Abstract
Web caches are useful in reducing the user perceived latencies and web traffic congestion. Multi-level classification of web objects in caching is relatively an unexplored area. This paper proposes a novel classification scheme for web cache objects which utilizes a multinomial logistic regression (MLR) technique. The MLR model is trained to classify web objects using the information extracted from web logs. We introduce a novel grading parameter worthiness as a key for the object classification. Simulations are carried out with the datasets generated from real world trace files using the classifier in Least Recently Used-Class Based (LRU-C) and Least Recently Used-Multilevel Classes (LRU-M) cache models. Test results confirm that the proposed model has good online learning and prediction capability and suggest that the proposed approach is applicable to adaptive caching.















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
There are six explanatory variables. Hence, we consider the nearest power of 2 as 8. This gives a flexibility to redefine W, according to an application.
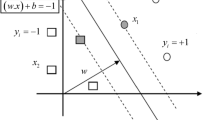
Maximum likelihood estimation begins with writing a mathematical expression known as the Likelihood Function of the sample data. The likelihood of a set of data is the probability of obtaining that particular set of data, given the chosen probability distribution model. This expression contains the unknown model parameters. The values of these parameters that maximize the sample likelihood are known as the Maximum Likelihood Estimator.
Here, we implement LRU-C method using binary LR method. Hence, worthiness factor will have only two classes; W = 0 and W = 1. Also, we do not consider the features from HTTP responses of the server and the HTML structure of the object.
References
Agresti A, Wiley J (1990) Categorical data analysis, vol 1, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Ahn H, Moon H, Fazzari M, Lim N, Chen J, Kodell R (2007) Classification by ensembles from random partitions of high-dimensional data. Comput Stat Data Anal 51(12):6166–6179
Attar V, Sinha P, Wankhade K (2010) A fast and light classifier for data streams. Evol Syst 1(3):199–207. doi:10.1007/s12530-010-9010-1
Bahn H, Koh K, Noh S, Lyul S (2002) Efficient replacement of nonuniform objects in web caches. Computer 35(6):65–73
Bian N, Chen H (2008) A least grade page replacement algorithm for web cache optimization. In: Knowledge discovery and data mining, 2008. WKDD 2008. First international workshop on, pp 469–472
Breslau L, Cao P, Fan L, Phillips G, Shenker S (1999) Web caching and Zipf-like distributions: evidence and implications. IEEE INFOCOM 1(1):126–134
Cao P, Irani S (2002) Cost-aware www proxy caching algorithms. IEEE Trans Comput 51(6):193–206
Chen X, Zhang X (2003) A popularity-based prediction model for web prefetching (No. 3). IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos
Chu F, Wang Y, Zaniolo C (2004) An adaptive learning approach for noisy data streams. In: Data mining, 2004. ICDM '04. Fourth IEEE international conference on, pp 351–354
Cobb J, ElAarag H (2008) Web proxy cache replacement scheme based on back-propagation neural network. J Syst Softw 81(9):1539–1558
Dill S, Kumar R, McCurley K, Rajagopalan S, Sivakumar D, Tomkins A (2002) Self-similarity in the web. ACM Trans Int Technol 2(3):205–223
Dreiseitl S, Ohno-Machado L (2002) Logistic regression and artificial neural network classification models: a methodology review. J Biomed Inform 35(5–6):352–359
Dreiseitl S, Ohno-Machado L, Kittler H, Vinterbo S, Billhardt H, Binder M (2001) A comparison of machine learning methods for the diagnosis of pigmented skin lesions. J Biomed Inform 34(1):28–36
Efron B, Gong G (1983) A leisurely look at the bootstrap, the jackknife, and cross-validation. Am Stat, pp 36–48
Foong AP, Hu Y-H, Heisey DM (1999) Logistic regression in an adaptive web cache. IEEE Int Comput 3(5):27–36
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2000) Additive logistic regression: a statistical view of boosting (With discussion and a rejoinder by the authors). Ann Stat 28(2):337–407
Gama J, Medas P, Castillo G, Rodrigues P (2004) Learning with drift detection. Lect Notes Comput Sci 1:286–295
Gao J, Fan W, Han J, Yu PS (2007) A general framework for mining concept-drifting data streams with skewed distributions. In: Proceedings of SDM
Gonzalez-Canete FJ, Casilari E, Trivino-Cabrera A (2006) Two new metrics to evaluate the performance of a web cache with admission control. In: Electrotechnical conference, 2006. MELECON 2006. IEEE mediterranean, pp 696–699
Green M, Björk J, Forberg J, Ekelund U, Edenbrandt L, Ohlsson M (2006) Comparison between neural networks and multiple logistic regression to predict acute coronary syndrome in the emergency room. (No. 3). Tecklenburg, Federal Republic of Germany, Burgverlag, c1989
Hosmer D, Lemeshow S (2000) Applied logistic regression, vol 354, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York. http://books.google.com/books?id=Po0RLQ7USIMC
Imai K, King G, Lau O (2006) Zelig: everyone’s statistical software. http://gking.harvard.edu/zelig
Jin S, Bestavros A (2000) Popularity-aware greedy dual-size web proxy caching algorithms. In: Distributed computing systems, 2000. Proceedings. 20th international conference on, pp 254–261
Klinkenberg R, Renz I (1998) Adaptive information filtering: learning in the presence of concept drifts. Learn Text Categor 1:33–40
Komarek P (2004) Logistic regression for data mining and high-dimensional classification. Biostatistics 4:138
Koskela T, Heikkonen J, Kaski K (2003) Web cache optimization with nonlinear model using object features. Comput Netw 43(6):805–817
Krashakov SA, Teslyuk AB, Shchur LN (2006) On the universality of rank distributions of website popularity. Comput Netw 50(11):1769–1780
Krashakov SA, Teslyuk AB, Shchur LN (2006) On the universality of rank distributions of website popularity. Comput Netw 50(11):1769–1780
Landwehr N, Hall M, Frank E (2005) Logistic model trees. Mach Learn 59(1):161–205
Li K, Nanya T, Qu W (2007) A minimal access cost-based multimedia object replacement algorithm. In: IEEE international parallel and distributed processing symposium, 2007. IPDPS 2007, pp 1–7
Lim T, Loh W, Shih Y (2000) A comparison of prediction accuracy, complexity, and training time of thirty-three old and new classification algorithms. Mach Learn 40(3):203–228
Long W, Griffith J, Selker H, D’agostino R (1993) A comparison of logistic regression to decision-tree induction in a medical domain. Comput Biomed Res 26:74–97
Lu Y, Abdelzaher T, Lu C, Tao G (2002) An adaptive control framework for QoS guarantees and its application to differentiated caching. In: Quality of service, 2002. Tenth IEEE International Workshop on, pp 23–32
Markatchev N and Williamson C (2002) Webtraff: A GUI for web proxy cache workload modeling and analysis. In: Modeling, analysis and simulation of computer and telecommunications systems, 2002. MASCOTS 2002. Proceedings. 10th IEEE international symposium on, p 356–363
Mierswa I, Wurst M, Klinkenberg R, Scholz M, Euler T (2006) Yale: rapid prototyping for complex data mining tasks. In: Ungar L, Craven M, Gunopulos D, Eliassi-Rad T (eds) Kdd ’06: Proceedings of the 12th acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM Press, New York, NY, USA, pp 935–940
Miller A (2002) Subset selection in regression. CRC Press, New York
NLANR (2010) Cache access logs [online]. ftp://ircache.nlanr.net/traces/
Pallis G, Thomos C, Stamos K, Vakali A, Andreadis G (2007) Content classification for caching under CDNs. In: Innovations in information technology, 2007. IIT '07. 4th international conference on, pp 586–590
Podlipnig S, Böszörmenyi L (2003) A survey of web cache replacement strategies. ACM Comput Surv 35(4):374–398
Sargent D (2001) Comparison of artificial neural networks with other statistical approaches. CA A Cancer J Clin 91(S8):1636–1642
Steyerberg EW, Harrell FE, Borsboom GJJM, Eijkemans MJC, Vergouwe Y, Habbema JDF (2001) Internal validation of predictive models: efficiency of some procedures for logistic regression analysis. J Clin Epidemiol 54(8):774–781
Sulaiman S, Shamsuddin SM, Forkan F, Abraham A (2008) Intelligent web caching using neurocomputing and particle swarm optimization algorithm. In: Ams ’08: Proceedings of the 2008 second asia international conference on modelling & simulation (ams). IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, pp 642–647
Team RDC (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Language software Team, Vienna
Tian W, Choi B, Phoha VV (2002) An adaptive web cache access predictor using neural network. In: Iea/aie ’02: Proceedings of the 15th international conference on industrial and engineering applications of artificial intelligence and expert systems. Springer, London, pp 450–459
TraceGraph (2005) Trace graph tool (online). http://www.tracegraph.com/traceconverter.html
Tsymbal A (2004) The problem of concept drift: definitions and related work. Computer Science Department, Trinity College, Dublin
Wang H, Fan W, Yu PS, Han J (2003) Mining concept-drifting data streams using ensemble classifiers. In: Proceedings of the ninth ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 226–235
Wang Y (2005) A multinomial logistic regression modeling approach for anomaly intrusion detection. Comput Secur 24(8):662–674
Xu L, Chow M-C, Gao XZ (2005) Comparisons of logistic regression and artificial neural network on power distribution systems fault cause identification. In: Soft computing in industrial applications, 2005. SMCia/05. Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Mid-summer workshop on, pp 128–131
Yang Q, Zhang HH (2003) Web-log mining for predictive web caching. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 15(4):1050–1053
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sajeev, G.P., Sebastian, M.P. A novel content classification scheme for web caches. Evolving Systems 2, 101–118 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12530-010-9026-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12530-010-9026-6