Abstract
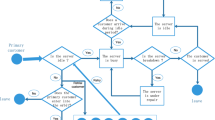
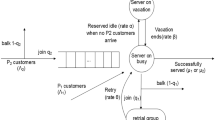
We consider the retrial queue with a repairable server (who suffers from breakdowns and repairs) as well as reserved times and setup times under N-policy, and analyze the customers’ strategic behavior and social optimization in the almost unobservable and fully unobservable cases. The linear reward-cost structure is adopted to decide whether the arriving customers enter the orbit or balk when the server is busy or dormant. Firstly, the stationary probabilities are obtained by the probability generating function. The equilibrium strategies for two cases are analyzed. In particular, for the almost unobservable queue, the concrete expression of equilibrium strategy is deduced. Then the social welfare functions for two cases are established and the socially optimal arrival rates are calculated by genetic algorithm. Finally, the sensitivity of optimal arrival rates and social welfare to some system parameters is discussed by numerical experiments.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghsami A, Jolai F (2020) Equilibrium threshold strategies and social benefits in the fully observable Markovian queues with partial breakdowns and interruptible setup/closedown policy. Qual Technol Quant M 17(6):685–722
Aissani A (1994) A retrial queue with redundancy and unreliable server. Queueing Syst 17(3–4):431–449
Balachandran KR (2011) Control policies for a single server system. Manag Sci 19(9):1013–1018
Cao JH, Kan C (1982) Analysis of an M/G/1 queueing system with repairable service station. Acta Math Appl Sin-E 5(2):113–127
Chang J, Wang J (2017) Unreliable M/M/1/1 retrial queues with set-up time. Qual Technol Quant M 15(5):1–13
Choudhury G, Ke JC (2014) An unreliable retrial queue with delaying repair and general retrial times under Bernoulli vacation schedule. Appl Math Comput 230:436–450
Cohen JW (1957) Basic problems of telephone traffic theory and the influence of repeated calls. Philips Telecomm Rev 18(2):49–100
Do N, Do T, Melikov A (2020) Equilibrium customer behavior in the M/M/1 retrial queue with working vacations and a constant retrial rate. Oper Res-Ger 20(2):627–646
Economou A, Kanta S (2008) Equilibrium balking strategies in the observable single-server queue with breakdowns and repairs. Oper Res Lett 36(6):696–699
Economou A, Kanta S (2011) Equilibrium customer strategies and social-profit maximization in the single-server constant retrial queue. Nav Res Log 58(2):107–122
Guo P, Hassin R (2011) Strategic behavior and social optimization in Markovian vacation queues. Oper Res 59(4):986–997
Guo P, Li Q (2013) Strategic behavior and social optimization in partially-observable Markovian vacation queues. Oper Res Lett 41(3):277–284
Hassin R, Haviv M (1997) Equilibrium threshold strategies: The case of queues with priorities. Oper Res 45(6):966–973
Kumar BK, Arivudainambi D (2002) The M/G/1 retrial queue with Bernoulli schedules and general retrial times. Comput Math Appl 43(1–2):15–30
Li L, Wang J, Zhang F (2013) Equilibrium customer strategies in Markovian queues with partial breakdowns. Comput Ind Eng 66(4):751–757
Neuts MF, Lucantoni DM (1979) A Markovian queue with N servers subject to breakdowns and repairs. Manag Sci 25(9):849–861
Sherman NP, Kharoufeh JP (2006) An M/M/1 retrial queue with unreliable sever. Oper Res Lett 34(6):697–705
Sun K, Wang J (2021) Equilibrium joining strategies in the single-server constant retrial queues with Bernoulli vacations. RAIRO-Oper Res 55(1):S481–S502
Tao L, Liu Z, Wang Z (2012) M/M/1 Retrial queue with collisions and working vacation interruption under N-policy. RAIRO-Oper Res 46(4):355–371
Tian R, Yue D, Yue W (2015) Optimal balking strategies in an M/G/1 queueing system with a removable server under N-policy. J Ind Manag Optim 11(3):715–731
Wang J (2006) Reliability analysis of M/G/1 queues with general retrial times and server breakdowns. Prog Nat Sci-Mater 16(5):464–473
Wang J, Zhang X, Huang p (2017) Strategic behavior and social optimization in a constant retrial queue with the N-Policy. Eur J Oper Res 256(3):841–849
Yu S, Liu Z, Wu J (2017) Strategic behavior in the partially observable Markovian queues with partial breakdowns. Oper Res Lett 45(5):471–474
Zhou M, Liu L, Chai X, Wang Z (2019) Equilibrium strategies in a constant retrial queue with setup time and the N-policy. Commun Stat-Theor M 49(7):1695–1711
Zhou W (2005) Analysis of a single-server retrial queue with FCFS orbit and Bernoulli vacation. Appl Math Comput 161(2):353–364
Zhu S, Wang J, Liu B (2018) Equilibrium joining strategies in the Mn/G/1 queue with server breakdowns and repairs. Oper Res-Ger 20(4):2163–2187
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 71971189.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Tian, R., Han, Y. et al. Optimal joining strategies in a repairable retrial queue with reserved time and N-policy. Oper Res Int J 24, 3 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-023-00808-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-023-00808-3