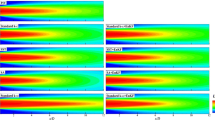
Abstract
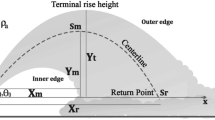
This research employs a continuous adjoint data assimilation (DA) algorithm to enhance the prediction of three-dimensional flow behavior in the inclined round jet in crossflow (JICF). To rectify model-form errors arising from the Boussinesq approximation, a force correction is implemented, and the linear part of the eddy viscosity is incorporated for numerical stability. The DA model is theoretically derived to minimize discrepancies between particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurement and the numerical predictions of the primary-adjoint system, thus enabling determination of the optimal contribution of the force correction. Observational data are acquired through planar PIV measurement in the centerplane of JICF with a fixed velocity ratio of 1.2 and a bulk Reynolds number of 150,000. Delayed detached eddy simulation is validated using PIV results and serves as supplementary data for evaluating the reconstruction capabilities of the DA method. The research explores various regularization parameters in the data assimilation procedure, emphasizing their impact on eddy viscosity, correction force, and overall flow prediction accuracy. The findings underscore the effectiveness of regularization in promoting smoothness in the optimized field, thereby mitigating overfitting and irregular solutions. In-depth analyses of critical flow features, including counter-rotating vortex pairs and Reynolds stress forcing, provide insights into the accuracy achieved by the data assimilation procedure. Despite limited measurement data, the study demonstrates the capability of the presented method to successfully recover global flow fields.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cortelezzi L, Karagozian AR (2001) On the formation of the counter-rotating vortex pair in transverse jets. J Fluid Mech 446:347–373. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022112001005894
Cruz MA, Thompson RL, Sampaio LEB, Bacchi RDA (2019) The use of the Reynolds force vector in a physics informed machine learning approach for predictive turbulence modeling. Comput Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2019.104258
Duraisamy K (2021) Perspectives on machine learning-augmented Reynolds-averaged and large eddy simulation models of turbulence. Phys Rev Fluids 6:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.6.050504
Duraisamy K, Iaccarino G, Xiao H (2019) Turbulence modeling in the age of data. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 51:357–377. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-fluid-010518-040547
Eivazi H, Tahani M, Schlatter P, Vinuesa R (2021) Physics-informed neural networks for solving Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes equations
Foures D, Dovetta N, Denis Sipp PJS (2014) A data-assimilation method for reynolds-averaged navier-stokes-driven mean flow reconstruction. J Fluid Mech 759:404–431. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2014.566
Franceschini L, Sipp D, Marquet O (2020) Mean-flow data assimilation based on minimal correction of turbulence models: application to turbulent high Reynolds number backward-facing step. Phys Rev Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.5.094603
Guo X, Schröder W, Meinke M (2006) Large-eddy simulations of film cooling flows. Comput Fluids 35:587–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2005.02.007
Hafez AM, Abd El-Rahman AI, Khater HA (2022) Field inversion for transitional flows using continuous adjoint methods. Phys Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0128522
He C, Liu Y, Gan L, Lesshafft L (2019) Data assimilation and resolvent analysis of turbulent flow behind a wall-proximity rib. Phys Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5074151
He C, Wang P, Liu Y (2021) Data assimilation for turbulent mean flow and scalar fields with anisotropic formulation. Exp Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-021-03213-8
Jin X, Cai S, Li H, Karniadakis GE (2021) NSFnets (Navier–Stokes flow nets): Physics-informed neural networks for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. J Comput Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2020.109951
Karagozian AR (2014) The jet in crossflow. Phys Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4895900
Kato H, Yoshizawa A, Ueno G, Obayashi S (2015) A data assimilation methodology for reconstructing turbulent flows around aircraft. J Comput Phys 283:559–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2014.12.013
Kim KC, Kim SK, Yoon SY (2000) PIV measurements of the flow and turbulent characteristics of a round jet in crossflow. J vis 3:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182408
Kraichnan RH (1970) Diffusion by a random velocity field. Phys Fluids 13:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1692799
Lemke M, Reiss J, Sesterhenn J (2014) Adjoint based optimisation of reactive compressible flows. Combust Flame 161:2552–2564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2014.03.020
Li S, He C, Liu Y (2022) A data assimilation model for wall pressure-driven mean flow reconstruction. Phys Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0076754
Li S, He C, Liu Y (2023a) Unsteady flow enhancement on an airfoil using sliding window weak-constraint four-dimensional variational data assimilation. Phys Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0152348
Li S, He C, Wang W, Liu Y (2023b) Flow enhancement from wall pressure observations: a compressible continuous adjoint data assimilation model. Phys Fluids 35:116119. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0172331
Li Z, Hoagg JB, Martin A, Bailey SCC (2018) Retrospective cost adaptive Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes k–ω model for data-driven unsteady turbulent simulations. J Comput Phys 357:353–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2017.11.037
Li Z, Zhang H, Bailey SCC et al (2017) A data-driven adaptive Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes k–ω model for turbulent flow. J Comput Phys 345:111–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2017.05.009
Ling J, Kurzawski A, Templeton J (2016) Reynolds averaged turbulence modelling using deep neural networks with embedded invariance. J Fluid Mech 807:155–166. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2016.615
Lucor D, Agrawal A, Sergent A (2021) Physics-aware deep neural networks for surrogate modeling of turbulent natural convection, 1–29
Mahesh K (2013) The interaction of jets with crossflow. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 45:379–407. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-fluid-120710-101115
Milani PM, Ling J, Eaton JK (2020) Turbulent scalar flux in inclined jets in crossflow: counter gradient transport and deep learning modelling. J Fluid Mech. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2020.820
Milani PM, Ling J, Eaton JK (2021) On the generality of tensor basis neural networks for turbulent scalar flux modeling. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 128:105626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105626
Moussa ZM, Trischka JW, Eskinazi S (1977) The near field in the mixing of a round jet with a cross-stream. J Fluid Mech 80:49–80. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112077001530
Muppidi S, Mahesh K (2005) Study of trajectories of jets in crossflow using direct numerical simulations. J Fluid Mech 530:81–100. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112005003514
Muppidi S, Mahesh K (2007) Direct numerical simulation of round turbulent jets in crossflow. J Fluid Mech 574:59–84. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112006004034
New TH, Lim TT, Luo SC (2006) Effects of jet velocity profiles on a round jet in cross-flow. Exp Fluids 40:859–875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-006-0124-y
New TH, Lim TT, Luo SC (2002) A visual study on elliptical jets in cross flow. J vis 5:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182421
Pope SB (2000) Turbulent flows. Cambridge University Press
Sakai E, Takahashi T, Watanabe H (2014) Large-eddy simulation of an inclined round jet issuing into a crossflow. Int J Heat Mass Transf 69:300–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.10.027
Singh AP, Duraisamy K (2016) Using field inversion to quantify functional errors in turbulence closures. Phys Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4947045
Smirnov A, Shi S, Celik I (2001) Random flow generation technique for large eddy simulations and particle-dynamics modeling. J Fluids Eng Trans ASME. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1369598
Smith SH, Mungal MG (1998) Mixing, structure and scaling of the jet in crossflow. J Fluid Mech 357:83–122. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112097007891
Symon S, Dovetta N, McKeon BJ et al (2017) Data assimilation of mean velocity from 2D PIV measurements of flow over an idealized airfoil. Exp Fluids 58:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-017-2336-8
Wang Q, Moosania M, Zhou C (2022) Effects of an incoming vortex on the film cooling jet. Int J Heat Mass Transf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2021.122323
Ye L, Liu CL, Zhu HR, Luo JX (2019) Experimental investigation on effect of cross-flow reynolds number on film cooling effectiveness. AIAA J. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J057943
Zhang X-L, Xiao H, Luo X, He G (2023a) Combining direct and indirect sparse data for learning generalizable turbulence models. J Comput Phys 489:112272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2023.112272
Zhang X, Wang K, Wen X et al (2022a) Experimental study of time-resolved simultaneous velocity and concentration fields of an inclined jet in crossflow. Int J Heat Mass Transf 188:122622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2022.122622
Zhang X, Wang K, Zhou W et al (2023b) Using data assimilation to improve turbulence modeling for inclined jets in crossflow. J Turbomach 145:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4063047
Zhang X, Zhou W, He C et al (2023c) Three-dimensional flow structures and scalar mixing of a sand dune-inspired jet in crossflow. Int J Heat Mass Transf 216:124601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2023.124601
Zhang XL, Xiao H, Luo X, He G (2022b) Ensemble Kalman method for learning turbulence models from indirect observation data. J Fluid Mech 949:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2022.744
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support for this study from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (12227803, 92152301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Zhang, X., Zhou, W. et al. Particle image velocimetry, delayed detached eddy simulation and data assimilation of inclined jet in crossflow. J Vis 27, 307–322 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-024-00974-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-024-00974-2