Abstract
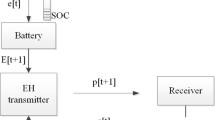
The binary symbol-pair constrained codes that can enable simultaneous transfer of information and energy is the topic of interest in this paper. The construction and properties of such binary symbol-pair code using the sliding window constraint are discussed in this paper. The sliding window constraint ensures the presence of at least t weighted symbols within any prescribed window of l consecutive symbol-pairs. The information capacity of (l,t)-constrained sequences has been obtained and analyzed. This paper provides the block code construction of (l,t) symbol-pair constrained codes of length n without using a n-step finite-state machine. The information capacity obtained in this paper is better than the information capacity of (l,t)-constrained codes in Schouhamer Immink and Kui (IEEE Commun Lett 24(9):1890–1893, 2020) [16].

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler R, Coppersmith D, Hassner M (1983) Algorithms for sliding block codes–An application of symbolic dynamics to information theory. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 29(1):5–22
Adler R, Coppersmith D, Hassner M (1983) Algorithms for sliding block codes—An application of symbolic dynamics to information theory. IEEE Trans Inf Theory IT-29(1):5–22
Cao C, Fair I (2019) Minimal sets for capacity-approaching variable-length constrained sequence codes. IEEE Trans Commun 67(2):890–902
Cao C, Fair I (2019) Construction of multi-state capacity-approaching variable-length constrained sequence codes with state-independent decoding. IEEE Access 7:54746–54759
Cassuto Y, Blaum M (2011) Codes for symbol-pair read channels. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 57(12):8011–8020
Flajolet P, Sedgewick R (2009) Analytic combinatorics. Cambridge Univ Press, Cambridge, U.K.
Franaszek PA (1968) Sequence-state encoding for digital transmission. Bell Syst Tech J 47:143–157
Franaszek PA (1968) Sequence-state encoding for digital transmission. Bell Syst Tech J 47:143–157
Freiman CV, Wyner AD (1964) Optimum block codes for noiseless input restricted channels. Inf Control 7(3):398–415
Guibas LJ, Odlyzko AM (1981) String overlaps, pattern matching, and nontransitive games. J Combinat Theory A 30(2):183–208
Hopcroft JE, Motwani R (2013) Introduction to automata theory, languages, and computation. Pearson, London U.K.
Immink KAS (1990) Run length-limited sequences. Proc IEEE 78(11):1745–1759
Marcus BH, Siegel PH, Wolf JK (1992) Finite-state modulation codes for data storage. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 10(1):5–37
Popovski P, Fouladgar AM, Simeone O (2013) Interactive joint transfer of energy and information. IEEE Trans Commun 61(5):2086–2097
Rosnes E, Barbero ÁI, Ytrehus Ø (2012) Coding for inductively coupled channels. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 58(8):5418–5436
Schouhamer Immink KE, Kui C (2020) Properties and constructions of energy-harvesting sliding-window constrained codes. IEEE Commun Lett 24(9):1890–1893
Schouhamer Immink KE, Kui C (2020) Block codes for energy-harvesting sliding-window constrained channels. IEEE Commun Lett 24(11):2383–2386
Schouhamer Immink KE, Siegel PH, Wolf JK (1998) Codes for digital recorders. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 44(6):2260–2299
Shannon CE (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst, Tech J 27(3):379–423
Stanley RP (1997) Enumerative combinatorics Volume 1 (Cambridge Studies in Advanced Mathematics Book 49). Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, U.K.
Tandon A, Motani M, Varshney LR (2016) Subblock-constrained codes for real-time simultaneous energy and information transfer. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 62(7):4212–4227
Tandon A, Kiah HM, Motani M (2018) Bounds on the size and asymptotic rate of subblock-constrained codes. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 64(10):6604–6619
Tandon A, Motani M, Varshney LR (2019) Are run-length limited codes suitable for simultaneous energy and information transfer. IEEE Trans Green Commun Netw 3(4):988–996
Cassuto Y, Blaum M (2010) Codes for symbol-pair read channels. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Inf. Theory, Austin, TX, USA, pp 988–992
Wu T-Y, Tandon A, Varshney LR, Motani M (2017) Skip-sliding window codes. arXiv:1711.09494
Wu T-Y, Tandon A, Motani M, Varshney LR (2019) On the outage constrained rate of skip-sliding window codes. In: Proc. IEEE Inf. Theory Workshop (ITW), Visby, Sweden, pp 1–5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Bhoi, S.S., Gupta, R. et al. Sliding window symbol-pair constrained codes for energy harvesting. Ann. Telecommun. 78, 71–77 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12243-022-00923-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12243-022-00923-w