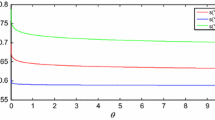
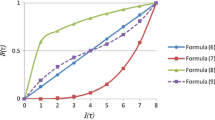
Abstract
In practice, the use of linguistic information is flexible and definite due to the complexity of problems, and therefore the linguistic models have been widely studied and applied to solve multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) problems under uncertainty. In this paper, intuitionistic hesitant linguistic sets (IHLSs) are defined on the basis of intuitionistic linguistic sets (ILSs) and hesitant fuzzy linguistic sets (HFLSs). As an evaluation value of one reference object, an intuitionistic hesitant linguistic number (IHLN) contains a linguistic term, a set of membership degrees and a set of non-membership degrees. There can be a consensus on the linguistic term and then decision makers can express their opinions on membership or non-membership degrees depending on their preferences. Therefore, by means of IHLSs, the flexibility in generating evaluation information under uncertainty can be achieved to a larger extent than either ILSs or HFLSs do. Besides, the basic operations and comparison method of IHLNs are studied, which is followed by the definitions of several aggregation operators, including the intuitionistic hesitant linguistic hybrid averaging (IHLHA) operator, the intuitionistic hesitant linguistic hybrid geometric (IHLHG) operator and the corresponding generalized operators. Using these operators, an approach to MCDM problems with intuitionistic hesitant linguistic information is proposed. Finally, an illustrative example is provided to verify the proposed approach and its accuracy and effectiveness have been demonstrated through the comparative analysis with ILSs and HFLSs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexopoulos S, Siskos Y, Tsotsolas N, Hristodoulakis N (2012) Evaluating strategic actions for a Greek publishing company. Oper Res Int J 12(2):253–269
Atanassov KT (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20(1):87–96
Bao GY, Lian XL, He M, Wang LL (2010) Improved two-tuple linguistic representation model based on new linguistic evaluation scale. Control Decis 5:780–784
Chen N, Xu ZS, Xia MM (2013a) Correlation coefficients of hesitant fuzzy sets and their applications to clustering analysis. Appl Math Model 37(4):2197–2211
Chen N, Xu ZS, Xia MM (2013b) Interval-valued hesitant preference relations and their applications to group decision making. Knowl-Based Syst 37:528–540
Du Y, Zuo J (2011) An extended TOPSIS method for the multiple attribute group decision making problems based on intuitionistic linguistic numbers. Sci Res Essays 19:4125–4132
Dubois D, Prade H (1980) Fuzzy sets and systems: theory and applications. Kluewer, New York
Farhadinia B (2013) Information measures for hesitant fuzzy sets and interval-valued hesitant fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 240:129–144
Grimaila MR, Badiru A (2013) A hybrid dynamic decision making methodology for defensive information technology contingency measure selection in the presence of cyber threats. Oper Res Int J 13(1):67–88
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E (2000) Linguistic decision analysis: steps for solving decision problems under linguistic information. Fuzzy Sets Syst 115(1):67–82
Herrera F, Martínez L (2000) A 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 8(6):746–752
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E, Verdegay JL (1996) A model of consensus in group decision making under linguistic assessments. Fuzzy Sets Syst 78(1):73–87
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E, Martínez L (2000) A fusion approach for managing multi-granularity linguistic term sets in decision making. Fuzzy Sets Syst 114(1):43–58
Hu JH, Zhang XL, Chen XH, Liu YM (2015) Hesitant fuzzy information measures and their applications in multi-criteria decision making. Int J Syst Sci. doi:10.1080/00207721.2015.1036476
Kahneman D, Tversky A (1979) Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk. Economica 47:263–291
Kitsios F, Doumpos M, Grigoroudis E, Zopounidis C (2009) Evaluation of new service development strategies using multicriteria analysis: predicting the success of innovative hospitality services. Oper Res Int J 9(1):17–33
Lee LW, Chen SM (2015) Fuzzy decision making based on likelihood-based comparison relations of hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and hesitant fuzzy linguistic operators. Inf Sci 294:513–529
Liao HC, Xu ZS, Zeng XJ (2014) Distance and similarity measures for hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and their application in multi-criteria decision making. Inf Sci 271:125–142
Liao HC, Xu ZS, Zeng XJ, Merigo JM (2015) Qualitative decision making with correlation coefficients of hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Knowl-Based Syst 76:127–138
Lin R, Zhao XF, Wei GW (2014) Models for selecting an ERP system with hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 26:2155–2165
Liu PD (2013a) Some generalized dependent aggregation operators with intuitionistic linguistic numbers and their application to group decision making. J Comput Syst Sci 79:131–143
Liu PD (2013b) Some geometric aggregation operators based on interval intuitionistic uncertain linguistic variables and their application to group decision making. Appl Math Model 37:2430–2444
Liu PD, Jin F (2012) Methods for aggregating intuitionistic uncertain linguistic variables and their application to group decision making. Inf Sci 205:58–71
Liu HB, Rodríguez RM (2014) A fuzzy envelope for hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set and its application to multicriteria decision making. Inf Sci 258:220–238
Liu PD, Su Y (2010) The multiple-attribute decision making method based on the TFLHOWA operator. Comput Math Appl 60(9):2609–2615
Martínez L, Herrera F (2012) An overview on the 2-tuple linguistic model for computing with words in decision making: extensions, applications and challenges. Inf Sci 207:1–18
Meng FY, Chen XH, Zhang Q (2014) Multi-attribute decision analysis under a linguistic hesitant fuzzy environment. Inf Sci 267:287–305
Montes R, Sánchez AM, Villar P, Herrera F (2015) A web tool to support decision making in the housing market using hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Appl Soft Comput. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2015.01.030
Peng JJ, Wang JQ, Wang J, Yang LJ, Chen XH (2015a) An extension of ELECTRE to multi-criteria decision-making problems with multi-hesitant fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 307:113–126
Peng JJ, Wang JQ, Wu XH, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2015b) The fuzzy cross-entropy for intuitionistic hesitant fuzzy sets and its application in multi-criteria decision-making. Int J Syst Sci 46(13):2335–2350
Qian G, Wang H, Feng X (2013) Generalized hesitant fuzzy sets and their application in decision support system. Knowl-Based Syst 37:357–365
Rabbani A, Zamani M, Yazdani-Chamzini A, Zavadskas EK (2014) Proposing a new integrated model based on sustainability balanced scorecard (SBSC) and MCDM approaches by using linguistic variables for the performance evaluation of oil producing companies. Expert Syst Appl 41(16):7316–7327
Rodriguez RM, Martinez L, Herrera F (2012) Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 20(1):109–119
Rodríguez RM, Martínez L, Torra V, Xu ZS, Herrera F (2014) Hesitant fuzzy sets: state of the art and future directions. Int J Intell Syst 29(6):495–524
Smarandache F (2005) Neutrosophic set: a generalization of the intuitionistic fuzzy set. Int J Pure Appl Math 24:287–297
Torra V (2010) Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 25:529–539
Valiakos A, Siskos Y (2015) Multicriteria decision support for the evaluation of agricultural units in Greece. Oper Res Int J. doi:10.1007/s12351-015-0186-9
Wang JH, Hao JY (2006) A new version of 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 14:435–445
Wang JQ, Li HB (2010) Multi-criteria decision making method based on aggregation operators for intuitionistic linguistic fuzzy numbers. Control Decis 25:1571–1574
Wang JQ, Wang DD, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2014a) Multi-criteria outranking approach with hesitant fuzzy sets. OR Spectr 36:1001–1019
Wang JQ, Wu JT, Wang J, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2014b) Interval-valued hesitant fuzzy linguistic sets and their applications in multi-criteria decision-making problems. Inf Sci 288:55–72
Wang J, Wang JQ, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2015a) Multi-criteria decision-making based on hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets: an outranking approach. Knowl-Based Syst 86:224–236
Wang JQ, Wang P, Wang J, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2015b) Atanassov’s interval-valued intuitionistic linguistic multi-criteria group decision-making method based on trapezium cloud model. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 23(3):542–554
Wang JQ, Wu JT, Wang J, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2015c) Multi-criteria decision-making methods based on the Hausdorff distance of hesitant fuzzy linguistic numbers. Soft Comput. doi:10.1007/s00500-015-1609-5
Wei CP, Zhao N, Tang XJ (2014) Operators and comparisons of hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 22(3):575–585
Xia MM, Xu ZS (2011) Hesitant fuzzy information aggregation in decision making. Int J Approx Reason 52:395–407
Xu ZS (2004) A method based on linguistic aggregation operators for group decision making with linguistic preference relations. Inf Sci 166(1):19–30
Xu ZS, Xia MM (2011) Distance and similarity measures for hesitant fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 181:2128–2138
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8:338–356
Zadeh LA (1975a) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application approximate reasoning—I. Inf Sci 8(3):199–249
Zadeh LA (1975b) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application approximate reasoning—II. Inf Sci 8(4):301–357
Zadeh LA (1975c) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application approximate reasoning—III. Inf Sci 9(1):43–58
Zhou H, Wang JQ, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2016) Linguistic hesitant fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making method based on evidential reasoning. Int J Syst Sci 47(2):314–327
Zhu B, Xu ZS, Xia MM (2012) Hesitant fuzzy geometric Bonferoni means. Inf Sci 205:72–85
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank the editors and anonymous referees for their valuable and constructive comments and suggestions that greatly assisted in the improvement of this paper. This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71271218, 71221061, and 71431006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Wang, J., Li, XE. et al. Intuitionistic hesitant linguistic sets and their application in multi-criteria decision-making problems. Oper Res Int J 16, 131–160 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-015-0199-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-015-0199-4