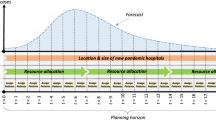
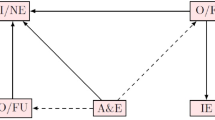
Abstract
Uncertainty analysis is an inevitable attribute of location-allocation problems due to unforecastable parameter changes. Although the simultaneous variation of parameters is more realistic than their instinct variation, the simultaneous sensitivity analysis (SSA) of mixed-integer mathematical models’ outputs upon simultaneous changes of parameters’ value has taken no attention. In the metamodeling process using machine learning tools like regression models and artificial neural networks, several combinations of input values are used for metamodel creation. This paper employs this feature of metamodeling to propose an approach for global sensitivity analysis of mixed-integer mathematical models. The proposed approach is applied in analyzing a newly developed multi-period mixed integer mathematical model for cancer hospitals’ location-allocation problem in a case study. The comparison of results using SSA based on using Regression metamodel (RMM) and traditional one-factor-at-a-time (OFAT) methods showed different ranks of parameters. In addition to more adaptation of SSA to simultaneous changes of parameters in the real world, the created machine learning tools aim to forecast the corresponding outputs approximately when the mixed-integer mathematical model is infeasible or long-run upon some combinations of input parameters’ value. Finally, some applicable managerial insights and recommendations for future works are provided.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alinaghian M et al (2023) A novel robust model for location-allocation of healthcare facilities considering pre-disaster and post-disaster characteristics. Sci Iran 30(2):619–641
Awasthi A et al (2011) A multi-criteria decision making approach for location planning for urban distribution centers under uncertainty. Math Comput Model 53(1–2):98–109
Azadeh A et al (2017) Optimum integrated design of crude oil supply chain by a unique mixed integer nonlinear programming model. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(19):5734–5746
Beheshtifar S, Alimoahmmadi A (2015) A multiobjective optimization approach for location-allocation of clinics. Int Trans Oper Res 22(2):313–328
Borgonovo E (2017) “Sensitivity analysis”. An introduction for the management scientist. International series in operations research and management science. Springe, Cham
Chu SC, Chu L (2000) A modeling framework for hospital location and service allocation. Int Trans Oper Res 7(6):539–568
Das SK et al (2024) Location–allocation problem for green efficient two-stage vehicle-based logistics system: a type-2 neutrosophic multi-objective modeling approach. Expert Syst Appl 238:122174
de Melo Sathler T et al (2019) Integration of facility location and equipment allocation in health care management. Brazil J Oper Prod Manag 16(3):513–527
Derhy M-F (2010) Linear programming, sensitivity analysis & related topics. Pearson Higher Ed, London
Devi Y, Patra S, Singh SP (2022) A location-allocation model for influenza pandemic outbreaks: a case study in India. Oper Manag Res 15:487–502
Ebrahimi SB (2018) A stochastic multi-objective location-allocation-routing problem for tire supply chain considering sustainability aspects and quantity discounts. J Clean Prod 198:704–720
Ghasemi P et al (2019) Uncertain multi-objective multi-commodity multi-period multi-vehicle location-allocation model for earthquake evacuation planning. Appl Math Comput 350:105–132
Ghodratnama A et al (2015) A stochastic approach for a novel p-hub location-allocation problem with opening and reopening modes. Int J Bus Perform Supply Chain Model 7(4):305–337
Gulzari A, Tarakci H (2021) A healthcare location-allocation model with an application of telemedicine for an earthquake response phase. Int J Disast Risk Reduct 55:102100
Haghshenas M, Nemati A, Asadi-Gangraj E (2021) A bi-objective model for Cancer hospitals’ location and cancer patients’ allocation in Iran. Int J Hosp Res 10(4):1–18
Haghshenas M et al (2023) Cancer-curing supply chain planning with regard to hospital bed-capacity efficiency: a plan for Iran in 2040. Int J Serv Oper Manag 45(2):170–186
Haghshenas M, Nemati A, Asadi-Gangraj E (2024) Using new fuzzy regression aptness and healthcare equity indices in cancer hospitals network design: a fuzzy multi-objective mathematical model. OPSEARCH 1:1–35
Hofmarcher T et al (2020) The cost of cancer in Europe 2018. Eur J Cancer 129:41–49
https://gco.iarc.fr/. "International Agency for Research in Cancer (2019) Global Cancer observatory, Malaysia Cancer Statistics. Available at: https://gco.iarc.fr/."
https://freshbooks.com "How Much Does It Cost to Build a Hospital: Construction Cost. available at : https://www.freshbooks.com/hub/estimates/how-much-does-it-cost-to-build-a-hospital#:~:text=The%20average%20construction%20costs%20for,built%20in%20a%20larger%20city.".
https://tehrantimes.com "Hospital construction cost in iran. available at: https://www.tehrantimes.com/news/431264/8-hospitals-built-in-9-months-costing-120m & https://www.tehrantimes.com/news/436772/40-new-hospitals-to-open-by-March-2020."
Iooss B, Lemaître P (2015) A review on global sensitivity analysis methods. Uncertainty management in simulation-optimization of complex systems. Springer, Cham, pp 101–122
Ivanov D, Dolgui A (2022) Stress testing supply chains and creating viable ecosystems. Oper Manag Res 15(1–2):475–486
Kamali A et al (2020) Optimising emergency medical centres location with a response-time-decreasing approach using hybrid methods of optimisation and simulation. Int J Serv Oper Manag 36(1):72–93
Karasakal O et al (2023) A partial coverage hierarchical location allocation model for health services. Eur J Ind Eng 17(1):115–147
Kaveh M et al (2020) Multiple criteria decision-making for hospital location-allocation based on improved genetic algorithm. Appl Geomat 12(3):291–306
Lin H et al (2023) Location and capacity planning for preventive healthcare facilities with congestion effects. J Ind Manag Optim 19(4):3044–3059
Linkov I, Trump BD, Trump J, Pescaroli G, Hynes W, Mavrodieva A, Panda A (2022) Resilience stress testing for critical infrastructure. Int J Disast Risk Reduct 82:103323
Maleki Rastaghi M et al (2018) A multi-objective hierarchical location-allocation model for the healthcare network design considering a referral system. Int J Eng 31(2):365–373
Mendoza-Gómez R, Ríos-Mercado RZ (2022) Location of primary health care centers for demand coverage of complementary services. Comput Ind Eng 169:108237
Mestre AM et al (2015) Location–allocation approaches for hospital network planning under uncertainty. Eur J Oper Res 240(3):791–806
Mitropoulos P et al (2006) A biobjective model for the locational planning of hospitals and health centers. Health Care Manag Sci 9(2):171–179
Mondal A, Roy SK (2021) Multi-objective sustainable opened-and closed-loop supply chain under mixed uncertainty during COVID-19 pandemic situation. Comput Ind Eng 159:107453
Mondal A, Roy SK (2022) Application of Choquet integral in interval type-2 Pythagorean fuzzy sustainable supply chain management under risk. Int J Intell Syst 37(1):217–263
Mondal A et al (2023) An integrated sustainable bio-fuel and bio-energy supply chain: A novel approach based on DEMATEL and fuzzy-random robust flexible programming with Me measure. Appl Energy 343:121225
Nickel S, Saldanha-da-Gama F (2019) Multi-period facility location. Springer, Berlin, pp 303–326
Olive DJ (2017) Linear regression. Springer, Berlin
Ouyang R et al (2020) Location-allocation models for healthcare facilities with long-term demand. Int J Oper Res 38(3):295–320
Poirier AE et al (2019) The future burden of cancer in Canada: long-term cancer incidence projections 2013–2042. Cancer Epidemiol 59:199–207
Praneetpholkrang P, Kanjanawattana S (2021) A multi-objective optimization model for shelter location-allocation in response to humanitarian relief logistics. Asian J Shipp Logist 37(2):149–156
Sahebi H, Nickel S (2014) Offshore oil network design with transportation alternatives. Eur J Ind Eng 8(6):739–761
Salami A et al (2023) A two-stage optimization approach for healthcare facility location-allocation problems with service delivering based on genetic algorithm. Int J Public Health 68:1605015
Saltelli A et al (2004) Sensitivity analysis in practice: a guide to assessing scientific models. Wiley, New York
Saltelli A et al (2006) Sensitivity analysis practices: Strategies for model-based inference. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 91(10–11):1109–1125
Saltelli A et al (2008) Global sensitivity analysis: the primer. Wiley, New York
Simchi-Levi D, Simchi-Levi E (2020) We need a stress test for critical supply chains. Harv Bus Rev 28:1
Simchi-Levi D et al (2014) From superstorms to factory fires. Harv Bus Rev 92(1):24
Simchi-Levi D, Schmidt W, Wei Y, Zhang PY, Combs K, Ge Y, Gusikhin O, Sanders M, Zhang D (2015) Identifying risks and mitigating disruptions in the automotive supply chain. Interfaces 45(5):375–390
Syam SS, Côté MJ (2010) A location–allocation model for service providers with application to not-for-profit health care organizations. Omega 38(3–4):157–166
Tirkolaee EB et al (2020) A robust green location-allocation-inventory problem to design an urban waste management system under uncertainty. Waste Manage 102:340–350
Vieira IFG, Barros MFD, Cormack A (2019) Hierarchical facility location model for allocating cancer treatment units in interior of Rio de Janeiro. Production 29:e20190026
Wang S et al (2024) Global sensitivity analysis methodology for construction simulation models: multiple linear regressions versus multilayer perceptions. J Constr Eng Manag 150(5):04024035
Xiao Z et al (2019) Location-allocation problem of reverse logistics for end-of-life vehicles based on the measurement of carbon emissions. Comput Ind Eng 127:169–181
Yi C, Lu M (2019) Mixed-Integer linear programming–based sensitivity analysis in optimization of temporary haul road layout design for earthmoving operations. J Comput Civ Eng 33(3):04019021
Zahiri B et al (2014) A robust possibilistic programming approach to multi-period location–allocation of organ transplant centers under uncertainty. Comput Ind Eng 74:139–148
Zarrinpoor N et al (2017) Design of a reliable hierarchical location-allocation model under disruptions for health service networks: a two-stage robust approach. Comput Ind Eng 109:130–150
Acknowledgements
No fund
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors verify that they have the same share in problem definition, problem-solving, data collection, coding, data analysis, and report writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kordi, A., Nemati, A. Simultaneous sensitivity analysis of mixed-integer location-allocation models using machine learning tools: cancer hospitals’ network design. Oper Res Int J 24, 22 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-024-00828-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-024-00828-7