Abstract
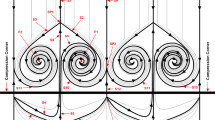
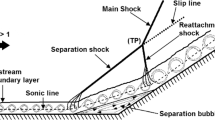
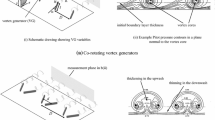
This paper brings out the ability of ‘ramped vane (RV)’ vortex generators in attenuating a shock-induced flow separation near an axisymmetric compression corner. Investigations were performed at Mach 2 over a cone–cylinder–flare geometry, with a flow deflection angle of 24° at the cylinder-flare juncture. The boundary layer thickness (δ) at the corner location was estimated to be 5 mm. A circumferential array of RVs was positioned 50 mm (10δ) upstream of the corner and their trailing edge height (h) was 2.8 mm, which was two-third of the local boundary layer thickness (h = 0.67δRV). The RVs produced streamwise counter-rotating vortices that replaced the low-momentum fluid near the model surface with high-momentum fluid from the outermost parts of the boundary layer. As a result, the onset of the interaction/separation was delayed throughout the entire circumference of the model. The interaction’s average upstream influence length was reduced by 36%, and the average thickness of the separation region was reduced by about 45%. The surface flow patterns also revealed that the RVs caused large-scale corrugations in the separation and reattachment lines. Furthermore, footprints of small tornado-like vortices could also be seen along the device centrelines, which were likely formed due to interactions between the streamwise vortices and the separation bubble.
Graphical Abstract


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MYM, Qin N (2010) Drag reduction using aerodisks for hypersonic hemispherical bodies. J Spacecr Rockets 47(1):62–80. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.46655
Anderson BH, Tinapple J, Surber L (2006) Optimal control of shock wave turbulent boundary layer interactions using micro-array actuation. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2006-3197
Babinsky H, Edwards JA (1996) On the incipient separation of a turbulent hypersonic boundary layer. Aeronaut J 100(996):209–214. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0001924000067166
Babinsky H, Li Y, Pitt Ford CW (2009) Microramp control of oblique shock-wave/boundary-layer interactions. AIAA J 47(3):668–675. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.38022
Blevins RD, Bofilios D, Holehouse I, Hwa VW, Tratt, MD, Laganelli AL, Pozefsky P and Pierucci P (2009) Thermo-Vibro-Acoustic loads and fatigue of hypersonic flight vehicle structure. AFRL-RB-WP-TR-2009-3139.
Bross M, Scharnowski S and Kahler CJ (2018) Influence of leading edge tripping devices on supersonic boundary layer characteristics. In: 5th International conference on experimental fluid mechanics, Munich, Germany
Cole HA, Erickson AL and Rainey AG (1970) Buffeting during atmospheric ascent. NASA SP-8001.
Coleman GT, Stollery JL (1973) Incipient separation of axially symmetric hypersonic turbulent boundary layers. AIAA J 12(1):119–120. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.49175
DeBonis JR (2015) Evaluation of industry standard turbulence models on an axisymmetric supersonic compression corner. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2015-0314
Delery JM (2013) Three-dimensional separated flow topology: Critical points, separation lines and vortical structres. John Wiley and Sons Inc, USA
Dolling DS (2001) Fifty years of shock-wave/boundary-layer interaction research: What next? AIAA J 39(8):1517–1531. https://doi.org/10.2514/2.1476
Dolling DS, Brusniak L (1989) Separation shock motion in fin, cylinder and compression ramp - induced turbulent interactions. AIAA J 27(6):734–742. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.10173
Edney B (1968) Anomalous heat transfer and pressure distributions on blunt bodies at hypersonic speeds in the presence of impinging shock. FFA Report, Aeronautical Research Institute of Sweden.
Erengil ME, Dolling DS (1993) Effect of sweepback on unsteady separation in Mach 5 compression ramp interactions. AIAA J 29(5):728–735. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.60176
Ericcson LE, Reding JP (1965) Analysis of flow separation effects on the dynamics of a large space booster. J Spacecr Rockets 2(4):481–490. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.28216
Estruch-samper D, Vanstone L, Hillier R, Ganapathisubramani B (2015) Micro vortex generator control of axisymmetric high-speed laminar boundary layer separation. Shock Waves 25(5):521–533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-014-0514-7
Fukuda MK, Hingst WR, Reshotko E (1977) Bleed effects on Shock/Boundary-layer interactionsin supersonic mixed compression inlets. J Aircraft 14(2):151–156. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.58756
Funderburk ML, Narayanaswamy V (2019) Experimental investigation of microramp control of an axisymmetric shock/boundary-layer interaction. AIAA J 57(8):3379–3394. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J057846
Geipmann RHM, Schrijer FFJ, van Oudheusden BW (2014) Flow control of an oblique shock wave reflection with micro-ramp vortex generators: effect of location and size. Phys Fluids 26:066101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4881941
Gejji R, Walters I, Beard S, Lemcherfi A, Sardeshmukh S, Heister S, Slabaugh C (2018) Transducer installation effects on pressure measurements in pressure gain combustion devices. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2018-0158
Ginoux JJ (1971) Streamwise vortices in reattaching high-speed flows: a suggested approach. AIAA J 9(4):759–760. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.6271
Grasso F, Marini M (1996) Analysis of hypersonic shock-wave laminar boundary-layer interaction phenomena. Comput Fluids 25(6):561–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-7930(96)00019-9
Heffner KS, Chpoun A, Lengrands JC (1993) Experimental study of transitional axisymmetric shock—boundary layer interactions at Mach 5. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1993-3131
Herges T, Kroeker L, Elliot G, Dutton C (2010) Microramp flow control of normal shock/boundary layer interactions. AIAA J 48(11):2529–2542. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J050313
Hu W, Hickel S, van Oudheusden B (2020) Influence of the upstream disturbances on the primary and secondary instabilities in a supersonic separated flow over a backward facing step. Phys Fluids 32:056102. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0005431
Huang W, Wu H, Yang Y, Yan L, Li S (2020) Recent advances in the shock wave/boundary layer interaction and its control in internal and external flows. Acta Astronaut 174:103–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.05.001
Kistler AL (1964) Fluctuating wall pressure under a separated supersonic flow. J Acoust Soc Am 36(3):543–550. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.19118998
Kontis K, Stollery JL (1999) Incipient separation on flared bodies at hypersonic speeds. Aeronaut J 103(1027):209–214. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0001924000027950
Korkegi RH (1971) Survey of viscous interactions associated with high Mach number flight. AIAA J 9(5):771–784. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.6275
Kuehn DM (1961) Turbulent boundary layer separation induced by flares on cylinders at zero angle of attack. Technical report R-117.
Lambourne NC (1962) Control surface buzz. Technical Report, Ministry of Aviation, Aeronautical Research Council, London.
Lee S, Loth E (2009) Supersonic boundary—layer interactions with various micro-vortex generator geometries. Aeronaut J 113(1149):683–697. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0001924000003353
Lee S, Loth E (2018) On ramped vanes to control normal shock boundary layer interactions. Aeronaut J 122(1256):1568–1585. https://doi.org/10.1017/aer.2018.88
Lee S, Loth E, Babinsky H (2011) Normal shock boundary layer control with various micro vortex generator geometries. Comput Fluids 49:233–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2011.06.003
Lighthill JM (1963) Attachment and separation in three dimensional flow. In: Rosenhead (Ed) Laminar boundary-layer theory, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 77–82
Liou MS, Steffen C (1993) A new flux splitting scheme. J Comput Phys 107(1):23–39. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.1993.1122
Martis RR, Misra A (2017) Separation attenuation in swept shock wave—boundary-layer interaction using different micro vortex generator geometries. Shock Waves 27(5):747–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-016-0690-8
Martis RR, Misra A, Singh A (2014) Effect of microramps on swept shock wave—boundary layer interaction. AIAA J 52(3):591–603. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J052470
Maull DJ (1960) Hypersonic flow over axially symmetric spiked bodies. J Fluid Mech 4:584–592. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112060000815
McCormick DC (1992) Shock—boundary layer interaction control with low-profile vortex generators and passive cavity. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1992-64
Narayanaswamy V, Raja LL, Clemens NT (2010) Characterization of a high-frequency pulsed-plasma jet actuator for supersonic flow control. AIAA J 48(2):297–305. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.41352
Navarro-Martinez S, Tutty OR (2005) Numerical simulations of Gortler vortices in hypersonic compression ramps. Comput Fluids 34:225–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2004.05.002
Nilavarasan T (2022) Flare-induced Shock Wave-Boundary Layer Interaction and its control using Micro Vortex Generators. Ph.D Thesis, Defence Institute of Advanced Technology, Pune, India
Nilavarasan T, Joshi GN (2023) Attenuation of compression ramp-induced flow separation using ramped vanes. In: Bhattacharyya S, Benim AC (eds) Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering, vol 2. Springer, pp 489–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6970-6_78
Nilavarasan T, Joshi GN, Misra A (2020) Effect of microramps on flare-induced shock—boundary-layer interaction. Aeronaut J 124(1271):121–149. https://doi.org/10.1017/aer.2019.138
Nilavarasan T, Joshi GN, Misra A, Manisankar C, Verma SB (2021) Topological modifications due to ramped vanes in a flare-induced shock—boundary layer interaction flowfield. J vis 24(5):991–1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-020-00735-x
Nilavarasan T, Joshi GN, Misra A, Manisankar C, Verma SB (2022) Control of flow separation over an axisymmetric flared body using ramped vanes. Euro J Mech B/fluids 95:160–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechflu.2022.04.010
Nilavarasan T, Joshi GN, Misra A, Manisankar C, Verma SB (2023a) Performance evaluation of different micro vortex generators in controlling a flare-induced shock—boundary layer interaction. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part G: J Aerospace Eng 237(8):1890–1915. https://doi.org/10.1177/09544100221139958
Nilavarasan T, Joshi GN, Misra A, Manisankar C, Verma SB (2023b) Spatial and temporal alterations due to vortex generators on a flare-induced shock-boundary layer interaction. Euro J Mech B/fluids 99:98–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechflu.2023.01.007
Nolan WR, Babinsky H (2011) Characterization of micro-vortex generators in supersonic flows. AIAA Paper 2011:71. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2011-71
Panaras AG, Lu FK (2015) Micro Vortex Generators for shock wave/boundary layer interactions. Prog Aero Sci 74:16–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paerosci.2014.12.006
Pauley WR, Eaton JK (1988) Experimental study of the development of longitudinal vortex pairs embedded in a turbulent boundary layer. AIAA J 26(7):816–823. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.9974
Pegg RJ, Hunt JL, Petley DH, Burkardt L, Stevens DR, Moses PL, Pinckney SZ, Kabis HZ, Spoth KA, Dziedzic WM, Kries RI, Marti JG (1993) Design of a hypersonic wave-rider derived airplane. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1993-401
Pickles JD, Narayanswamy V (2020) Control of fin shock induced flow separation using vortex generators. AIAA J 58(11):4794–4806. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J059624
Priebe S, Martin MP (2012) Low-frequency unsteadiness in shock wave-turbulent boundary layer interaction. J Fluid Mech 699:1–49. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2011.560
Raman KR (1974) A study of surface pressure fluctuations in hypersonic turbulent boundary layers. NASA CR-2386
Ramaswamy DP, Schreyer A-M (2021) Control of shock-induced separation of a turbulent boundary layer using air-jet vortex generators. AIAA J 59(3):927–939. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J059674
Roghelia A, Olivier H, Egorov IV, Chuvakhov P (2017) Experimental investigation of Gortler vortices in hypersonic ramp flows. Exp Fluids 58:139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-017-2422-y
Roshko A, Thomke GJ (1966) Observations of turbulent reattachment behind an axisymmetric downstream-facing step iin supersonic flow. AIAA J 4(6):976–980. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.3590
Roshko A, Thomke GJ (1976) Flare induced interaction lengths in supersonic turbulent boundary layers. AIAA J 14(7):873–879. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.61429
Running CL, Juliano TJ, Jewell JS, Borg MP, Kimmel RL (2019) Hypersonic shock-wave/boundary-layer interactions on a cone/flare. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 109:109911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2019.109911
Sajeev S, Sandhu JPS, Ghosh S, Edwards JR (2020) Effectiveness of micro-vortex generators in tandem in high speed flows. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2020-2961
Spalart PR, Allmaras SR (1992) A one-equation turbulence model for aerodynamic flows. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1992-439
Taylor GI, Macoll JW (1933) The air pressure on a cone moving at high speeds—I. Proc R Soc Lond Ser A 139(838):278–297. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1933.0018
Titchener N, Babinsky H (2013) The effects of various vortex generator configurations on a Normal shock wave/boundary layer interaction. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2013-18
Titchener N, Babinsky H (2015) A review of the use of vortex generators for mitigating shock induced separation. Shock Waves 25(5):473–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-015-0551-x
Verma SB, Hadjadj A (2015) Supersonic flow control. Shock Waves 25(5):443–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00191-015-0587-y
Verma SB, Koppenwallner G (2002) Unsteady separation in flare-induced hypersonic shock-wave-boundary-layer interaction flowfield. J Spacecr Rockets 39(3):467–470. https://doi.org/10.2514/2.3831
Verma SB, Manisankar C (2017) Assessment of various low-profile mechanical vortex generators in controlling a shock—induced separation. AIAA J 55(7):2228–2240. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J055446
Verma SB, Manisankar C (2018) Control of incident shock—induced separation using vane-type vortex generating devices. AIAA J 56(4):1600–1615. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J056460
Verma SB, Manisankar C (2019) Control of compression corner induced interaction with steady microjets. AIAA J 57(7):2892–2904. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J057509
Verma SB, Hadjadj A, Haidn O (2017) Origin of side-loads in a subscale truncated ideal contour nozzle. Aero Sci Tech 71:725–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2017.10.014
Wagner JL, Yuceil KB, Valdivia A, Clemens NT, Dolling DS (2009) Experimental investigation of unstart in an inlet/isolator model in Mach 5 flow. AIAA J 47(6):1528–1542. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.40966
Wong WF (1974) The application of boundary layer suction to suppress strong shock-induced separation in supersonic inlets. AIAA Paper. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1974-1063
Zheltovodov AA, Knight DD (2011) Ideal-gas shock-wave turbulent boundary-layer interactions in supersonic flows and their modelling: three-dimensional interactions. In: Babinsky H, Harvey JK (eds) Shock wave—boundary layer interactions. Cambridge University Press, UK. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511842727.005
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology (DST-SERB), Government of India through their Core Research Grant (CRG) scheme (Grant No: CRG/2018/003925). The authors thank A. Narayana, V. Biju and M. S. Eshwar for their assistance during the wind tunnel tests. The support of Bhushan Lokhande, Vaibhav. A. Gonjari, Mandar Mate and Gabriel Joseph is also gratefully acknowledged. The first author thanks DIAT for the institutional fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nilavarasan, T., Joshi, G.N., Misra, A. et al. Mitigation of shock-induced flow separation over an axisymmetric flared body using ramped vanes. J Vis 26, 1279–1297 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-023-00933-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-023-00933-3