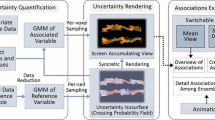
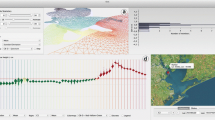
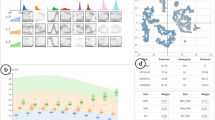
Abstract
Sophisticated numerical computation is widely used in weather forecast. Various computation models exist, and each of them is designed for different meteorological elements, areas, or seasons. Therefore, multimodel ensemble forecast is aimed at integrating various numerical model forecasts to obtain an accurate forecast result. The existence of deviations compels forecasters to calibrate ensemble forecast result. Traditional calibration methods are strongly dependent on the experience of the forecaster and are usually performed inefficiently with grid-by-grid or station-by-station mode. Such calibration methods experience several drawbacks, including the high complexity and the low comprehensiveness of searching for similar historical forecast results in a limited dataset and the lack of real-time interactive analysis. To solve these problems and improve the efficiency and the accuracy of calibration, we propose a visualization system for calibrating multimodel ensemble forecast result. This system can assist forecasters to quickly locate potential calibrating stations by visualizing the deviation of historical forecast and observation result. Then, associated regions are calculated automatically under similarity and connectivity constraints, and corresponding coefficients between associated stations are generated based on parameter learning of the factor graph. These associated regions and coefficients are used as a guide for forecasters in setting unified deviation and weight for each numerical model. Finally, automatic calibration is conducted on the rest stations in the associated area. The performance of the visualization system is evaluated with real meteorological data.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernard J, Steiger M, Widmer S et al (2014) Visual interactive exploration of interesting multivariate relations in mixed research data sets. Comput Graph Forum 33(3):291–300
Fraley C, Raftery AE, Gneiting T (2010) Calibrating multimodel forecast ensembles with exchangeable and missing members using Bayesian model averaging. Mon Weather Rev 138(1):190–202
Geman S, Bienenstock E, Doursat R (1992) Neural networks and the bias/variance dilemma. Neural Comput 4(1):1–58
Hamill TM, Whitaker JS (2006) Probabilistic quantitative precipitation forecasts based on reforecast analogs: theory and application. Mon Weather Rev 134(11):3209–3229
Hastings WK (1970) Monte Carlo sampling methods using Markov chains and their applications. Biometrika 57(1):97–109
Hoeting JA, Madigan D, Raftery AE et al (1999) Bayesian model averaging: a tutorial. Stat Sci 14(4):382–401
Kalman RE (1960) A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. J Fluids Eng 82(1):35–45
Krishnamurti TN, Kishtawal CM, LaRow TE et al (1999) Improved weather and seasonal climate forecasts from multimodel superensemble. Science 285(5433):1548–1550
Krishnamurti TN, Kishtawal CM, Zhang Z et al (2000) Multimodel ensemble forecasts for weather and seasonal climate. J Clim 13(23):4196–4216
Kschischang FR, Frey BJ, Loeliger HA (2001) Factor graphs and the sum-product algorithm. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 47(2):498–519
Lee DT, Schachter BJ (1980) Two algorithms for constructing a Delaunay triangulation. Int J Comput Inform Sci 9(3):219–242
Li B, Zhi X (2008) Comparative study of four correction schemes of the ECMWF surface temperature forecasts. Meteorol Mon 38(8):897–902
Ma Q, Gong J, Li L, Li Y (2008) Study of bias-correction and consensus in regional multi-model super-ensemble forecast. Meteorol Mon 34(3):42–48
Maes F, Collignon A, Vandermeulen D et al (1997) Multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 16(2):187–198
Morris A (2002) An information theoretic measure of sequence recognition performance. IDIAP
Qu H, Chan WY, Xu A et al (2007) Visual analysis of the air pollution problem in Hong Kong. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 13(6):1408–1415
Rixen M, Ferreira-Coelho E (2007) Operational surface drift prediction using linear and non-linear hyper-ensemble statistics on atmospheric and ocean models. J Mar Syst 65(1):105–121
Sauber N, Theisel H, Seidel HP (2006) Multifield-graphs: an approach to visualizing correlations in multifield scalar data. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 12(5):917–924
Schreiber T (2000) Measuring information transfer. Phys Rev Lett 85(2):461
Shepard D (1968) A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM national conference. ACM, pp 517–524
Sisneros R, Johnson CR, Huang J (2008) Concurrent viewing of multiple attribute specific subspaces. Computer Graphics Forum. Blackwell Publishing Ltd 27(3): 783–790
Sukharev J, Wang C, Ma KL et al (2009) Correlation study of time-varying multivariate climate data sets. In: IEEE Pacific Visualization Symposium (PacificVis), pp 161–168
Tong H, Guo P, Zhu Y et al (2014) Bias correction and statistical downscaling meteorological parameters forecast technique based on large-scale numerical model products. Meteorol Mon 40(1):66–75
Wang C, Yu H, Ma KL (2008) Importance-driven time-varying data visualization. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 14(6):1547–1554
Wang C, Yu H, Grout RW et al (2011) Analyzing information transfer in time-varying multivariate data. In: IEEE Pacific Visualization Symposium (PacificVis), pp 99–106
Xie L, Zhang E (2014) Rules visualization based on metric of mutual information. Comput Eng Appl 50(17):146–149
Zhao Y, Liang X, Fan X et al (2014) MVSec: multi-perspective and deductive visual analytics on heterogeneous network security data. J Vis 17(3):181–196
Zhi X, Qi H, Bai Y et al (2012) A comparison of three kinds of multimodel ensemble forecast techniques based on the TIGGE data. Acta Meteorol Sin 26(1):41–51
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Special Scientific Research Fund of Meteorological Public Welfare Profession of China through Grant GYHY201306002 and GYHY201406004, and in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China through Grant 61272225, 61572274, 91315302 and 51261120376. We thank the National Meteorological Center for providing multimodel ensemble forecast data and station observation data, and anonymous reviewers for their constructive criticism.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, C., Chen, L. & Zhu, Z. A visualization system for calibrating multimodel ensembles in weather forecast. J Vis 19, 769–782 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-015-0341-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-015-0341-7