Abstract
Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has been widely used in autonomous control due to its superior performance. DRL-based autonomous control model (ACM) aims to train an agent to achieve self-control and learn optimal policy through pre-defined rewards. Despite the super-human performance, ACM is regarded as a black box, and the interpretation of its internal working mechanism remains a challenge to domain experts. In addition, adjusting the reward settings of ACM is also challenging due to the uncertain relationship between rewards setting and strategies. In this paper, we propose ACMViz, a visual analytics system to explore control strategies at different stages and reveal the relationship between rewards and action patterns. Focusing on controlling a lunar lander, ACMViz investigates different landing trajectories and action sequences to interpret the model and control the training. From our visual analytics of the action patterns, we diagnose and improve reward settings for different control targets. Through our case studies with deep learning experts, we validate the effectiveness of ACMViz.
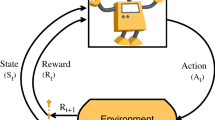
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Alemzadeh S, Niemann U, Ittermann T, Völzke H, Schneider D, Spiliopoulou M, Bühler K, Preim B (2020) Visual analysis of missing values in longitudinal cohort study data. In: Computer graphics forum, vol 39. Wiley Online Library, pp 63–75
Arbesser C, Spechtenhauser F, Mühlbacher T, Piringer H (2016) Visplause: visual data quality assessment of many time series using plausibility checks. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 23(1):641–650
Berger M, McDonough K, Seversky LM (2016) cite2vec: citation-driven document exploration via word embeddings. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 23(1):691–700
Bezerianos A, Dragicevic P, Fekete JD, Bae J, Watson B (2010) Geneaquilts: a system for exploring large genealogies. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 16(6):1073–1081
Bilal A, Jourabloo A, Ye M, Liu X, Ren L (2017) Do convolutional neural networks learn class hierarchy? IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 24(1):152–162
Blumenschein M, Behrisch M, Schmid S, Butscher S, Wahl DR, Villinger K, Renner B, Reiterer H, Keim DA (2018) Smartexplore: simplifying high-dimensional data analysis through a table-based visual analytics approach. In: 2018 IEEE conference on visual analytics science and technology (VAST). IEEE, pp 36–47
Bors C, Gschwandtner T, Miksch S (2019) Capturing and visualizing provenance from data wrangling. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 39(6):61–75
Chen C, Yuan J, Lu Y, Liu Y, Su H, Yuan S, Liu S (2020) Oodanalyzer: interactive analysis of out-of-distribution samples. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 27(7):3335–3349
Dextras-Romagnino K, Munzner T (2019) Segmentifier: interactive refinement of clickstream data. Comput Graph Forum 38(3):623–634
Gotz D, Stavropoulos H (2014) Decisionflow: visual analytics for high-dimensional temporal event sequence data. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 20(12):1783–1792
Jaunet T, Vuillemot R, Wolf C (2020) Drlviz: understanding decisions and memory in deep reinforcement learning. Comput Graph Forum 39(3):49–61
Li G, Wang J, Shen HW, Chen K, Shan G, Lu Z (2020) Cnnpruner: pruning convolutional neural networks with visual analytics. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 27(2):1364–1373
Liu M, Shi J, Cao K, Zhu J, Liu S (2017a) Analyzing the training processes of deep generative models. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 24(1):77–87
Liu M, Shi J, Li Z, Li C, Zhu J, Liu S (2017b) Towards better analysis of deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 23(1):91–100
Mikolov T, Sutskever I, Chen K, Corrado GS, Dean J (2013) Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 3111–3119
Ming Y, Cao S, Zhang R, Li Z, Chen Y, Song Y, Qu H (2017) Understanding hidden memories of recurrent neural networks. In: 2017 IEEE conference on visual analytics science and technology (VAST). IEEE, pp 13–24
Perer A, Sun J (2012) Matrixflow: temporal network visual analytics to track symptom evolution during disease progression. In: AMIA annual symposium proceedings, vol 2012, p 716
Plaisant C, Milash B, Rose A, Widoff S, Shneiderman B (1996) Lifelines: visualizing personal histories. In: Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems, pp 221–227
Wang J, Gou L, Shen HW, Yang H (2018a) Dqnviz: a visual analytics approach to understand deep q-networks. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 25(1):288–298
Wang J, Gou L, Yang H, Shen HW (2018b) Ganviz: a visual analytics approach to understand the adversarial game. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 24(6):1905–1917
Wang J, Zhang W, Yang H, Yeh CCM, Wang L (2021) Visual analytics for RNN-based deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph
Wongsuphasawat K, Guerra Gómez JA, Plaisant C, Wang TD, Taieb-Maimon M, Shneiderman B (2011) Lifeflow: visualizing an overview of event sequences. In: Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems, pp 1747–1756
Xiang S, Ye X, Xia J, Wu J, Chen Y, Liu S (2019) Interactive correction of mislabeled training data. In: 2019 IEEE conference on visual analytics science and technology (VAST). IEEE, pp 57–68
Yuan J, Chen C, Yang W, Liu M, Xia J, Liu S (2021) A survey of visual analytics techniques for machine learning. Comput Vis Media 7(1):3–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41095-020-0191-7
Zhao Y, Luo F, Chen M, Wang Y, Xia J, Zhou F, Wang Y, Chen Y, Chen W (2018) Evaluating multi-dimensional visualizations for understanding fuzzy clusters. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 25(1):12–21
Zhao Y, Luo X, Lin X, Wang H, Kui X, Zhou F, Wang J, Chen Y, Chen W (2019) Visual analytics for electromagnetic situation awareness in radio monitoring and management. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 26(1):590–600
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFB0204802).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, S., Li, X., Shan, G. et al. ACMViz: a visual analytics approach to understand DRL-based autonomous control model. J Vis 25, 427–442 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-021-00793-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-021-00793-9