for wireless x networks with full-duplex relays. IEEE Trans Veh Tech 66(1):421–432
Jin DS, No JS, Shin DJ (2014) New interference alignment schemes with full and half-duplex relays for the quasi-static X channel. IET Commun 8(3):351–359
Tang J, Lambotharan S, Pomeroy S (2013) Interference cancellation and alignment techniques for multiple-input and multiple-output cognitive relay networks. IET Sig Process 7(3):188–200
Chen Y, Liu C, Fu Y, Song Y, Qian M (2020) Optimal transceiver design for SWIPT in interference alignment network. Adv Electr Comput Eng 20(2):19–26
Jeffrey A, Zwillinger D (2007) Table of integrals, series, and products. Elsevier, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namdar, M., Basgumus, A., Aldirmaz-Colak, S. et al. Iterative interference alignment with spatial hole sensing in MIMO cognitive radio networks. Ann. Telecommun. 77, 177–185 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12243-021-00869-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12243-021-00869-5