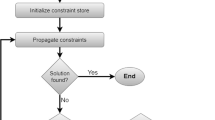
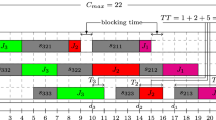
Abstract
This paper addresses the hybrid flow shop scheduling problem by considering job rejection to minimize the sum of the total tardiness cost of the scheduled jobs and total cost of the rejected jobs as a single-objective problem. A mixed-integer linear programming model is proposed to solve small-sized problems within an acceptable computational time. Also, this paper exhibits two innovative heuristic algorithms, which are presented to discover fast solutions for the problem along with five meta-heuristics are adapted to solve large-sized problems in the model. Another contribution of this paper is to illustrate the different encoding and decoding methods adapted to algorithms, which are capable of obtaining a feasible schedule and furthermore, to guarantee the efficiency of the solutions based on the schedule. The results obtained from the computational study demonstrate the mathematical model and proposed algorithms effectiveness. Additionally, this paper studies the efficacy of job rejection noting the scheduling for a real-world hybrid flow shop in the tile industry production system. As well as, in this paper, the problem is viewed from a bi-objective problem perspective, so that the tardiness costs of the scheduled jobs and rejection costs of rejected jobs as two objectives are minimized simultaneously to obtain the Pareto solutions. We analyze relationship between the results of the single-objective and bi-objective approaches on small and large-sized problems.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldowaisan T, Allahverdi A (2004) New heuristics for m-machine no-wait flowshop to minimize total completion time. Omega 32(5):345–352
Asgari TM, Zandieh M (2014) A cloud-based simulated annealing algorithm for order acceptance problem with weighted tardiness penalties in permutation flow shop scheduling. J Indus Eng Manage Stud 1(1):1–19
Baptiste P, Le Pape C (2005) Scheduling a single machine to minimize a regular objective function under setup constraints. Discret Optim 2(1):83–99
Bartal Y, Leonardi S, Marchetti-Spaccamela A, Sgall J, Stougie L (2000) Multiprocessor scheduling with rejection. SIAM J Discret Math 13(1):64–78
Brah S, Loo L (1999) Heuristics for scheduling in a flow shop with multiple processors. Eur J Oper Res 113(1):113–122
Caldeira RH, Gnanavelbabu A, Vaidyanathan T (2020) An effective backtracking search algorithm for multi-objective flexible job shop scheduling considering new job arrivals and energy consumption. Comput Ind Eng 149:106863
Cao Z, Yang X (2009) A PTAS for parallel batch scheduling with rejection and dynamic job arrivals. Theoret Comput Sci 410(27–29):2732–2745
Cao Z, Zhang Y (2007) Scheduling with rejection and non-identical job arrivals. J Syst Sci Comple 20(4):529–535
Cao Z, Wang Z, Liu S (2006) On several scheduling problems with rejection or discretely compressible processing times. Lect Notes Comput Sci 3959:90–98
Chaurasia SN, Kim JH (2019) An artificial bee colony based hyper-heuristic for the single machine order acceptance and scheduling problem. In: Deep K, Jain M, Salhi S (eds) Decision science in action. Asset analytics (performance and safety management). Springer
Cheng Y, Sun S (2009) Scheduling linear deteriorating jobs with rejection on a single machine. Eur J Oper Res 194(1):18–27
Chung TP, Liao CJ (2013) An immunoglobulin-based artificial immune system for solving the hybrid flow shop problem. Appl Soft Comput 13(8):3729–3736
Cordone R, Hosteins P (2019) A bi-objective model for the single-machine scheduling problem with rejection cost and total tardiness minimization. Comput Oper Res 102:130–140
Dabiri M, Darestani SA, Naderi B (2019) Multi-machine flow shop scheduling problems with rejection using genetic algorithm. Int J Serv Oper Manage 32(2):158–172
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan TAMT (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197
Della Croce F, Koulamas C, T’kindt V (2017) A constraint generation approach for two-machine shop problems with jobs selection. Eur J Oper Res 259(3):898–905
Dong X, Huang H, Chen P (2008) An improved NEH-based heuristic for the permutation flowshop problem. Comput Oper Res 35(12):3962–3968
Emami S, Sabbagh M, Moslehi G (2016) A Lagrangian relaxation algorithm for order acceptance and scheduling problem: a globalised robust optimisation approach. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 29(5):535–560
Emami S, Moslehi G, Sabbagh M (2017) A Benders decomposition approach for order acceptance and scheduling problem: a robust optimization approach. Comput Appl Math 36(4):1471–1515
Engels DW, Karger DR, Kolliopoulos SG, Segupta S, Uma RN, Wein J (2003) Techniques for scheduling with rejection. Journal of Algorithms 49:175–191
Esmaeilbeigi R, Charkhgard P, Charkhgard H (2016) Order acceptance and scheduling problems in two-machine flow shops: new mixed integer programming formulations. Eur J Oper Res 251(2):419–431
Fernandez-Viagas V, Framinan J (2015) NEH-based heuristics for the permutation flowshop scheduling problem to minimise total tardiness. Comput Oper Res 60:27–36
Fiszman S, Mosheiov G (2018) Minimizing total load on a proportionate flowshop with position-dependent processing times and job-rejection. Inf Process Lett 132:39–43
Framinan JM, Leisten R, Ruiz R (2014) Manufacturing scheduling systems: an integrated view on models, methods and tools. Springer
Garcia C (2016) Resource-constrained scheduling with hard due windows and rejection penalties. Eng Optim 48(9):1515–1528
Geramipour S, Moslehi G, Reisi-Nafchi M (2017) Maximizing the profit in customer’s order acceptance and scheduling problem with weighted tardiness penalty. J Oper Res Soc 68(1):89–101
Gupta JND (1988) Two-stage, hybrid flowshop scheduling problem. J Oper Res Soc. https://doi.org/10.1057/jors.1988.63
Hermelin D, Pinedo M, Shabtay D, Talmon N (2019) On the parameterized tractability of single machine scheduling with rejection. Eur J Oper Res 273(1):67–73
Khalouli S, Ghedjati F, Hamzaoui A (2010) A meta-heuristic approach to solve a jit scheduling problem in hybrid flow shop. Eng Appl Artif Intell 23(5):765–771
Khuller S, Mestre J (2008) An optimal incremental algorithm for minimizing lateness with rejection. Lect Notes Comput Sci 5193:601–610
Kong M, Liu X, Pei J, Zhou Z, Pardalos PM (2019) Parallel-batching scheduling of deteriorating jobs with non-identical sizes and rejection on a single machine. Optim Lett, pp 1–15
Koulamas C, Panwalkar SS (2015) Job selection in two-stage shops with ordered machines. Comput Ind Eng 88:350–353
Lei D, Guo X (2015) A parallel neighborhood search for order acceptance and scheduling in flowshop environment. Int J Prod Econ 165:12–18
Li J-Q, Pan Q-K, Wang F-T (2014) A hybrid variable neighborhood search for solving the hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. Appl Soft Comput 24:63–77
Liao C-J, Tjandradjaja E, Chung T-P (2012) An approach using particle swarm optimization and bottleneck heuristic to solve hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. Appl Soft Comput 12(6):1755–1764
Lin SW, Ying KC (2015) Order acceptance and scheduling to maximize total net revenue in permutation flowshops with weighted tardiness. Appl Soft Comput 30:462–474
Lu L, Zhang L, Yuan J (2008) The unbounded parallel batch machine scheduling with release dates and rejection to minimize makespan. Theoret Comput Sci 396(1–3):283–289
Lu L, Cheng TCE, Yuan J, Zhang L (2009) Bounded single-machine parallel-batch scheduling with release dates and rejection. Comput Oper Res 36(10):2748–2751
Marichelvam M, Prabaharan T, Yang X-S, Geetha M (2013) Solving hybrid flow shop scheduling problems using bat algorithm. Int J Logist Econ Glob 5(1):15–29
Marichelvam M, Prabaharan T, Yang X-S (2014) Improved cuckoo search algorithm for hybrid flow shop scheduling problems to minimize makespan. Appl Soft Comput 19:93–101
Mohsen N, Iraj M (2014) Multi-job lot streaming to minimize the weighted completion time in a hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with work shift constraint. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70:501–514
Mokhtari H (2015) A nature inspired intelligent water drops evolutionary algorithm for parallel processor scheduling with rejection. Appl Soft Comput 26:166–179
Naderi B, Gohari S, Yazdani M (2014) Hybrid flexible flowshop problems: Models and solution methods. Appl Math Model 38(24):5767–5780
Nagano MS, Rossi FL, Tomazella CP (2017) A new efficient heuristic method for minimizing the total tardiness in a no-idle permutation flow shop. Prod Eng Res Devel 11(4–5):523–529
Nawaz M, Enscore EE Jr, Ham I (1983) A heuristic algorithm for the m-machine, n-job flow-shop sequencing problem. Omega 11(1):91–95
Nguyen S (2016) A learning and optimizing system for order acceptance and scheduling. Int J Adv Manufact Technol 86(5–8):2021–2036
Nguyen S, Zhang M, Johnston M (2014a) Enhancing branch-and-bound algorithms for order acceptance and scheduling with genetic programming. In: Nicolau M, Krawiec K, Heywood MI, Castelli M, Garcia-Sanchez P, Merelo JJ, Rivas Santos VM, Sim K (eds) Genetic programming, 1st edn. Springer, pp 124–136
Nguyen S, Zhang M, Johnston M (2014) A sequential genetic programming method to learn forward construction heuristics for order acceptance and scheduling. In: 2014 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (CEC). IEEE, pp 1824–1831
Ou J, Zhong X (2017) Order acceptance and scheduling with consideration of service level. Ann Oper Res 248(1–2):429–447
Ou J, Zhong X, Wang G (2015) An improved heuristic for parallel machine scheduling with rejection. Eur J Oper Res 241(3):653–661
Pan Q-K, Dong Y (2014) An improved migrating birds optimisation for a hybrid flowshop scheduling with total flowtime minimisation. Inf Sci 277:643–655
Pan Q-K, Wang L, Li J-Q, Duan J-H (2014) A novel discrete artificial bee colony algorithm for the hybrid flowshop scheduling problem with makespan minimisation. Omega (United Kingdom) 45(42):56
Pan QK, Gao L, Li XY, Gao KZ (2017) Effective metaheuristics for scheduling a hybrid flowshop with sequence-dependent setup times. Appl Math Comput 303:89–112
Pan QK, Ruiz R, Alfaro-Fernández P (2017) Iterated search methods for earliness and tardiness minimization in hybrid flowshops with due windows. Comput Oper Res 80:50–60
Rahman HF, Sarker R, Essam D (2015) A real-time order acceptance and scheduling approach for permutation flow shop problems. Eur J Oper Res 247(2):488–503
Reisi-Nafchi M, Moslehi G (2015) ‘A hybrid genetic and linear programming algorithm for two-agent order acceptance and scheduling problem. Appl Soft Comput 33:37–47
Sengupta S (2003) Algorithms and approximation schemes for minimum lateness/tardiness scheduling with rejection. Lect Notes Comput Sci 2748:79–90
Shabtay D, Gasper N (2012) Two-machine flow-shop scheduling with rejection. Comput Oper Res 39(5):1087–1096
Shabtay D, Oron D (2016) Proportionate flow-shop scheduling with rejection. J Oper Res Soc 67(5):752–769
Shabtay D, Gaspar N, Yedidsion L (2012) A bicriteria approach to scheduling a single machine with job rejection and positional penalties. J Comb Optim 23(4):395–424
Silva YLT, Subramanian A, Pessoa AA (2018) Exact and heuristic algorithms for order acceptance and scheduling with sequence-dependent setup times. Comput Oper Res 90:142–160
Thevenin S, Zufferey N (2019) Learning Variable Neighborhood Search for a scheduling problem with time windows and rejections. Discret Appl Math 261:344–353
Thevenin S, Zufferey N, Widmer M (2015) Metaheuristics for a scheduling problem with rejection and tardiness penalties. J Sched 18(1):89–105
Thevenin S, Zufferey N, Widmer M (2016) Order acceptance and scheduling with earliness and tardiness penalties. J Heurist 22(6):849–890
Wang S, Ye B (2019) Exact methods for order acceptance and scheduling on unrelated parallel machines. Comput Oper Res 104:159–173
Wang S, Wang L, Liu M, Xu Y (2013) An enhanced estimation of distribution algorithm for solving hybrid flow-shop scheduling problem with identical parallel machines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68(9):2043–2056
Wang X, Huang G, Hu X, Cheng TE (2015) Order acceptance and scheduling on two identical parallel machines. J Oper Res Soc 66(10):1755–1767
Wang DJ, Yin Y, Liu M (2016) Bicriteria scheduling problems involving job rejection, controllable processing times and rate-modifying activity. Int J Prod Res 54(12):3691–3705
Wang J, Zhuang X, Wu B (2017) A new model and method for order selection problems in flow-shop production. In: Choi TM, Gao J, Lambert J, Ng CK, Wang J (eds) Optimization and control for systems in the big-data era. International series in operations research & management science, vol 252. Springer
Wang D, Yin Y, Cheng TCE (2018) Parallel-machine rescheduling with job unavailability and rejection. Omega
Wang Z, Qi Y, Cui H, Zhang J (2019) A hybrid algorithm for order acceptance and scheduling problem in make-to-stock/make-to-order industries. Comput Ind Eng 127:841–852
Xiao Y, Yuan Y, Zhang RQ, Konak A (2015) Non-permutation flow shop scheduling with order acceptance and weighted tardiness. Appl Math Comput 270:312–333
Xie X, Wang X (2016) An enhanced ABC algorithm for single machine order acceptance and scheduling with class setups. Appl Soft Comput 44:255–266
Xu Y, Wang L, Wang S, Liu M (2013) An effective shuffled frog-leaping algorithm for solving the hybrid flow-shop scheduling problem with identical parallel machines. Eng Optim 45(12):1409–1430
Xu L, Wang Q, Huang S (2015) Dynamic order acceptance and scheduling problem with sequence-dependent setup time. Int J Prod Res 53(19):5797–5808
Yavari M, Marvi M, Akbari AH (2019) Semi-permutation-based genetic algorithm for order acceptance and scheduling in two-stage assembly problem. Neural Comput Appl, pp 1–15
Yazdani M, Zandieh M, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2019) Evolutionary algorithms for multi-objective dual-resource constrained flexible job-shop scheduling problem. Opsearch 56(3):983–1006
Ye H, Li W, Abedini A, Nault B (2017) An effective and efficient heuristic for no-wait flow shop production to minimize total completion time. Comput Ind Eng 108:57–69
Zandieh M, Roumani M (2017) A biogeography-based optimization algorithm for order acceptance and scheduling. J Ind Prod Eng 34(4):312–321
Zhang Y, Lu L, Yuan J (2009) Single machine scheduling with release dates and rejection. Eur J Oper Res 198:975–978
Zhang Y, Ren J, Wang C (2009) Scheduling with rejection to minimize the makespan. Lect Notes Comput Sci 5573:411–420
Zhang B, Pan QK, Gao L, Zhang XL, Sang HY, Li JQ (2017) An effective modified migrating birds optimization for hybrid flowshop scheduling problem with lot streaming. Appl Soft Comput 52:14–27
Zhong X, Ou J (2017) Parallel machine scheduling with restricted job rejection. Theoret Comput Sci 690:1–11
Zhong XL, Ou JW (2017) Improved approximation algorithms for parallel machine scheduling with release dates and job rejection. 4OR-A Q. J Oper Res 15:387–406
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dabiri, M., Yazdani, M., Naderi, B. et al. Modeling and solution methods for hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with job rejection. Oper Res Int J 22, 2721–2765 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-021-00629-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-021-00629-2
Keywords
- Scheduling
- Hybrid flow shop
- Mixed-integer linear programming model
- Meta-heuristic algorithm
- Heuristic algorithm