Abstract
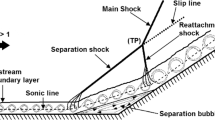
Effect of ′ramped vane′-type vortex generators on a shock-induced flow separation in the vicinity of an axisymmetric compression corner was evaluated. Numerical simulations were performed at Mach 2 on a cone–cylinder–flare model with a flare angle of 24°. The undisturbed boundary layer thickness (δ) at the location of the compression corner was 5 mm. A single array of these vortex generators with a device height of 0.28δ (1.4 mm) was placed on the cylinder surface at different streamwise positions, viz. 5δ, 10δ and 15δ upstream of the compression corner, and their ability to manipulate the shock–boundary layer interaction flowfield was compared. The presence of these devices caused substantial changes in the interaction region and the separation bubble structure. The separation bubble transformed into a series of spade-shaped structures with pockets of attached flow in between them. The ramped vanes increased the separation length along the device centreline, but this effect was attenuated considerably, by bringing them closer to the interaction region. Moving the ramped vanes closer also had a collapsing effect on the spade-shaped structures, which simultaneously widened the attached flow zones in between them.
Graphic Abstract




















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- F1, F2 :
-
Separation foci
- h:
-
Height of the ramped vane device (1.4 mm)
- HU :
-
Height of the triple point in the uncontrolled interaction
- L:
-
Upstream influence length (mm)
- LAvg :
-
Average upstream influence length in the controlled interactions (mm)
- LU :
-
Upstream influence length for the uncontrolled interaction (mm)
- N:
-
Attachment node
- P:
-
Local mean wall static pressure (kPa)
- PInf :
-
Freestream static pressure (kPa)
- PO :
-
Stagnation pressure (kPa)
- R:
-
Radial coordinate (mm)
- RV:
-
Ramped vane
- S:
-
Separation length/thickness (mm)
- SU :
-
Separation length/thickness for the uncontrolled interaction (mm)
- SP:
-
Saddle point
- V:
-
Local velocity (m/s)
- VInf :
-
Freestream velocity (m/s)
- X:
-
Axial coordinate (mm)
- XRV :
-
Axial position of the RV array (mm)
- β:
-
Main shock angle (~ 41°)
- δ:
-
Boundary layer thickness (5 mm)
- θ:
-
Azimuthal coordinate (deg)
- ρ:
-
Local density (kg/m3)
- ρInf :
-
Freestream density (kg/m3)
- ωx :
-
Streamwise vorticity (s−1)
References
Ahmed MYM, Qin N (2010) Drag reduction using aerodisks for hypersonic hemispherical bodies. J Spacecr Rockets 47(1):62–80. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.46655
Anderson BH, Tinapple J. and Surber J (2006) Optimal Control of Shock Wave Turbulent Boundary Layer Interaction using Micro Array Actuation. 3rd AIAA Flow Control Conference, AIAA Paper 2006 – 3197. doi: https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2006-3197
Andreopoulos J, Muck KC (1987) Some new aspects of the shock wave boundary layer interaction in compression ramp flows. J Fluid Mech 180:405–428. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112087001873
Ashill PR, Fulker JL and Hackett KC, (2002) Studies of flows induced by Sub Boundary layer Vortex Generators (SBVGs). AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2002-968
Babinsky H, Edwards JA (1996) On the incipient separation of a turbulent hypersonic boundary layer. Aeronaut J 100(996):209–214. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0001924000067166
Babinsky H, Li Y, Pitt Ford CW (2009) Microramp control of oblique shock-wave/boundary-layer interactions. AIAA J 47(3):668–675. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.38022
Barter JW, Dolling DS (1995) Reduction of Fluctuating Pressure Loads in Shock/Boundary Layer Interactions using Vortex Generators. AIAA J 33(10):1842–1849. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.12736
Blevins RD, BofIlios D, Holehouse I, Hwa VW, Tratt MD, Laganelli AL, Pozefsky P and Pierucci M (2009) Thermo-Vibro-Acoustic loads and fatigue of hypersonic flight vehivle structure. AFRL-RB-WP-TR-2009–3139
Cole HA, Erickson AL and Rainey AG (1970) Buffeting during atmospheric ascent. NASA SP-8001
Coleman GT, Stollery JL (1973) Incipient Separation of Axially symmetric Hypersonic Turbulent Boundary Layers. AIAA Journal 12(1):119–120. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.49175
Delery J (2013) Three-dimensional Separated Flow Topology: Critical Points. Separation Lines and Vortical Structures, John Wiley and Sons Inc, USA
Dolling DS, Murphy MT (1983) Unsteadiness of the separation shock wave structure in a supersonic compression ramp flow field. AIAA J 21(12):1628–1634. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.60163
Dolling DS, Brusniak L (1989) Separation shock motion in fin, cylinder, and compression ramp - induced turbulent interactions. AIAA J 27(6):734–742. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.10173
Dolling DS (2001) Fifty years of shock-wave/boundary-layer interaction research: what next? AIAA J 39(8):1517–1531. https://doi.org/10.2514/2.1476
Edney B (1968) Anomalous heat transfer and pressure distributions on blunt bodies at hypersonic speeds in the presence of impinging shock FFA Report. Bromma, Aeronautical Research Institute of Sweden
Erengil ME, Dolling DS (1993) Effect of sweepback on unsteady separation in Mach 5 compression ramp interactions. AIAA J 31(2):302–311. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.60176
Ericcson LE, Reding JP (1965) Analysis of flow separation effects on the dynamics of a large space booster. J of Spacecr Rockets 2(4):481–490. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.28216
Estruch-Samper D, Vanstone L, Hillier R, Ganapathisubramani B (2015) Micro vortex generator control of axisymmetric high-speed laminar boundary layer separation. Shock Waves 25(5):521533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-014-0514-7
Giepman RHM, Schrijer FFJ, van Oudheusden BW (2014) Flow control of an oblique shock wave reflection with micro-ramp vortex generators: Effect of location and size. Phys Fluids 26(066101):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4881941
Ginoux JJ (1971) Streamwise vortices in reattaching high speed flows: A suggested approach. AIAA J 9(4):759–760. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.6271
Grilli M, Hickel S, Adams NA (2013) Large eddy simulation of a supersonic turbulent boundary layer over a compression-expansion ramp. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 42:79–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2012.12.006
Heffener KS, Chpoun A, and Lengrand JC (1993) Experimental Study of Transitional Axisymmetric Shock-Boundary Layer Interactions at Mach 5. 23rd Fluid Dynamics, Plasmadynamics and Lasers Conference, AIAA Paper 1993–3131, doi: https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1993-3131
Holden HA, and Babinsky H (2004) Vortex Generators Near Shock/Boundary Layer Interactions. 42nd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, AIAA Paper 2004–1242. doi: https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2004-1242
Kistler AL (1964) Fluctuating wall pressure under a separated supersonic flow. J Acoust Soc Am 36(3):543–550. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1918998
Kontis K, Stollery JL (1999) Incipient Separation on flared bodies at hypersonic speeds. Aeronaut J 103(1027):405–414. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0001924000027950
Kuehn DM (1962) Laminar boundary-layer separation induced by flares on cylinders at zero angle of attack. Technical Report R-146.
Lee S, Loth E, Babinsky H (2011) Normal shock boundary layer control with various vortex generator geometries. Computer and Fluids. 49:233–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2011.06.003
Lee S, Loth E (2012) Impact of ramped vanes on normal shock boundary layer interaction. AIAA J 50(10):2069–2079. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J051253
Lee S, Loth E (2018) On ramped vanes to control normal shock boundary layer interactions. Aeronaut J 122(1256):1568–1585. https://doi.org/10.1017/aer.2018.88
Lighthill JM (1963) Attachment And Separation In Three-Dimensional Flow. In: Rosenhead L (ed) Laminar Boundary-Layer Theory. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, pp 77–82
Liou MS, Steffen C (1993) A new flux splitting scheme. J Comput Phys 107(1):23–39. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.1993.1122
Lu FK (2015) Visualization of supersonic flow around a sharp-edged, sub boundary-layer protuberance. J Visualization 18(4):619–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-014-0272-8
Martis RR, Misra A (2017) Separation attenuation in swept shock wave-boundary layer interactions using different micro vortex generator geometries. Shock Waves 27(5):747–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-016-0690-8
Maull DJ (1960) Hypersonic flow over axially symmetric spiked bodies. J Fluid Mech 4:584–592. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112060000815
Narayanaswamy V, Raja LL, Clemens NT (2010) Characterization of a high-frequency pulsed-plasma jet actuator for supersonic flow control. AIAA J 48(2):297–305. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.41352
Nilavarasan T, Joshi GN, Misra A, Manisankar C, and Verma SB (2019) Control of Flare Induced Shock–Boundary Layer Interaction using Micro Vortex Generators. Proceedings of the 32nd International Symposium on Shock Waves, Singapore, 2019. doi: https://doi.org/10.3850/978-981-11-2730-4_0094-cd
Nilavarasan T, Joshi GN, Misra A (2020) Effect of microramps on flare induced shock–boundary layer interaction. The Aeronaut J 124(1271):121–149. https://doi.org/10.1017/aer.2019.138
Panaras AG, Lu FK (2015) Micro-vortex generators for shock wave/boundary layer interactions. Prog Aerosp Sci 74:16–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paerosci.2014.12.006
Priebe S, Martin MP (2012) Low frequency unsteadiness in shock wave - turbulent boundary layer interaction. J Fluid Mech 699:1–49. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2011.560
Raman KR (1974) A study of surface pressure fluctuations in hypersonic turbulent boundary layers. NASA CR-2386.
Ramaswamy DP, Schreyer A-M (2019) Effect of jet spacing in separation control with air jet vortex generators. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2019-1653
Roshko A, Thomke GJ (1976) Flare-induced interaction lengths in supersonic. Turbul Bound Layers AIAA J 14(7):873–879. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.61429
Rybalko M, Babinsky H, Loth E (2010) VGs for a normal SBLI with a downstream diffuser. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/2010-4464
Schreyer A-M, Sahoo D, Smits AJ (2011) Experiments on the influence of a microramp array on a hypersonic shock turbulent boundary layer interaction. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2011-3428
Settles GS (2001) Schlieren and Shadowgraph techniques Visualizing phenomena in transparent media. Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-56640-0
Settles GS, Bogdonoff SM, Vas IE (1976) Incipient separation of a supersonic turbulent boundary layer at high reynolds numbers. AIAA Journal 14(1):50–56. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.61331
Souverein LJ, Debieve JF (2010) Effects of air jet vortex generators on a shock wave boundary layer interaction. Exp Fluids 49(5):1053–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-010-0854-8
Spalart PR and Allmaras SR (1992) A One-Equation Turbulence Model for Aerodynamic Flows. 30th Aerospace Sciences Exhibit, AIAA Paper 1992–0439. doi: https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1992-439
Sriram R, Jagadeesh G (2014) Shock tunnel experiments on control of shock induced large separation bubble using boundary layer bleed. Aerosp Sci Technol 36(7):87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2014.04.003
Su C, Li Y, Cheng B, Wang J, Cao J (2010) MHD flow control of oblique shock waves around ramps in low-temperature supersonic flows. Chin J Aeronaut 23(1):22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/P1000-9361(09)60183-7
Taylor GI, Maccoll JW (1933) The air pressure on a Cone Moving at High Speeds–I. Proc R Soc Lond Ser A 139(838):278–297. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1933.0018
Titchener N, Babinsky H (2015) A review of the use of vortex generators for mitigating shock-induced separation. Shock Waves 25(5):473–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-015-0551-x
Upadhya AR and Somashekar BR (1984) Review of launch vehicle related aeroelastic instability studies at NAL. In: Analysis of structures – A commemorative volume published on the occasion of the 60th anniversary of Dr. S.R. Valluri, NAL Bengaluru, India.
Verma SB, Koppenwallner G (2002) Unsteady separation in flare-induced hypersonic shock-wave-boundary-layer interaction flowfield. J Spacecr Rockets 39(3):467–470. https://doi.org/10.2514/2.3831
Verma SB, Manisankar C, Raju C (2012) Control of shock unsteadiness in shock boundary layer interaction on a compression corner using a mechanical vortex generators. Shock Waves 22(4):327–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-012-0369-8
Verma SB, Manisankar C (2017) Assessment of various low-profile Mechanical vortex generators in controlling a shock induced separation. AIAA J 55(7):1–13. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J055446
Verma SB, Manisankar C (2018) Control of incident shock – induced separation using vane-type vortex generating devices. AIAA J 56(4):1600–1615. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J056460
Verma SB, Manisankar C (2019) Study of Compression-Ramp-Induced Interaction with Steady Microjets. AIAA J 57(7):2892–2904. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J057509
Volpiani PS, Bernardini M, Larsson J (2018) Effects of a non-adiabatic wall on supersonic shock boundary layer interactions. Phy Rev Fluids. 3(8):083401. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2018-1806
Xue DW, Chen ZH, Jiang XH, Fan BC (2014) Numerical investigations on the wake structures of micro-ramps and micro-vanes. Fluid Dyn Res 46(015505):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1088/0169-5983/46/1/015505
Yan Y, Chen L, Lee Q and Liu C, (2017) Numerical study of micro-ramp vortex generator for supersonic ramp flow control at Mach 2.5. Shock Waves 27(1): 79–96. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-016-0633-4
Acknowledgements
The first author wishes to thank DIAT for the institute fellowship. The technical support of Mr. A. Narayana, Mr. M. S. Eshwar and Mr. V. Biju during the wind tunnel testing at CSIR-NAL is gratefully acknowledged. Special thanks to Mr. Bhushan Lokhande, Mr. Mandar Mate, Mr. Vaibhav Gonjari of the Department of Aerospace Engineering, DIAT for their assistance during the procurements and model fabrication process. The support of Mr. Gabriel Joseph during the computations is also recognized.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nilavarasan, T., Joshi, G.N., Misra, A. et al. Topological modifications due to ramped vanes in a flare-induced shock–boundary layer interaction flowfield. J Vis 24, 991–1010 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-020-00735-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-020-00735-x