Abstract
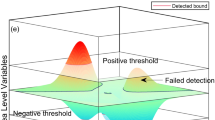
Ocean surface current (or ocean flow) visualization plays a significant role in the understanding of dynamical processes of ocean. It has been a hot research topic in both computer science and oceanography. Ocean surface current is a turbulent flow field mixing of multi-scale ocean dynamics such as large-scale ocean circulations (\(100\,\hbox {km}\sim\)), mesoscale eddies (10–\(100\,\hbox {km}\)), submesoscale processes (1–\(10\,\hbox {km}\)). Mesoscale eddies, which are strong but short-life movement relative to the large-scale ocean circulations, have great importance on the transportation of ocean water masses, momentum and energy. However, their detection and recognition, which are treated as the foundation of exploring their dynamical mechanisms, is still a challenging issue. For one thing, in the mixed ocean flow field, different ocean flows depended and influence with each other making existing methods difficult to identify among them. For another, mesoscale eddies are active signals on the ocean. They may change their forms and velocities at any time. This challenges existing works to deal with their boundary ambiguity and unremitting transitions. To solve these problems, this paper proposes a novel 2D and 3D ocean surface current visualization approach based on an amended Helmholtz–Hodge decomposition (HHD), which can be widely used for mesoscale eddy detection. In our method, HHD decomposes each mixed ocean flow field to two components: curl component and divergence component. Different ocean flows can be represented by these two components independently. In addition, to improve the performance of eddy identification and to reveal the 3D structure of ocean flows simultaneously, HHD transforms the 2D ocean flow field to 3D potential surfaces. Finally, comprehensive experiments are performed on both global and local ocean flow field (Black Sea and Mediterranean Sea) calculated from satellite maps of sea level anomaly to verify our method. Experimental results demonstrate the good effectiveness of our method.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhatia H, Norgard G, Pascucci V, Bremer PT (2013) The Helmholtz–Hodge decomposition—a survey. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 19(8):1386
Bi C, Yuan Y, Zhang J, Shi Y, Xiang Y, Wang Y, Zhang R (2018) Dynamic mode decomposition based video shot detection. IEEE Access 6:21397–21407
Bi C, Yuan Y, Zhang R, Xiang Y, Wang Y, Zhang J (2017) A dynamic mode decomposition based edge detection method for art images. IEEE Photon J 6(6):1–13
Chelton D, Schlax M, Samelson R, Early J (2011) Global satellite altimeter observations of nonlinear mesoscale eddies. Prog Oceanogr 91:167–216
Faghmous JH, Frenger I, Yao Y, Warmka R, Lindell A, Kumar V (2015) A daily global mesoscale ocean eddy dataset from satellite altimetry. Sci Data 2:150028
Isernfontanet J, Garcaladona E, Font J (2003) Identification of marine eddies from altimetric maps. J Atmos Ocean Technol 20(5):772–778
Ji P, Tian F, Liu S, Chen G (2016) 3D streamline visualization for irregular flow field data. J Comput Theor Nanosci 13(11):8909–8916
Liang X, Zhang C, Matsuyama T (2014) Inlier estimation for moving camera motion segmentation. In: Proceedings of Asian conference on computer vision (ACCV). Springer, pp 352–367
Liang X, Zhang C, Matsuyama T (2015) A general inlier estimation for moving camera motion segmentation. IPSJ Trans Comput Vis Appl 7:163–174
Liu Z, Du Y, Xu K (2015) An improved scheme of identifying loops using Lagrangian drifters. In: IEEE international conference on spatial data mining and geographical knowledge services, pp 125–128
Liu Z, James R, Scan M, Ziegeler B (2003) Ocean flow visualization in virtual environment. Technical Report, pp 1–49
Liu Z, Moorhead R II (2016) High-performance flow visualization for effective data analysis. J Flow Vis Image Process 23(1–2):41–57
Mkhinini N, Coimbra ALS, Stegner A, Arsouze T, TaupierLetage I, Branger K (2015) Longlived mesoscale eddies in the eastern Mediterranean Sea: analysis of 20 years of AVISO geostrophic velocities. J Geophys Res Oceans 119(12):8603–8626
Nencioli F, Dong C, Dickey T, Washburn L, Mcwilliams JC (2010) A vector geometry–based eddy detection algorithm and its application to a high-resolution numerical model product and high-frequency radar surface velocities in the southern california bight. J Atmos Ocean Technol 27(3):564
Petersen MR, Williams SJ, Maltrud ME, Hecht MW, Hamann B (2013) A threedimensional eddy census of a highresolution global ocean simulation. J Geophys Res Oceans 118(4):1759–1774
Petronetto F, Paiva A, Lage M, Tavares G, Lopes H, Lewiner T (2010) Meshless Helmholtz–Hodge decomposition. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 16(2):338–349
Polthier K, Preu E (2003) Identifying vector fields singularities using a discrete Hodge decomposition. In: Hege HC, Polthier K (eds) Visualization and mathematics III, Mathematics and Visualization. Springer, Berlin, pp 123–134
Ren B, Li CF, Lin MC, Kim T, Hu SM (2013) Flow field modulation. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 19(10):1708–19
Sadarjoen IA, Post FH (2000) Detection, quantification, and tracking of vortices using streamline geometry. Comput Graph 24(3):333–341
Samsel F, Petersen M, Abram G, Turton TL, Rogers D, Ahrens J (2015) Visualization of ocean currents and eddies in a high-resolution global ocean-climate model. In: Proceedings of the international conference on high performance computing, networking, storage and analysis, vol 2, issue 3, pp 1–4
Souza JMAC, Montgut CDB, Traon PYL (2011) Comparison between three implementations of automatic identification algorithms for the quantification and characterization of mesoscale eddies in the South Atlantic Ocean. Ocean Sci 7(3):317–334
Sun Y (2006) Visualizing oceanic and atmospheric flows with streamline splatting. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng 6060:606002–606012
Tandeo P, Chapron B, Ba S, Autret E, Fablet R (2013) Segmentation of mesoscale ocean surface dynamics using satellite SST and SSH observations. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52(7):4227–4235
Tao J, Wang C, Shene CK, Kim SH (2014) A deformation framework for focus + context flow visualization. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 20(1):42–55
Tong Y, Lombeyda S, Hirani A, Desbrum M (2003) Discrete multiscale vector field decomposition. In: ACM SIGRAPH, pp 27–31
Wiebel A (2004) Feature detection in vector fields using the Helmholtz–Hodge decomposition. Diploma Thesis, University of Kaiserslautern, pp 1–61
Williams S, Petersen M, Bremer PT, Hecht M, Pascucci V, Ahrens J, Hlawitschka M, Hamann B (2011) Adaptive extraction and quantification of geophysical vortices. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 17(12):2088–2095
Xiu P, Chai F, Shi L, Xue H, Chao Y (2010) A census of eddy activities in the South China Sea during 1993–2007. J Geophys Res Atmos 115(C3):132–148
Yang L, Wang B, Zhang R, Zhou H, Wang R (2018) Analysis on location accuracy for the binocular stereo vision system. IEEE Photon J 10(1):1–16
Zhang C, Liang X, Matsuyama T (2013) Mixed-motion segmentation using Helmholtz decomposition. IPSJ Trans Comput Vis Appl 5:55–59
Zhang C, Liu Z-L (2017) Prior-free dependent motion segmentation using Helmholtz–Hodge decomposition based object-motion oriented map. J Comput Sci Technol 32(3):520–535
Zhang C, Wei H, Bi C, Liu Z (2018) Helmholtz–Hodge decomposition based 2D and 3D ocean flow visualization for mesoscale eddy detection. J Vis (ChinaVis 2018) 1–8
Zhang Z, Tian J, Bo Q, Wei Z, Ping C, Wu D, Wan X (2016) Observed 3D structure, generation, and dissipation of oceanic mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea. Sci Rep 6:24349
Zhang Z, Wang W, Qiu B (2014) Oceanic mass transport by mesoscale eddies. Science 345(6194):322–324
Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Wang W (2017) Three-compartment structure of subsurface-intensified mesoscale eddies in the ocean. J Geophys Res Oceans 122(3):1653–1664
Zheng Q, Tai CK, Hu J, Lin H, Zhang RH, Su FC, Yang X (2011) Satellite altimeter observations of nonlinear Rossby eddy–Kuroshio interaction at the Luzon Strait. J Oceanogr 67(4):365
Zhu Z, Ii RJM (1995) Extracting and visualizing ocean eddies in time-varying flow fields. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on flow visualization, pp 206–211
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2017YFC1404403) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 4180060167, 61503277, 61702360).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Wei, H., Bi, C. et al. Helmholtz–Hodge decomposition-based 2D and 3D ocean surface current visualization for mesoscale eddy detection. J Vis 22, 231–243 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-018-0534-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-018-0534-y