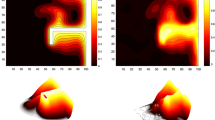
Abstract
The interior of a square cavity containing nanofluid with copper (Cu) nanoparticles (NPs) was simulated by a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) method. The flow rate parameters were obtained with different directions of the computing elements and temperature of the fluid inside the cavity. The CFD outputs were studied using an adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) to create an artificial fluid flow domain. The CFD outputs were used as the input and output data in the ANFIS method. Subtractive clustering was applied used for data clustering to look at the impact of the cluster influence range on the performance of the ANFIS method. After the highest level of performance was reached, the cavity nodes that were not involved in the learning process were predicted. Very good accordance was observed between the ANFIS method prediction and the results of the CFD method. The ANFIS method reduced the calculation time dramatically compared to the CFD method and has the ability to predict far more nodes in a short period of time. The results show that the clustering framework can visualize the flow pattern in the square-shaped cavity in a short time. Additionally, the combination of CFD and smart modeling enables us to specifically analyze and visualize one part of a fluid structure without several complex CFD analyses.
Graphic abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Nada E (2008) Application of nanofluids for heat transfer enhancement of separated flows encountered in a backward facing step. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 29(1):242–249
Aminossadati S, Kargar A, Ghasemi B (2012) Adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system analysis of mixed convection in a two-sided lid-driven cavity filled with a nanofluid. Int J Therm Sci 52:102–111
Ayala Alvarez FJ, Blazquez Parra EB, Montes Tubio F (2017) Improving graphic expression training with 3D models. J Vis 20(4):889–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-017-0424-8
Azwadi CSN et al (2013) Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system analysis to predict the temperature and flow fields in a lid-driven cavity. Numer Heat Transf, Part A: Appl 63(12):906–920
Babanezhad N, Rezakazemi M, Hajilary N, Shirazian S (2019) Liquid-phase chemical reactors: Development of 3D hybrid model based on CFD-adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system. Can J Chem Eng 97(S1):1676–1684
Bararnia H, Soleimani S, Ganji DD (2011) Lattice Boltzmann simulation of natural convection around a horizontal elliptic cylinder inside a square enclosure. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 38(10):1436–1442
Brinkmann HC (1952) The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J Chem Phys 20:571
Cao Y, Babanezhad M, Rezakazemi M et al (2019) Prediction of fluid pattern in a shear flow on intelligent neural nodes using ANFIS and LBM. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04677-w
Dashti A, Harami HR, Rezakazemi M (2018) Accurate prediction of solubility of gases within H2-selective nanocomposite membranes using committee machine intelligent system. Int J Hydrog Energy 43(13):6614–6624
Daungthongsuk W, Wongwises S (2007) A critical review of convective heat transfer of nanofluids. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 11(5):797–817
Deng Z, He C, Liu YZ (2018) Recovering turbulent flow field from local quantity measurement: turbulence modeling using ensemble-Karman-filter-based data assimilation. J Vis 21(6):1043–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-018-0508-0
Haghshenas Fard M, Esfahany MN, Talaie MR (2010) Numerical study of convective heat transfer of nanofluids in a circular tube two-phase model versus single-phase model. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 37(1):91–97
Kefayati GHR et al (2012) Lattice Boltzmann simulation of natural convection in an open enclosure subjugated to water/copper nanofluid. Int J Therm Sci 52:91–101
Khanafer K, Vafai K, Lightstone M (2003) Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two-dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 46(19):3639–3653
Khodadadi JM, Hosseinizadeh SF (2007) Nanoparticle-enhanced phase change materials (NEPCM) with great potential for improved thermal energy storage. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 34(5):534–543
Koehler C, Durscher R, Beran P, Bhagat N (2018) Adjoint-enhanced flow visualization. J Vis 21(5):819–834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-018-0490-6
Nabavitabatabayi M, Shirani E, Rahimian MH (2011) Investigation of heat transfer enhancement in an enclosure filled with nanofluids using multiple relaxation time lattice Boltzmann modeling. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 38(1):128–138
Noto D, Tasaka Y, Yanagisawa T, Park HJ, Murai Y (2018) Vortex tracking on visualized temperature fields in a rotating Rayleigh–Benard convection. J Vis 21(6):987–998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-018-0510-63
Panella M, Gallo AS (2005) An input-output clustering approach to the synthesis of ANFIS networks. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 13(1):69–81
Pourtousi M, Zeinali M, Ganesan P, Sahu JN (2015a) Prediction of multiphase flow pattern inside a 3D bubble column reactor using a combination of CFD and ANFIS. RSC Adv 5(104):85652–85672
Pourtousi M, Sahu JN, Ganesan P, Shamshirband S, Redzwan G (2015b) A combination of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy system (ANFIS) for prediction of the bubble column hydrodynamics. Powder Technol 274:466–481
Safdari A, Dabir H, Kim KC (2018) Cubic-interpolated pseudo-particle model to predict thermal behavior of a nanofluid. Comput Fluids 164:102–113
Sudhakar T, Balaji C, Venkateshan S (2009) Optimal configuration of discrete heat sources in a vertical duct under conjugate mixed convection using artificial neural networks. Int J Therm Sci 48(5):881–890
Takagi T, Sugeno M (1985) Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 1:116–132
Tian E, Babanezhad M, Rezakazemi M et al (2019) Simulation of a bubble-column reactor by three-dimensional CFD: multidimension- and function-adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system. Int J Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00741-8
Varol Y et al (2007) Prediction of flow fields and temperature distributions due to natural convection in a triangular enclosure using adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and artificial neural network (ANN). Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 34(7):887–896
Wang S, Wu Y, Wu B (2018) Geometrical characteristic-based stream surface of 3D flow field. J Vis 21(2):281–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-017-0447-1
Wasp FJ (1977) Solid-liquid slurry pipeline transportation. Trans. Tech
Wee MC (2017) An improved diversity visualization system for multivariate data. J Vis 20(1):163–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-016-0380-8
Xu P, Babanezhad M, Yarmand H et al (2019) Flow visualization and analysis of thermal distribution for the nanofluid by the integration of fuzzy c-means clustering ANFIS structure and CFD methods. J Vis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-019-00614-0
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National High-end Foreign Experts Recruitment Plan of China (No. G20190023036), and Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant No. 2018HH0101). This study was also supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant, which is funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (Nos. 2011-0030013, 2018R1A2B2007117).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., Safdari, A. & Kim, K.C. Visualization of nanofluid flow field by adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) with cubic interpolation particle approach. J Vis 23, 259–267 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-019-00623-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-019-00623-z