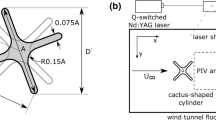
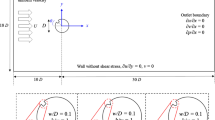
Abstract
The turbulent flow over a cactus-analogue grooved cylinder at a Reynolds number of 5.4 × 104 was investigated using large eddy simulation integrated in OpenFOAM, with particular emphasis on the flow within grooves and its effect on the near wake immediately behind the cylinder. The baseline configuration of a smooth cylinder was examined for comparison. The wall-pressure fluctuation intensity, wall-pressure spectra, and time-averaged velocity field were in favorable agreement with previous experimental measurements. The fluctuation intensity of the lift coefficient for the cactus-analogue grooved cylinder was approximately 50 % less than for the smooth one. Different flow regions around the cylinder were selected for the proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) analysis, with a view to elucidating the production of the fine vortices by the grooves and their coupling with the dynamics of the near wake. Taking the correlation of the first two POD mode coefficients as the phase indicator, the phase-dependent variations of the flow fields and wall-pressure fluctuations were determined. Finally, the POD analysis of the three-dimensional velocity fields confirmed that the vortical structure on the spanwise direction for the grooved cylinder was more scattered and irregular.
Graphical abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a i :
-
Coefficient of the POD mode i
- A :
-
Reference area of the cylinder
- C L :
-
Dimensionless lift coefficient
- C s :
-
Smagorinsky coefficient
- D :
-
Diameter of cylinder
- l s :
-
\(C_{\text{s}} \Delta\)
- L :
-
Cavity depth
- f :
-
Frequency
- F y :
-
Transverse force acting on the surface of the cylinder
- p :
-
Instantaneous pressure
- \(p_{\text{RMS}}^{'}\) :
-
RMS of instantaneous pressure fluctuation
- \(\overline{S}_{ij}\) :
-
Rate-of-stain tensor
- t :
-
Time
- u x :
-
Component of instantaneous velocity
- u i :
-
i Component of instantaneous velocity
- \(u_{\text{RMS}}^{'}\) :
-
RMS of streamwise velocity fluctuation
- \(U_{0}\) :
-
Free-stream velocity
- \(v\) :
-
y component of instantaneous velocity
- \(w\) :
-
z component of instantaneous velocity
- y :
-
Cell-to-wall distance
- y + :
-
Non-dimensional wall-distance
- \(\delta_{ij}\) :
-
Kronecker delta
- \(\Delta\) :
-
Grid scale, \(\left( {\Delta_{1} \Delta_{2} \Delta_{3} } \right)^{{{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 3}} \right. \kern-0pt} 3}}}\)
- \(\Delta t\) :
-
Time step
- \(\theta\) :
-
Angle defined in the coordinate system
- \(\lambda_{i}\) :
-
Eigenvalue of the POD mode i
- \(\nu\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- \(\nu_{\text{t}}\) :
-
Turbulent kinematic viscosity
- ρ :
-
Density
- \(\tau_{ij}\) :
-
Sub-grid scale residual stress tensor
- GAMG:
-
Generalized geometric-algebraic multi-grid
- HPC:
-
High-performance computing
- LES:
-
Large eddy simulation
- LIC:
-
Line integral convolution
- LUST:
-
Linear-upwind stabilized transport
- PIMPLE:
-
Merged PISO-SIMPLE
- POD:
-
Proper orthogonal decomposition
- RANS:
-
Reynolds averaged Navier–Stokes
- RMS:
-
Root mean square
- SGS:
-
Sub-grid scale
References
Babu P, Mahesh K (2008) Aerodynamic loads on cactus-shaped cylinders at low Reynolds numbers. Phys Fluids 20:035–112
Brandt A (1980) Multilevel adaptive computations in fluid dynamics. AIAA J 18:1165–1172
Breuer M (1998) Large eddy simulation of the subcritical flow past a circular cylinder: numerical and modeling aspects. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 28:1281–1302
El-Makdah AM, Oweis GF (2013) The flow past a cactus-inspired grooved cylinder. Exp Fluids 54:1464
Forssell LK, Cohen SD (1995) Using line integral convolution for flow visualization: curvilinear grids, variable-speed animation, and unsteady flows. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 1:133–141
Gad-El-Hak M (2007) Flow control: passive, active, and reactive flow management. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Geller GN, Nobel PS (1984) Cactus ribs: influence on PAR interception and CO2 uptake. Photosynthetica 18:482–494
Geurts BJ (2004) Elements of direct and large-eddy simulation. Edwards, Philadelphia
Henson VE, Yang UM (2002) BoomerAMG: a parallel algebraic multigrid solver. Appl Numer Math 41:155–177
Hunt JCR, Wray AA, Moin P (1998) Eddies stream and convergence zones in turbulent flows. In: Proceedings of the 1998 Summer Program (CTR), 193–208
Jasak H (1996) Error analysis and estimation for the finite volume method with applications to fluid flows. Imperical College, London
Levy B, Liu Y (2013) The effects of cactus inspired spines on the aerodynamics of a cylinder. J Fluids Struct 39:335–346
Liu YZ, Shi LL, Yu J (2011) TR-PIV measurement of the wake behind a grooved cylinder at low Reynolds number. J Fluids Struct 27:394–407
Lysenko DA, Ertesvåg IS, Rian KE (2012) Large-eddy simulation of the flow over a circular cylinder at Reynolds number 3900 using the OpenFOAM Toolbox. Flow Turbul Combust 89:491–518
Norberg C (2003) Fluctuating lift on a circular cylinder: review and new measurements. J Fluids Struct 17:57–96
Oudheusden BW Van, Scarano F, Hinsberg NP Van, Watt DW (2005) Phase-resolved characterization of vortex shedding in the near wake of a square-section cylinder at incidence. Exp Fluids 39:86–98
Prothin S, Djeridi H, Billard JY (2014) Coherent and turbulent process analysis of the effects of a longitudinal vortex on boundary layer detachment on a NACA0015 foil. J Fluids Struct 47:2–20
Rhie CM, Chow WL (1983) Numerical study of the turbulent flow past an airfoil with trailing edge separation. AIAA J 21:1525–1532
Sirovich L (1987) Turbulence and the dynamics of coherent structures. Part I-Coherent structures. Part II-Symmetries and transformations. Part III-Dynamics and scaling. Q Appl Math 45:561–571
Smagorinsky J (1963) General circulation experiments with the primitive equations, part I. The basic experiment. Mon Weather Rev 91:99–164
Talley S, Mungal G (2002) Flow around cactus-shaped cylinders. Cent Turbul Res Annu Res Br 12:363–376
Talley BS, Iaccarino G, Mungal G, Mansour NN (2001) An experimental and computational investigation of flow past cacti. Annu Res Briefs, Center for Turbulence Research, Stanford University
Wang SF, Liu YZ, Zhang QS (2014) Measurement of flow around a cactus-analogue grooved cylinder at ReD = 5.4 × 104: wall pressure fluctuations and flow pattern. J Fluids Struct 50:120–136
Weller H (2012) Controlling the computational modes of the arbitrarily structured C grid. Mon Weather Rev 140:3220–3234
Weller H, Tabor G, Jasak H, Fureby C (1998) A tensorial approach to computational continuum mechanics using object-oriented techniques. J Comput Phys 12(6):620–31
Williamson CHK (1996) Vortex dynamics in the Cylinder wake. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 26:477–539
Wissink JG, Rodi W (2008) Numerical study of the near wake of a circular cylinder. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 29:1060–1070
Yamagishi Y, Oki M (2004) Effect of groove shape on flow characteristics around a circular cylinder with grooves. J Vis 7:209–216
Yamagishi Y, Oki M (2005) Effect of the number of grooves on flow characteristics around a circular cylinder with triangular grooves. J Vis 8:57–64
Zhang QS, Liu YZ (2012) Wall pressure fluctuations of separated and reattaching flow over blunt plate with chord-to-thickness ratio c/d = 9.0. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 42:125–135
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support for this study from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51176108 and 11372189). Additionally, the authors would like to thank the Center for High Performance Computing at Shanghai Jiao Tong University for providing the HPC computational resources and useful technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jie, H., Liu, Y.Z. Large eddy simulation of turbulent flow over a cactus-analogue grooved cylinder. J Vis 19, 61–78 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-015-0294-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-015-0294-x