Abstract
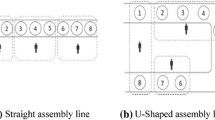
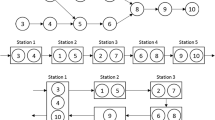
U-type assembly line is one of the important tools that may increase companies’ production efficiency. In this study, two different modeling approaches proposed for the assembly line balancing problems have been used in modeling type-II U-line balancing problems, and the performances of these models have been compared with each other. It has been shown that using mathematical formulations to solve medium and large size problem instances is impractical since the problem is NP-hard. Therefore, a grouping genetic and simulated annealing algorithms have been developed, and a particle swarm optimization algorithm is adapted to compare with the proposed methods. A special crossover operator that always obtains feasible offspring has been suggested for the proposed grouping genetic algorithm. Furthermore, a local search procedure based on problem-specific knowledge was applied to increase the intensification of the algorithm. A set of well-known benchmark instances was solved to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed and existing methods. Results showed that while the mathematical formulations can only be used to solve small size instances, metaheuristics can obtain high quality solutions for all size problem instances within acceptable CPU times. Moreover, grouping genetic algorithm has been found to be superior to the other methods according to the number of optimal solutions, or deviations from the lower bound values.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Bui LT, Binh HTT (2016) A survivable design of last mile communication networks using multi-objective genetic algorithms. Memet Comput 8(2):97–108
De Lit P, Falkenauer E, Delchambre A (2000) Grouping genetic algorithms: an efficient method to solve the cell formation problem. Math Comput Simul 51(3):257–271
Dijkstra EW (1959) A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numer Math 1(1):269–271
Dong J, Zhang L, Xiao T, Mao H (2014) Balancing and sequencing of stochastic mixed-model assembly U-lines to minimise the expectation of work overload time. Int J Prod Res 52(24):7529–7548
Eberhart RC, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. Proc Sixth Int Symp Micro Mach Hum Sci 1:39–43
Fattahi A, Elaoud S, Sadeqi Azer E, Turkay M (2014) A novel integer programming formulation with logic cuts for the U-shaped assembly line balancing problem. Int J Prod Res 52(5):1318–1333
Falkenauer E (1996) A hybrid grouping genetic algorithm for bin packing. J Heuristics 2(1):5–30
Gökçen H, Ağpak K, Gencer C, Kizilkaya E (2005) A shortest route formulation of simple U-type assembly line balancing problem. Appl Math Model 29(4):373–380
Gutjahr AL, Nemhauser GL (1964) An algorithm for the line balancing problem. Manag Sci 11(2):308–315
Holland JH (1975) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor
Jayaswal S, Agarwal P (2014) Balancing U-shaped assembly lines with resource dependent task times: a simulated annealing approach. J Manuf Syst 33(4):522–534
Jonnalagedda V, Dabade B (2014) Application of simple genetic algorithm to U-shaped assembly line balancing problem of type II. IFAC World Congr 19(1):6168–6173
Kara Y, Tekin M (2009) A mixed integer linear programming formulation for optimal balancing of mixed-model U-lines. Int J Prod Res 47(15):4201–4233
Kim YK, Song WS, Kim JH (2009) A mathematical model and a genetic algorithm for two-sided assembly line balancing. Comput Oper Res 36(3):853–865
Kim YK, Kim YJ, Kim Y (1996) Genetic algorithms for assembly line balancing with various objectives. Comput Ind Eng 30(3):397–409
Klein R, Scholl A (1996) Maximizing the production rate in simple assembly line balancing—a branch and bound procedure. Eur J Oper Res 91(2):367–385
Laarhoven VPJ, Aarts EH (1987) Simulated annealing. Springer, Dordrecht
Miltenburg GJ, Wijngaard J (1994) The U-line line balancing problem. Manag Sci 40(10):1378–1388
Nearchou AC (2007) Balancing large assembly lines by a new heuristic based on differential evolution method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34(9–10):1016–1029
Özcan U, Kellegöz T, Toklu B (2011) A genetic algorithm for the stochastic mixed-model U-line balancing and sequencing problem. Int J Prod Res 49(6):1605–1626
Petropoulos DI, Nearchou AC (2011) A particle swarm optimization algorithm for balancing assembly lines. Assem Autom 31(2):118–129
Rezoug A, Bader-El-Den M, Boughaci D (2017) Guided genetic algorithm for the multidimensional knapsack problem. Memet Comput (in press). doi:10.1007/s12293-017-0232-7
Scholl A, Klein R (1999) ULINO: optimally balancing U-shaped JIT assembly lines. Int J Prod Res 37(4):721–736
Scholl A (1999) Balancing and sequencing of assembly lines. Physica, Heidelberg
Simopoulos DN, Kavatza SD, Vournas CD (2006) Unit commitment by an enhanced simulated annealing algorithm. IEEE Trans Power Syst 21(1):68–76
Syswerda G (1991) Schedule optimization using genetic algorithms. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Şahin M, Kellegöz T (2017) Increasing production rate in U-type assembly lines with sequence-dependent set-up times. Eng Optim 49(8):1401–1419
Talbi EG (2009) Metaheuristics: from design to implementation. Wiley, New York
Tawhid MA, Ali AF (2017) A Hybrid grey wolf optimizer and genetic algorithm for minimizing potential energy function. Memet Comput (in press). doi:10.1007/s12293-017-0234-5
Tran B, Xue B, Zhang M (2016) Genetic programming for feature construction and selection in classification on high-dimensional data. Memet Comput 8(1):3–15
Urban TL (1998) Note: optimal balancing of U-shaped assembly lines. Manag Sci 44(5):738–741
Yoosefelahi A, Aminnayeri M, Mosadegh H, Ardakani HD (2012) Type II robotic assembly line balancing problem: an evolution strategies algorithm for a multi-objective model. J Manuf Syst 31(2):139–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şahin, M., Kellegöz, T. An efficient grouping genetic algorithm for U-shaped assembly line balancing problems with maximizing production rate. Memetic Comp. 9, 213–229 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12293-017-0239-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12293-017-0239-0