Abstract
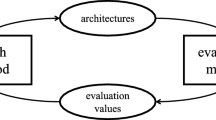
In recent years, deep neural networks (DNNs) have achieved great successes in many areas, such as cognitive computation, pattern recognition, and computer vision. Although many hand-crafted deep networks have been proposed in the literature, designing a well-behaved neural network for a specific application requires high-level expertise yet. Hence, the automatic architecture design of DNNs has become a challenging and important problem. In this paper, we propose a new reinforcement learning method, whose action policy is to select neural blocks and construct deep networks. We define the action search space with three types of neural blocks, i.e., dense block, residual block, and inception-like block. Additionally, we have also designed several variants for the residual and inception-like blocks. The optimal network is automatically learned by a Q-learning agent, which is iteratively trained to generate well-performed deep networks. To evaluate the proposed method, we have conducted experiments on three datasets, MNIST, SVHN, and CIFAR-10, for image classification applications. Compared with existing hand-crafted and auto-generated neural networks, our auto-designed neural network delivers promising results. Moreover, the proposed reinforcement learning algorithm for deep networks design only runs on one GPU, demonstrating much higher efficiency than most of the previous deep network search approaches.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker B, Gupta O, Naik N, Raskar R. 2017. Designing neural network architectures using reinforcement learning. In: ICLR.
Bengio Y. Gradient-based optimization of hyperparameters. Neural Comput 2000;12(8):1889–1900.
Bergstra J, Bengio Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J Mach Learn Res 2012;13:281–305.
Bergstra J, Yamins D, Cox DD. 2013. Making a science of model search: hyperparameter optimization in hundreds of dimensions for vision architectures. In: ICML, pp 115–123.
Botev A, Lever G, Barber D. 2017. Nesterov’s accelerated gradient and momentum as approximations to regularised update descent. In: IJCNN, pp 1899–1903.
Cai H, Chen T, Zhang W, Yu Y, Wang J. 2018. Efficient architecture search by network transformation. In: AAAI.
Gepperth A, Karaoguz C. A bio-inspired incremental learning architecture for applied perceptual problems. Cogn Comput 2016;8(5):924–934.
Glorot X, Bordes A, Bengio Y. 2011. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks. In: AISTATS, pp 315–323.
Goodfellow IJ, Warde-farley D, mirza M, courville AC, bengio Y. 2013. Maxout networks. In: ICML, pp 1319–1327.
Guo T, Zhang L, Tan X. Neuron pruning-based discriminative extreme learning machine for pattern classification. Cogn Comput 2017;9(4):581–595.
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. 2015. Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification. In: ICCV, pp 1026–1034.
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. 2016. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR, pp 770–778.
Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ. 2017. Densely connected convolutional networks. In: CVPR, pp 2261–2269.
Huang G, Sun Y, Liu Z, Sedra D, Weinberger KQ. 2016. Deep networks with stochastic depth. In: ECCV, pp 646–661.
Ioffe S, Szegedy C. 2015. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: ICML, pp 448–456.
Jia Y, Shelhamer E, Donahue J, Karayev S, Long J, Girshick RB, Guadarrama S, Darrell T. 2014. Caffe: convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In: ACM MM, pp 675–678.
Kingma DP, Ba J. 2014. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. CoRR arXiv:http://arXiv.org/abs/1412.6980.
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE. 2012. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: NeurIPS, pp 1106–1114.
Lin LJ. 1993. Reinforcement learning for robots using neural networks. Technical report, DTIC Document.
Lin M, Chen Q, Yan S. 2013. Network in network. In: ICLR.
Liu C, Zoph B, Neumann M, Shlens J, Hua W, Li L, Fei-fei L, yuille AL, huang J, murphy K. 2018. Progressive neural architecture search. In: ECCV, pp 19–35.
Liu H, Simonyan K, Vinyals O, Fernando C, Kavukcuoglu K. 2018. Hierarchical representations for efficient architecture search. In: ICLR.
Luo B, Hussain A, Mahmud M, Tang J. Advances in brain-inspired cognitive systems. Cogn Comput 2016;8(5):795–796.
Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, Rusu AA, Veness J, Bellemare MG, Graves A, Riedmiller MA, Fidjeland A, Ostrovski G, Petersen S, Beattie C, Sadik A, Antonoglou I, King H, Kumaran D, Wierstra D, Legg S, Hassabis D. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015;518(7540):529–533.
Pham H, Guan MY, Zoph B, Le QV, Dean J. 2018. Efficient neural architecture search via parameter sharing. In: ICML, pp 4092–4101.
Romero A, Ballas N, Kahou SE, Chassang A, Gatta C, Bengio Y. 2014. Fitnets: Hints for thin deep nets. CoRR arXiv:http://arXiv.org/abs/1412.6550.
Saxena S, Verbeek J. 2016. Convolutional neural fabrics. In: NeurIPS, pp 4053–4061.
Schulman J, Wolski F, Dhariwal P, Radford A, Klimov O. 2017. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. CoRR arXiv:http://arXiv.org/abs/1707.06347.
Simonyan K, Zisserman A. 2014. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. CoRR arXiv:http://arXiv.org/abs/1409.1556.
Snoek J, Larochelle H, Adams RP. 2012. Practical bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms. In: NeurIPS, pp 2960–2968.
Snoek J, Rippel O, Swersky K, Kiros R, Satish N, Sundaram N, Patwary MMA, Prabhat Adams RP. 2015. Scalable bayesian optimization using deep neural networks. In: ICML, pp 2171–2180.
Srivastava RK, Greff K, Schmidhuber J. 2015. Highway networks. CoRR arXiv:http://arXiv.org/abs/1505.00387.
Stanley KO, D’Ambrosio DB, Gauci J. A hypercube-based encoding for evolving large-scale neural networks. Artif Life 2009;15(2):185–212.
Stanley KO, Miikkulainen R. Evolving neural networks through augmenting topologies. Evol Comput. 2002:99–127.
Suganuma M, Shirakawa S, Nagao T. 2017. A genetic programming approach to designing convolutional neural network architectures. In: GECCO, pp 497–504.
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed SE, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A. 2015. Going deeper with convolutions. In: CVPR, pp 1–9.
Taylor JG. Cognitive computation. Cogn Comput 2009;1(1):4–16.
Williams RJ. Simple statistical gradient-following algorithms for connectionist reinforcement learning. Mach Learn 1992;8:229–256.
Zhang S, Huang K, Zhang R, Hussain A. Learning from few samples with memory network. Cogn Comput 2018;10 (1):15–22.
Zhao F, Zeng Y, Wang G, Bai J, Xu B. A brain-inspired decision making model based on top-down biasing of prefrontal cortex to basal ganglia and its application in autonomous UAV explorations. Cogn Comput 2018;10(2):296–306.
Zhong G, Yan S, Huang K, Cai Y, Dong J. Reducing and stretching deep convolutional activation features for accurate image classification. Cogn Comput 2018;10(1):179–186.
Zhong Z, Yan J, Liu C. 2018. Practical block-wise neural network architecture generation. In: CVPR.
Zoph B, Le QV. 2017. Neural architecture search with reinforcement learning. In: ICML.
Zoph B, Vasudevan V, Shlens J, Le QV. 2018. Learning transferable architectures for scalable image recognition. In: CVPR.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China under Grant 2016YFC1401004, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant No. 41706010 and 61876155, the Science and Technology Program of Qingdao under Grant No. 17-3-3-20-nsh, the CERNET Innovation Project under Grant No. NGII20170416, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China. In addition, we would like to thank Tao Li for his helpful comments and discussions. We also would like to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their helpful reviews.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, G., Jiao, W., Gao, W. et al. Automatic Design of Deep Networks with Neural Blocks. Cogn Comput 12, 1–12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-019-09677-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-019-09677-5